Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the product of the oxidation of the following aldehyde. Include all hydrogen atoms in your structure.
Draw the product of the oxidation of the following aldehyde. Include all hydrogen atoms in your structure.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The chemical reaction that takes place by the addition of oxygen and the removal of hydrogen is represented as oxidation reaction. Loss of electrons also represents oxidation.
Fundamentals
Oxidation reaction is used for the functional group transformation. There are two steps involved in the formation of carboxylic acid from aldehyde.
Step 1:
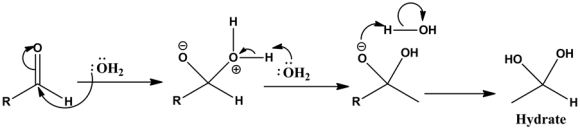
Adding water to aldehyde in the presence of acid catalyst leads to the formation of hydrate. General mechanism:
Step 2:
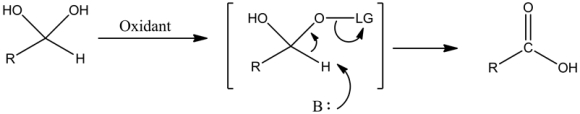
With the help of oxidant, E2 elimination undergoes carboxylic acid formation by eliminating the leaving group (LG).

First, water is added to the carbonyl group. This addition leads to the shifting of carbonyl bond \((\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O})\) and creates a negative charge on oxygen and positive charge on oxygen that is formed by the addition of water. Then, the deprotonation reaction undergoes to stabilize the positive charge on oxygen. Finally, protonation reaction undergoes by the carbonyl oxygen \(\mathrm{n}\) which leads to the formation of hydrate.
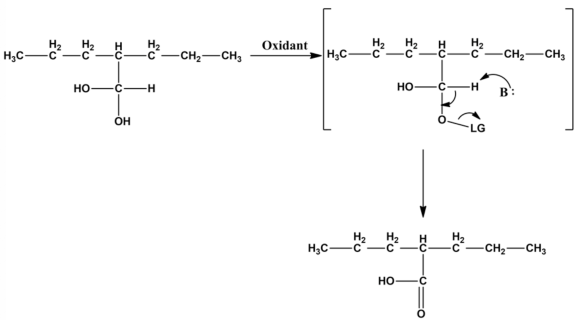
Oxidation of aldehyde:
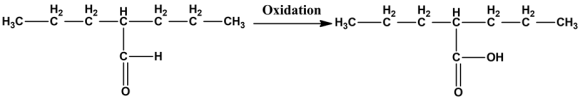
The leaving group gets attached to one of the oxygen molecule if any oxidant is added to the hydrate. Carboxylic acid is formed with the help of E2 mechanism by eliminating the leaving group.
Related Solutions
Draw the organic product (if any) expected from the following reaction: (include all hydrogen atoms) CH3CH2CH2OH + K2Cr2O7(aq) H2SO4
Draw the alcohol that is oxidized to give the product shown below. Show all hydrogen atoms.
Draw a Lewis structure for PSF3 in which the octet rule is satisfied on all atoms...
Draw a Lewis structure for SO2 in which all atoms obey the octet rule.
Draw the Lewis structure for SiH4. Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and...
Draw the Lewis structure for I3-. Draw the molecule by placing atoms on the grid and...
DRAW THE LEWIS STRUCTURE OF EACH. Part A SO42− Draw the molecule by placing atoms on...
Assign oxidation states to all atoms in each compound. (Enter your answer using the format +1...
Draw the structure of the aromatic product from the following reaction
William Prout (1815) proposed that all other atoms are built up of hydrogen atoms, suggesting that all elements
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago