Question
In: Chemistry
One mole of acetyl chloride was mixed with one mole of dimethylamine.
One mole of acetyl chloride was mixed with one mole of dimethylamine. After the reaction is complete, what species can be found in the mixture? Draw only the organic structures (i.e., omit inorganic ions). Show charges where necessary.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
- The carbonyl compounds readily undergo a nucleophilic addition reaction that involves in the breaking of carbon\((\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O})_{\text {double }}\) bond.
oxygen
- The reactivity of carbonyl compounds is due to the electronegative difference between oxygen and carbon.
- The oxygen attached to carbon is more electronegative. So, the oxygen can partially pull the electrons from the carbon atom making it more electron-deficient. Due to this, the nucleophile readily attacks the carbonyl carbon and undergoes an addition reaction.
Fundamentals
The mechanism of the nucleophilic addition depends on the nature of the nucleophile.
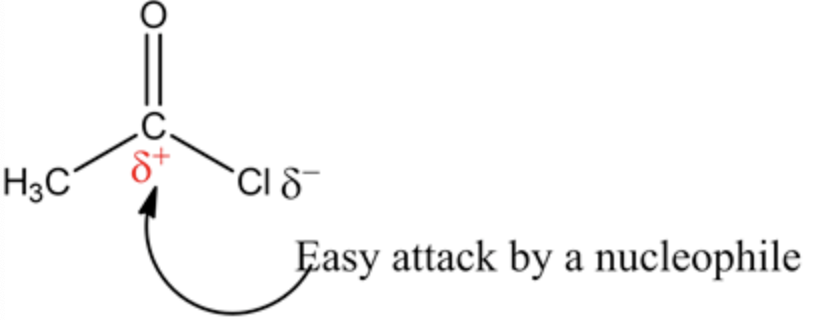
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are species that donate an electron pair and are also termed as electron hating species.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are species that accept an electron pair and are also termed as electron loving species. Dimethyl amine contains nitrogen so it acts as nucleophile as well as base. Nitrogen has negative charge due to the more electronegativity than carbon and hydrogen atom.
The nucleophilic addition reaction of ethanoyl chloride and dimethylamine is
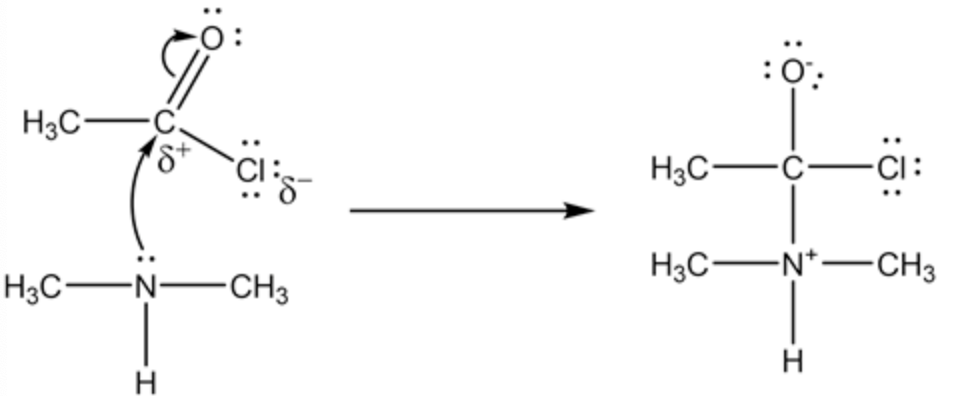
In reaction between ethanoyl chloride and dimethylamine, the dimethylamine acts as nucleophile. The carbon atom
in the -COCl has positive charge on it. So the carbon atom is attacked by the lone pair in the nitrogen atom in the dimethylamine.
The elimination reaction involved in the reaction is given as
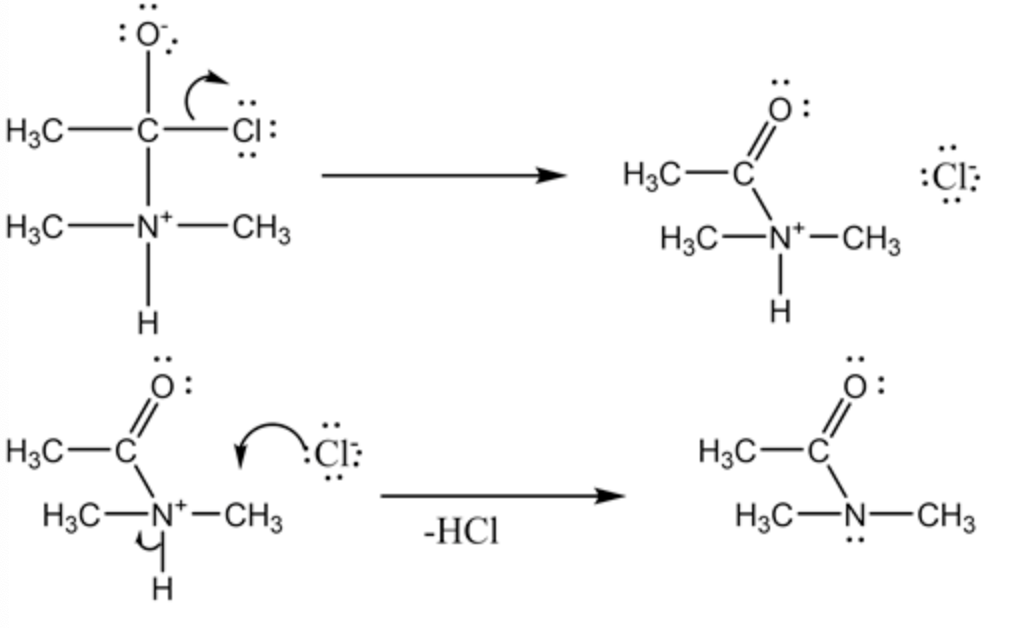
In this elimination step, chlorine is eliminated as chloride ion and carbon-oxygen double bond reform. Then the hydrogen atom which is attached on the nitrogen is removed and formed
The formation of dimethyl ammonium ion is shown below:
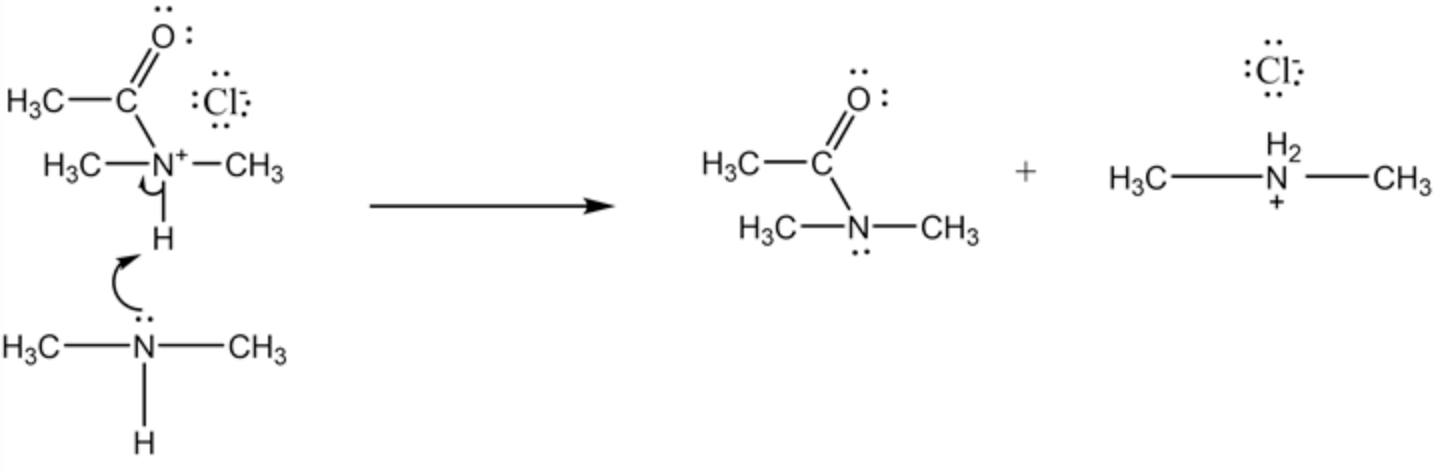
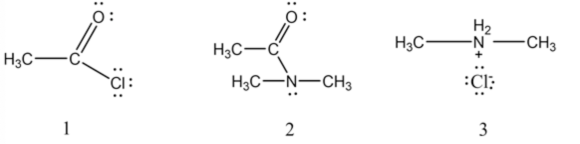
The three organic species are shown below.
Dimethyl ammonium ion is formed by the removal of hydrogen ion by the dimethylamine molecule. The given reaction needs two moles of dimethyl amine for the complete reaction because only half moles of dimethyl amine is reacted with acetyl chloride and other half moles of dimethyl amine (acts as a base) reacts with a
strong acid ( \(\mathrm{HCl}\) ) produced in this reaction. During a reaction, three species are always found at any time in the reaction due to non-stoichiometry.
The three organic species are shown below.
Related Solutions
in the synthesis of propyl acetate 4ml of propanol and 4.5 ml of acetyl chloride was...
If you use 100 mg of ferrocene and 0.08 mL of acetyl chloride, what is your...
If you use 100 mg of ferrocene and 0.08 mL of acetyl chloride, what is your...
What is the limiting reagent in esterification using isopentyl alcohol and acetyl chloride to make isopentyl...
Show step by step reactions with structures; and clear writing Acetyl chloride reacted with: - hexane...
When solutions of silver nitrate and magnesium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution...
When solutions of silver nitrate and calcium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution...
When solutions of silver nitrate and calcium chloride are mixed, silver chloride precipitates out of solution...
one mole of ice at 0 C is put into contact with one mole of steam...
Calculate the number of moles of ammonia needed to dissolve 0.0010 mole of silver chloride in...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago