Question
In: Chemistry
A protein with a high percentage of lysine and arginine residues would be BEST purified and...
A protein with a high percentage of lysine and arginine residues would be BEST purified and concentrated with which type of column? Explain
A. cation exchange
B. anion exchange
C. size exclusion chromotagraphy
D. affinity chromotagraphy
Solutions
Expert Solution
Answer (A)
:- Cation-exchange
chromatography:
2) negatively charged resin (negative charges on the surface);
therefore, there is an exchange of cations
- generally bound to Na+ or K+
Answer (B)
:- Anion-exchange
chromatography:
3) positively charged resin (positive charges on the surface);
therefore, there is an exchange of anions
- generally bound to Cl-
4) Exchange resin is bound to counterions
5) Mixture of proteins is loaded on the column and allowed to flow
through
6) Proteins that have a net charge opposite to that of the
exchanger stick to the column, exchanging places w/ the bound
counterions
7) Proteins that have no net charge or same charge as the exchanger
elute
8) After unwanted proteins are eluted, eluent is changed either to
a buffer that has a pH that removes the charge on the bound
proteins or to one w/ a higher salt concentration
9) Higher salt concentration will outcompete the bound proteins for
the limited binding space on the column
10) Desired molecules are eluted
Answer (C)
:- Size-exclusion (or gel filtration)
chromatography is a form of column chromatography
Advantages:
1) proteins are separated by size
2) estimate molecular weight by comparing the sample w/ a set of
standards
Stationary phase composed of cross-linked gel particles:
1) particles are in bead form
2) consists of one of two kinds of polymers; a carbohydrate polymer
(dextran or agarose) or polyacrylamide
How it works:
1) Cross-linked structure of these polymers produce pores in the
material
2) Extent of cross-linking can be controlled to produced desired
pore size
3) Smaller molecules enter the pores and are delayed in elution
time (only after escaping the pores)
4) Larger molecules do not enter and elute from column before
smaller ones

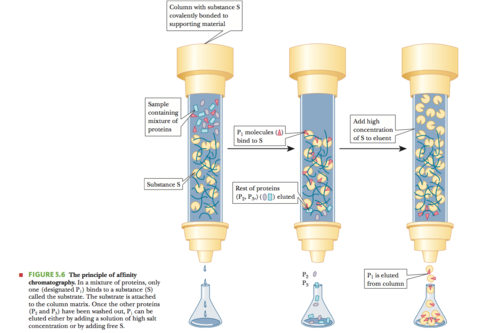
Answer (D)
:- Form of column chromatography
Advantages:
1) Uses specific binding properties of molecules/proteins
2) Produces very pure proteins
How it works:
1) Stationary phase has a polymer that can be covalently linked to
a compound called a ligand that specifically binds to the desired
protein
2) After the unwanted proteins are eluted, more ligand or salt is
added
3) Salt weakens the binding of protein to the ligand and extra free
ligand competes with the column ligand in protein binding
-a change of pH or ionic strength will disrupt the
ligand-protein interaction-
Use this after getting partially pure protein to get pure
protein
Problems:
1) ligand doesn't bind properly to polymer
2) ligand binds too strongly; can't remove
3) expensive
Related Solutions
How would the mutation described above, changing a lysine to an arginine alter the histone code...
How many lysine residues become aldehydes in the Schiff base crosslink? How many hydrogen atoms are...
Intercations between residues on seperate polypeptide chains would be best classified as: A) Primary B) Secondary...
BIOCHEM LAB: You measured the total protein in a sample of purified protein via the Bradford...
A protein is purified using ultracentrifugation and found to have a mass of 300 kDa. It...
A 0.15 g sample of a purified protein is dissolved in water to 2.0ml of solution....
You have purified a novel protein and have a small aliquot of it. Unfortunately, there’s no...
A nurse identifies 12 mm of induration at the site of a tuberculin purified protein derivative...
If you think of the protein as a traveler, what kind of vehicle would best describe...
After running your purified DHFR fusion protein+Laemmli 40uL sample, along with a protein ladder (Kaleidoscope standard...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago