Question
In: Chemistry
The Fischer esterification mechanism is examined in the following two questions in the assignment.
The Fischer esterification mechanism is examined in the following two questions in the assignment. Part 1 involves MeOH addition to form the key tetrahedral intermediate. Part 2 will involve loss of H2O to form the ester.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
Fischer esterification:
It is an esterification reaction, in which carboxylic acid changes to ester when it reacts with alcohol in the presence of strong acid.
Fundamentals
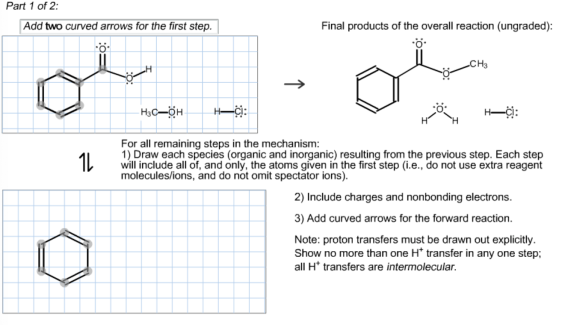
The mechanism for Fischer esterification reaction:
1)Abstraction of the proton from an acid by carbonyl oxygen.
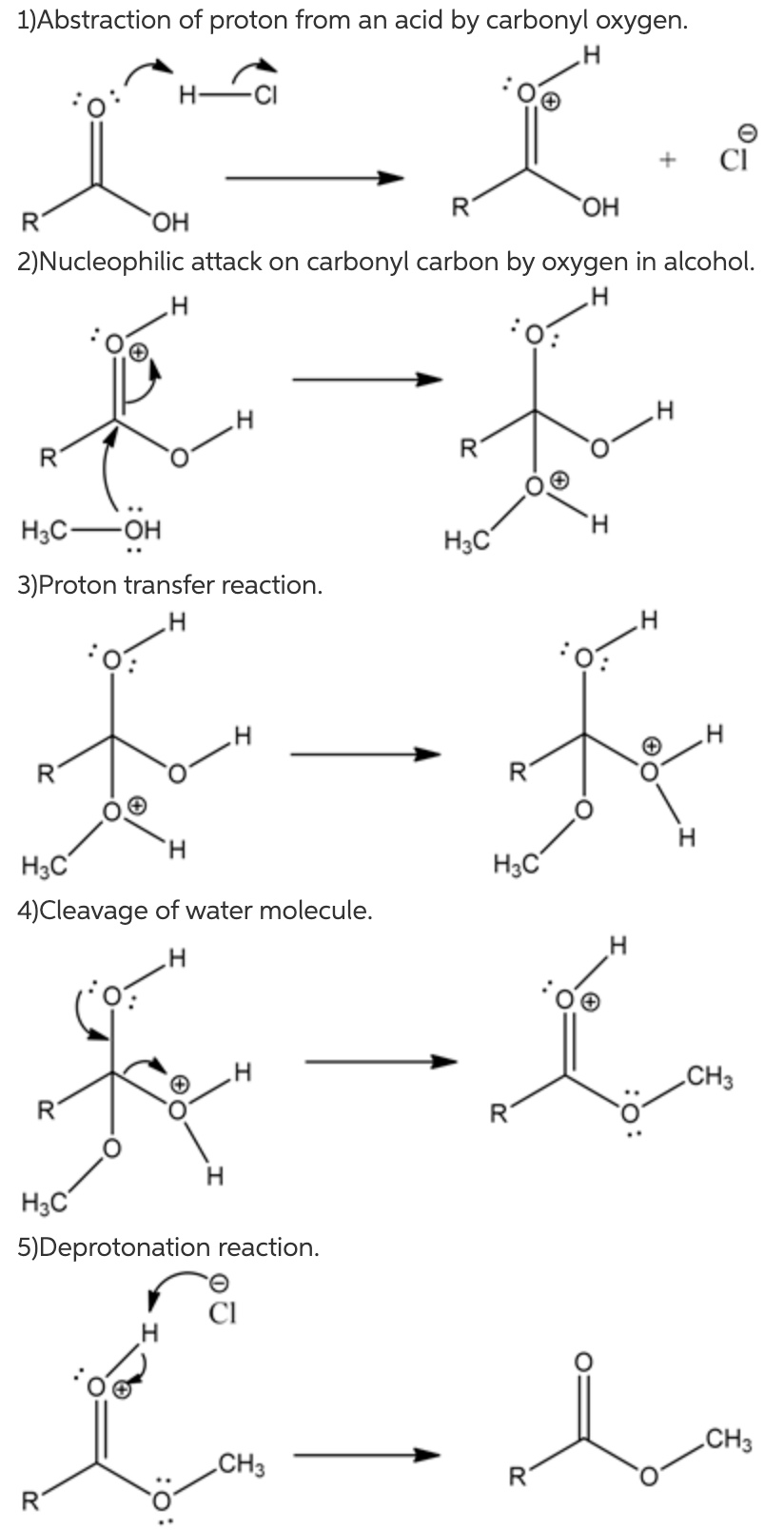
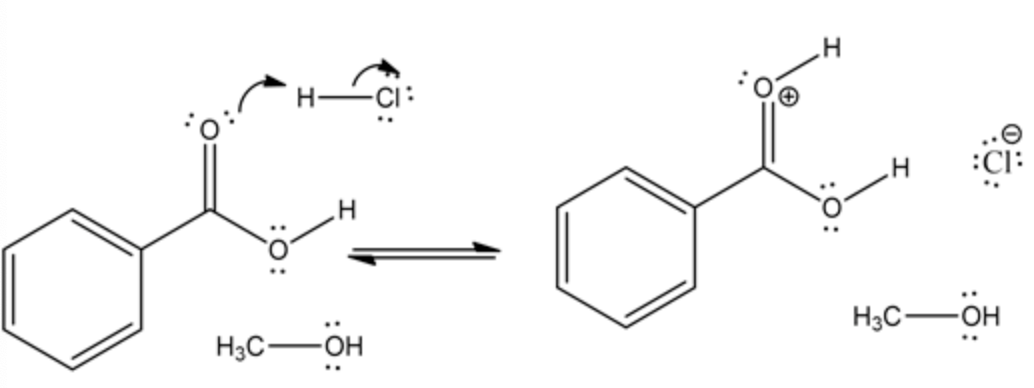
The lone pair of carbonyl oxygen in carboxylic acid abstracts proton from an acid by cleaving chlorine. This abstraction of hydrogen produces a positive charge on oxygen.
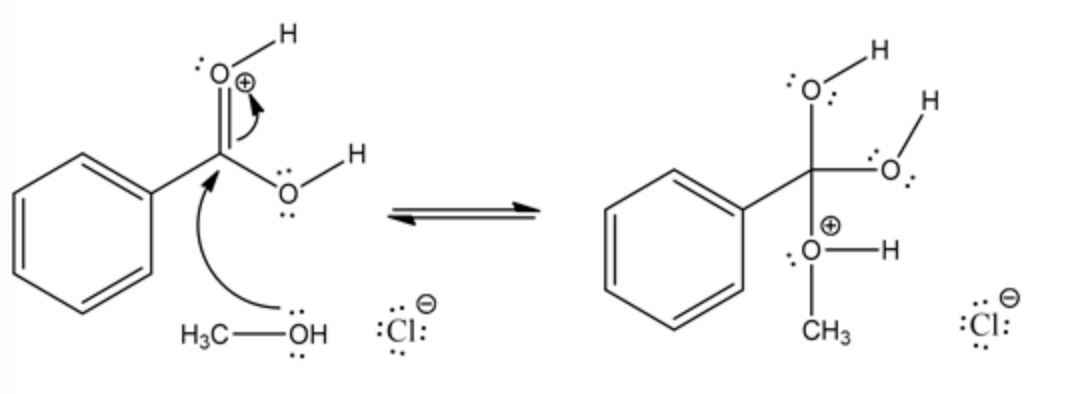
The lone pair electron of oxygen in alcohol attacks the carbonyl carbon and stabilizes the positive charge on carbonyl oxygen by resonance. The carbonyl attack by an alcoholic oxygen creates a positive charge on alcoholic oxygen.
The intermediate is formed by the abstraction of proton by chloride ion and stabilize the positive charge on alcoholic oxygen.
Related Solutions
please explain the Fischer Esterification and mechanism of the Fischer Esterification concretely in your words!!!! Then...
The mechanism for the Fischer esterification is shown on page 762 of your textbook. The acid...
Describe the process of each step in the experiment (Fischer esterification/ Isopentyl acetate lab). a. The...
Fischer esterification Reaction: n-Butyl Acetate Which one of the following choices describes most accurately the actual,...
Organic II lab: Fischer Esterification: Preparation of Benzocaine The protocol for this week’s experiment calls for...
Fischer Esterification: Synthesis of Isoamyl Acetate (Banana Oil) 4) a) What is the role of sulfuric...
Fischer Esterification Acetic Acid + Ethanol in the presence of Dowex, a solid catalyst. 4 samples...
Fischer Esterification Post lab question 1. Provide a brief description of how microwave works in the...
How would I find the theoretical and percent yield of a Fischer esterification? I used 1.5...
Good evening! I have synthetized benzocaine by Fischer esterification of para-aminobenzoic acid with ethanol and concentrated...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago