Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the structure of the organic product of each reaction in the following two-step synthesis.
Draw the structure of the organic product of each reaction in the following two-step synthesis.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The concept used to solve the given problem is the knowledge of the nucleophilic addition reaction on the carbonyl carbon.
Fundamentals
The carbonyl carbon has the electrophilic carbon which is deficient in electrons and is fulfilled by the nucleophilic attack which results in the nucleophilic addition product. The nucleophile attacks the \(\pi^{*}\) antibonding orbital of the carbonyl carbon result in the breakage of the \(\pi\) bond between \(C\) and \(O\).
In the given reactant the proton attacks the lone pair of oxygen which further proceed with the intramolecular attack of \(\mathrm{NH}_{2}\) as a nucleophile on the carbonyl results in the formation of cyclic imine. The mechanism of this reaction is given below:
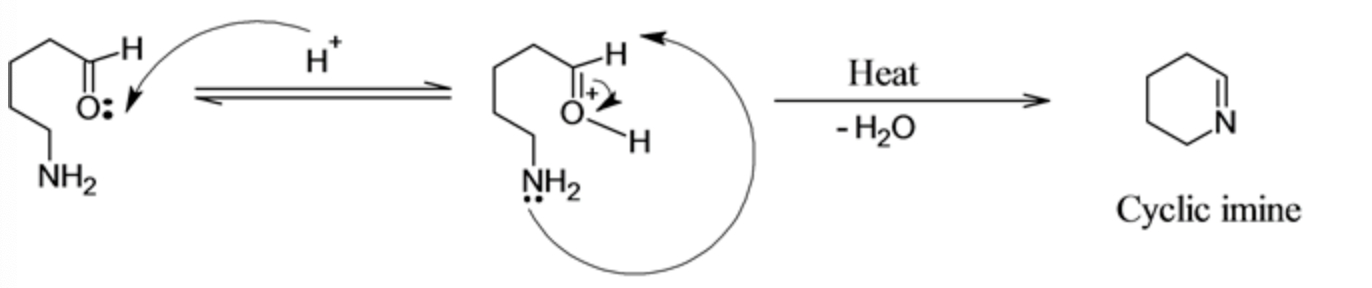
The proton attacks on the lone pair of oxygen creates the positive charge on oxygen, this increases the electrophilicity of carbonyl carbon. Now the internal amino group as a nucleophile attack on the carbonyl carbon, results in the formation of cyclic imine and water leaves as the leaving group.
When the cyclic imine reacts with reducing agent such as \(\mathrm{NaBH}_{3} \mathrm{CNorH}_{2} / \mathrm{PdorNi}\) undergoes reduction and the imine group converts into the cyclic secondary amine which is commonly known as piperdine. The reaction of reduction of cyclic imine is as follows:
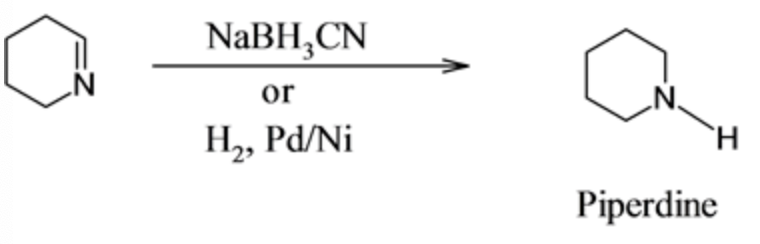
The given reagents \(\mathrm{NaBH}_{3} \mathrm{CNorH}_{2} / \mathrm{PdorNi}\) selectively reduces the cyclic imine group into secondary amine. It does not break the ring to form the primary amine.
The structure of the organic product of each reaction for the two-step synthesis are as follows:
Related Solutions
Draw the structures of the organic products in each reaction of the following two-step synthesis.
Draw the major organic product of the reaction shown below.Draw the major organic product of...
Draw the structure of the aromatic product from the following reaction
For the following SN1 reaction, draw the major organic product, identify the nucleophile, substrate, and leaving group, and determine the rate limiting step.
Draw the organic product for the following reaction. Omit any inorganic byproducts or ions.
Draw the organic products formed in the following reaction.
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: Draw a balanced chemical reaction for the synthesis of methyl salicylate from aspirin tablets....
For the following SN2 reaction, draw the organic and inorganic products of the reaction, and identify...
Draw the major organic product(s) for the following reaction. Multiple products may be drawn in one...
What is the major organic product of the following reaction?
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago