Question
In: Physics
Two Forces Acting at a Point Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
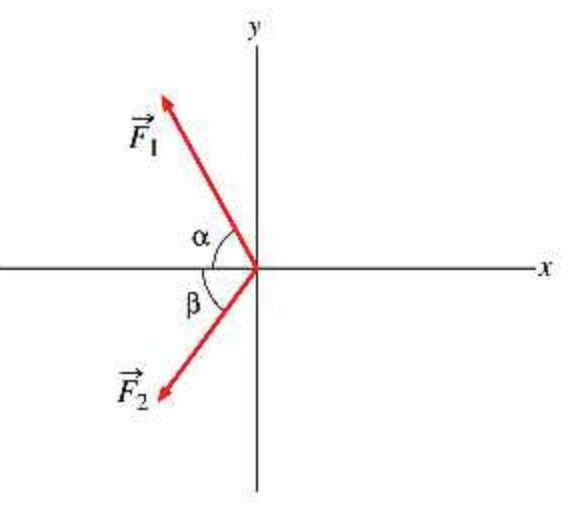
Two forces, F1 and F2, act at a point, as shown in the picture. F1 has a magnitude of 8.40N and is directed at an angle of α = 60.0° above the negative x axis in the second quadrant. F2 has a magnitude of 6.20 N and is directed at an angle of β = 52.7° below the negative x axis in the third quadrant.
Part A
What is the x component Fx of the resultant force?
Part B
What is the y component Fy of the resultant force?
Part C
What is the magnitude F of the resultant force?
Part D
What is the angle γ that the resultant force forms with the negative x axis? In this problem, assume that positive angles are measured clockwise from the negative x axis.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Part A Answer
Since both forces are in the same overall, x-direction (negative), just solve by (remember to include the negative signs):
Fx = -cos(60)F1 + -cos(52.7)F2
Fx = -0.5(8.40N) + -0.606(6.20N)
Fx = -7.96N
Part B Answer
Same concept as Part A. Except that the first force is going up, the second is going down. Solve by:
Fy = sin(60)F1 – sin(52.7)F2
Fy = 7.27 – 4.93
Fy = 2.34N
Part C Answer
Since we already found the resultant x and y components, we can just use these to solve for the resultant magnitude:
F = sqrt(F2x + F2y)
F = sqrt(-7.962 + 2.342)
F = sqrt(68.84)
F = 8.29N
Part D Answer
Since we have all 3 sides to a triangle (x and y components, plus the magnitude/hypotenuse), we can easily solve using trigonometric ratios. For example, using tangent (opposite / adjacent):
tan(γ) = Fy / Fx
tan(γ) = 2.34 / -7.96
tan(γ) = -0.294
γ = tan-1(-0.294)
γ = 16.4°
Related Solutions
Motion of a Block with Three Forces Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Motion of a Block with Three Forces Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Two Blocks and a Pulley Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Two Hanging Masses Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Pushing a Lawnmower Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Mechanical Advantage Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
A Book on a Table Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Mechanical Advantage Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
Suspending a Speaker Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
A Gymnast on a Rope Solution(Mastering Physics Chapter 04: Force and Motion)
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago