Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the organic product in each of the following reactions. Include formal charges, if applicable. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Draw the organic product in each of the following reactions. Include formal charges, if applicable. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
One or more substances that react together to form a product is called a chemical reaction. Most chemical reactions take place with the help of reagents. Reagents are substances that are used to transform one form of a substance to another. The reactions undergo substitution and reduction reactions to reach the final organic product.
Fundamentals
Sodium azide \(\left(\mathrm{NaN}_{3}\right)\) and sodium cyanide \((\mathrm{NaCN})\) are good nucleophiles. When it reacts with an alkyl bromide, it undergoes a substitution reaction. Example:
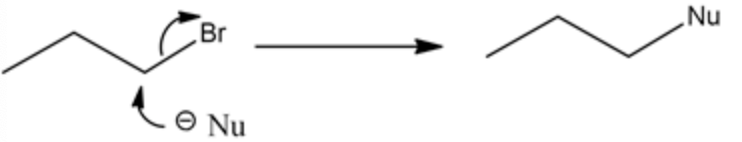
\(\mathrm{Nu}=\mathrm{NaN}_{3}\) and \(\mathrm{NaCN}\)
The substituted product then undergoes reduction to form the final organic product. Lithium aluminum hydride \(\left.(\operatorname{li} \mathrm{A}] \mathrm{H}_{4}\right)\) is the best reducing agent. The reduced product undergoes protonation to form the final organic product.
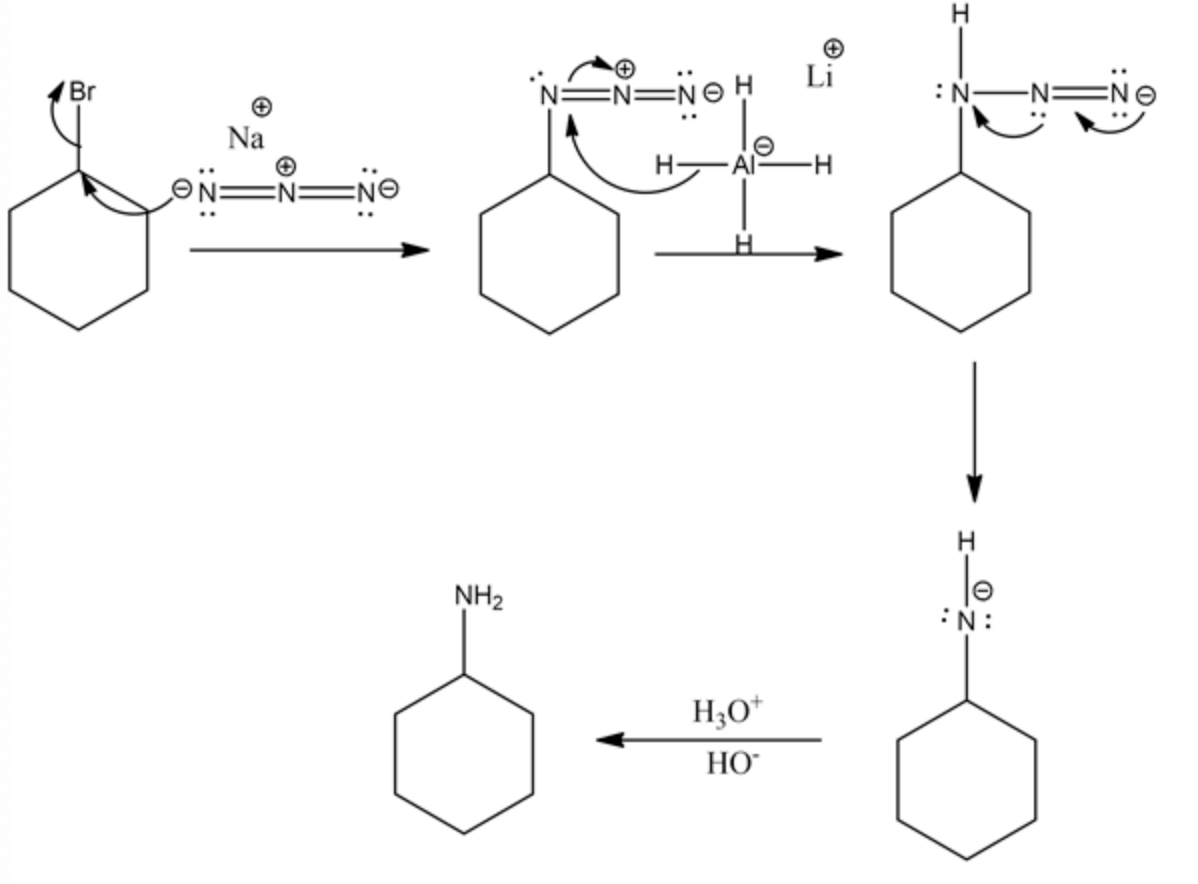
Cyclohexyl bromide reacts with sodium azide to form cyclohexyl azide. The hydride ion in lithium aluminium hydride acts as a nucleophile and attacks nitrogen in cyclohexyl azide. The azide nitrogen forms an anion by losing the nitrogen molecule. Then, it undergoes protonation and forms cyclohexylamine as the product.
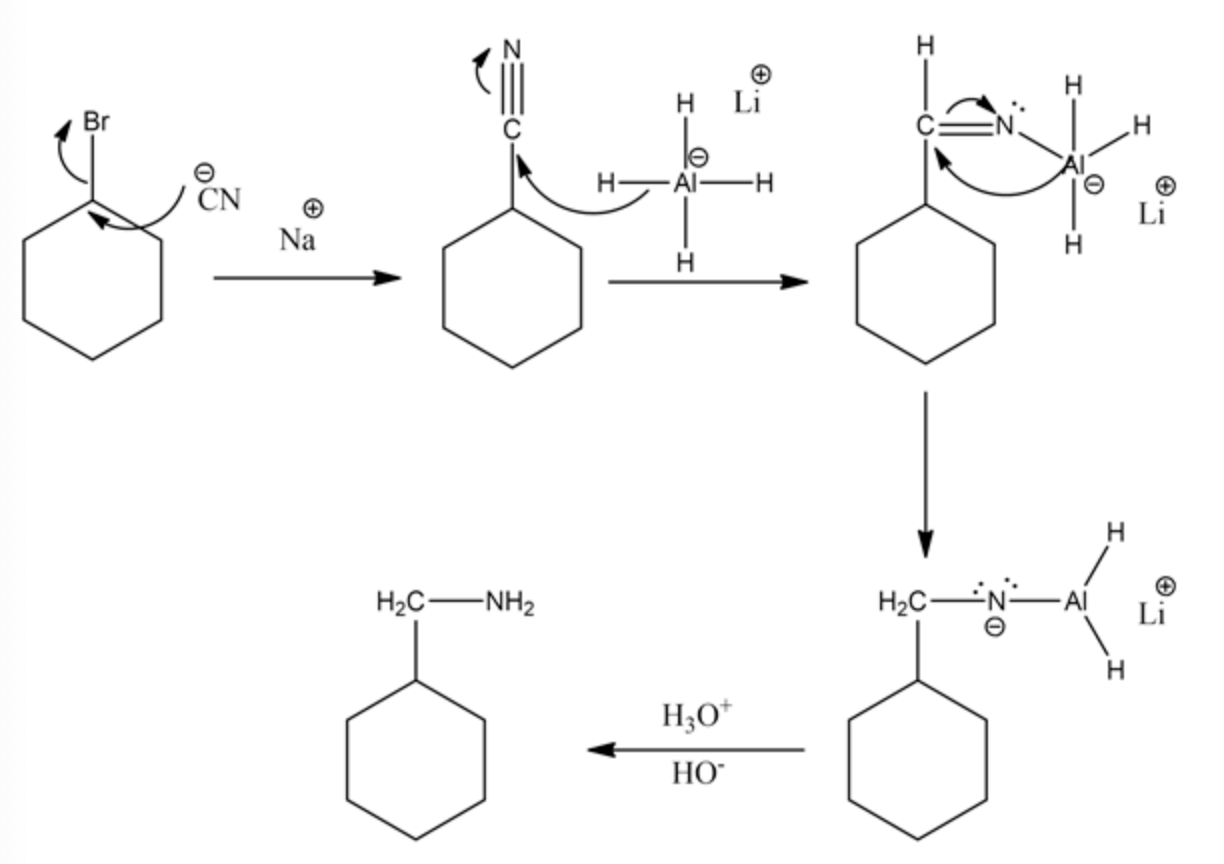
Cyanide ion acts as a nucleophile which undergoes the backside attack and forms cyclohexyl cyanide. The hydride ion in lithium aluminium hydride undergoes a nucleophilic attack twice on nitrile carbon to form an anion on nitrogen atom. Then, it undergoes protonation to form an amine as the product.
Related Solutions
Draw the organic product for the following reaction. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Draw the structures of organic compounds A and B. Omit all of the byproducts.
Use formal charges to determine which resonance form of each of the following ions is preferred....
For the following SN2 reaction, draw the organic and inorganic products of the reaction, and identify...
Determine the Lewis structure of each of the following molecules. Include formal charges, where appropriate: (a)...
Draw the organic product (if any) expected from the following reaction: (include all hydrogen atoms) CH3CH2CH2OH + K2Cr2O7(aq) H2SO4
Draw the structure of the organic product of each reaction in the following two-step synthesis.
Classify each of the following disposal methods as organic or inorganic. 1. Dumping into the sea....
part 1: Draw the Lewis structure for urea, H2N(CO)NH2. Add any any non-zero formal charges to...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago