Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the organic product (if any) expected from the following reaction: (include all hydrogen atoms) CH3CH2CH2OH + K2Cr2O7(aq) H2SO4
Draw the organic product (if any) expected from the following reaction: (include all hydrogen atoms)
| $$ \begin{aligned} &\mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}(a q) \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}}{\longrightarrow}\\ &\text { Note: } \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7} \text { is present in excess. } \end{aligned} $$ |  |
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The problem is based on the concept of oxidation of alcohol. Oxidation of alcohol with strong oxidizing reagent results in the formation of carboxylic acid.
Fundamentals
An oxidizing reagent has the ability to gain electrons. Therefore, it reduces itself and oxidize the other compound.
The reagent, \(\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}\) is a strong oxidizing reagent. It oxidizes primary alcohol to carboxylic acid.
Consider the reaction for the oxidation of \(\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}\) as:
$$ \mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4} \longrightarrow \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7} \quad \mathrm{CrO}_{3}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} $$
The reagent \(\mathrm{CrO}_{3}\) is the strong oxidizing reagent.
In the reaction, \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}\) acts as a catalyst. The reagent, \(\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}\) is oxidized to \(\mathrm{CrO}_{3},\) which is a strong oxidizing agent.
Consider the reaction for the oxidation of alcohol as follows:
$$ \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{CrO}_{3} \longrightarrow \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CHO} $$
Consider the mechanism for the oxidation of aldehyde to carboxylic acid as follows:
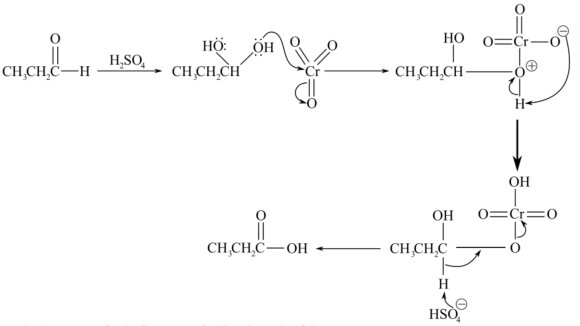
Consider the reaction for the formation of carboxylic acid as follows:
$$ \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}(a q) \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{COOH} $$
The organic product from the reaction is as follows:
$$ \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{OH}+\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}(a q) \stackrel{\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{CH}_{3} \mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{COOH} $$
In the reaction, \(\mathrm{K}_{2} \mathrm{Cr}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{7}\) and \(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}\) reacts in situ and forms \(\mathrm{CrO}_{3}\) which is a strong oxidizing reagent. The oxidation of alcohol results in the formation of aldehyde as an intermediate. The aldehyde is further oxidized to a carboxylic acid.
Related Solutions
Draw the major organic product of the reaction shown below. K2Cr2O7 H2SO4, H2O
Draw the product of the oxidation of the following aldehyde. Include all hydrogen atoms in your structure.
What is the major organic product obtained from the following reaction? H2SO4
Draw the organic product for the following reaction. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Draw the alcohol that is oxidized to give the product shown below. Show all hydrogen atoms.
Draw the major organic product of the reaction shown below.Draw the major organic product of...
Complete the following reaction. Add hydrogen atoms and charges to the appropriate atoms.
Draw the organic product in each of the following reactions. Include formal charges, if applicable. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Draw the structure of the organic product of each reaction in the following two-step synthesis.
_______________________ are stripped from the intermediate organic molecules of the Krebs Cycle. carbon and hydrogen atoms...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago