Question
In: Physics
For the conditions given in the previous question, the charge's actual trajectory is:
In the figure below, a magnetic field of 0.6 Tesla points into the page. A particle of charge \(-12 n C\) and mass \(0.6 ? g\) is shot into the field as shown in the figure with a velocity of \(0.1 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{s} .\) What is the radius of the orbit (in meters)? (The radius is a positive quantity.) Be careful with the powers of 10. Hint: k=kilo, m=milli, ?=micro, \(n=\) nano and the SI units for B-field, charge, mass, length and time are: tesla (T), coulomb (C), kilogram (kg), meter (m) and second (s), respectively.
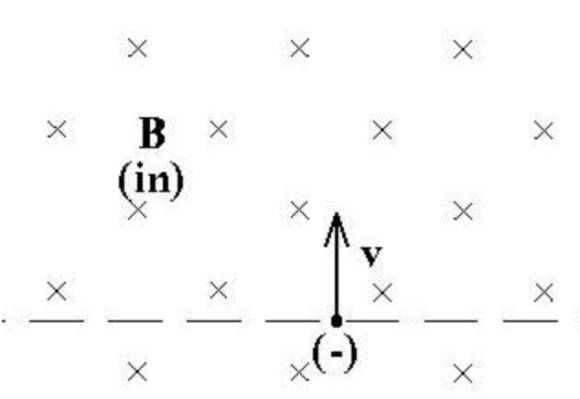
For the conditions given in the previous question, the charge's actual trajectory is:
A. a circle bending to the left
B. a parabola bending to the left
C. a circle bending to the right
D. a parabola bending to the right
Solutions
Expert Solution
(1) When the charge particle enters perpendicular to the magnetic field it follows a circular path. The centripetal force acting on the particle is equal to the force acting on the particle due to magnetic field. The centripetal force acting on the charge is, \(F_{\mathrm{c}}=\frac{m v^{2}}{r}\) The force acting on the particle due to magnetic field is, \(F_{\mathrm{b}}=q v B \sin 90^{\circ}\) $$ =q v B $$ The radius of the orbit is calculated as follows: $$ \begin{aligned} F_{\mathrm{b}} &=F_{\mathrm{c}} \\ q v B &=\frac{m v^{2}}{r} \\ r &=\frac{m v}{q B} \\ &=\frac{\left(0.6 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~g}\left(\frac{10^{-3} \mathrm{~kg}}{1 \mathrm{~g}}\right)\right)\left(0.1 \times 10^{3} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\right)}{\left(12 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{C}\right)(0.6 \mathrm{~T})} \\ &=8.333 \mathrm{~m} \end{aligned} $$
(2) The force acting on the negative charge is pointing towards the positive \(x\) axis. Hence, the trajectory is a circle bending to the right. Hence, the correct option is (c).
(1) =8.333
(2) the correct option is (c).
Related Solutions
As in the previous question: Quantity demanded for good A is given by the following: Q(A)...
Given the below pension assumptions (same as the previous question), answer the following question. Starting salary...
MATLAB 2017b The trajectory of a projectile is given by: Write a program which will draw...
Question: Explain the method so that a line integral is independent of the trajectory. Offer an...
It is the beginning of January. Actual sales for the previous quarter (Q4) and estimated sales...
Similar conditions as in previous question. A simple 3-phase power system includes generator G, step-up transformer...
QUESTION 19 The measure in the previous question was: a. Prevalence b....
Students will design a mutually operating gear system under the conditions given in this question. (Sizing...
Suppose that whether or not it rains today depends on previous weather conditions through the last...
Suppose that whether or not it rains today depends on previous weather conditions through the last...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago