Question
In: Chemistry
Draw the product(s) formed by heating the following compound in acidic methanol.
Draw the product(s) formed by heating the following compound in acidic methanol.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
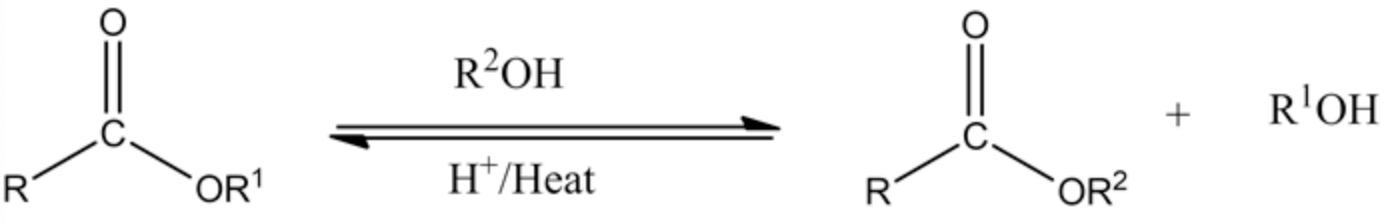
Transesterification is a reaction process where the ester reacts with the alcohol in acid catalyst and heat to produce a new ester and alcohol. In this process, the ester can be converted into other esters using the alcohol group with an acid catalyst.
Fundamentals
Transesterification: Ester conversion to the other ester in the presence of acid catalyst and heat is known as transesterification.
Acid catalyst protonates the carbonyl oxygen in the ester functional group, which leads to oxonium ion. Then, carbonyl electrons are moved towards the oxonium ion while the alcohol group attacks the positively charged carbon in the carbonyl, leading to the formation of a new ester.
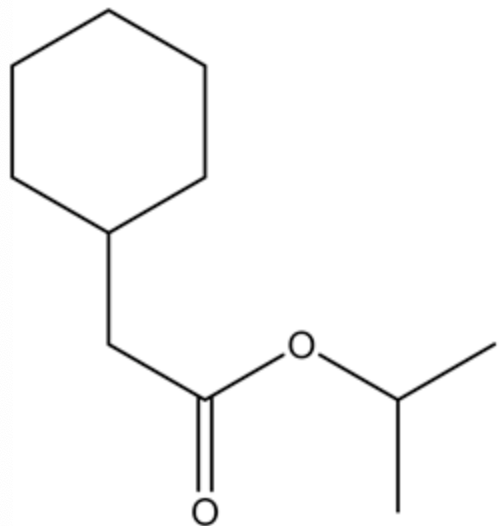
From the given ester, the structure is shown below.
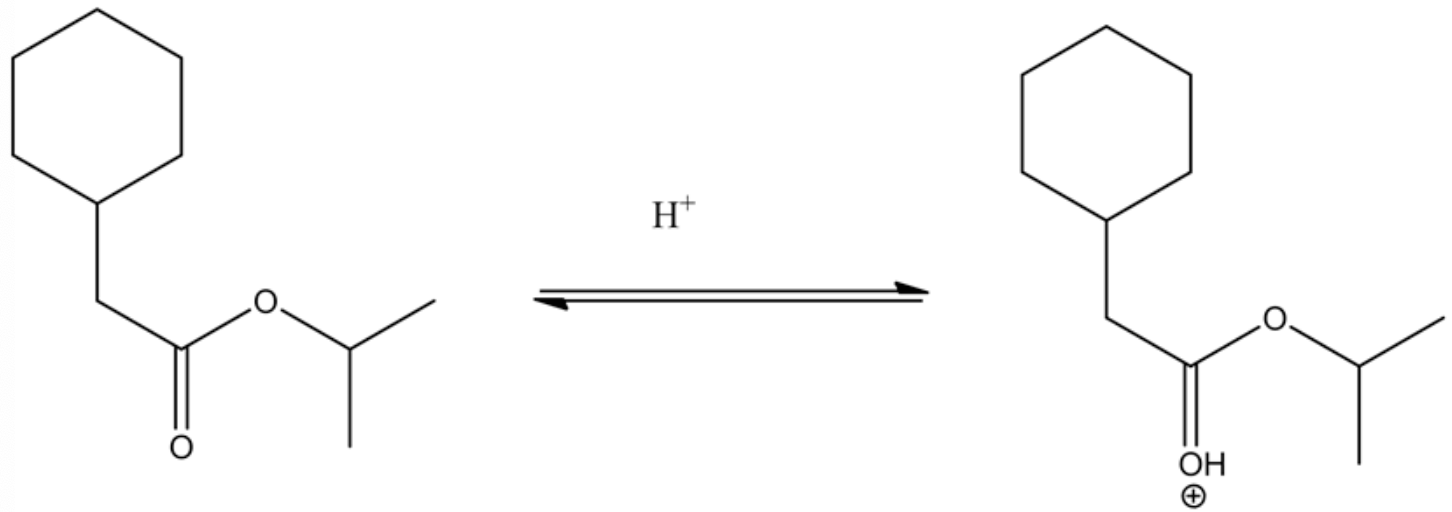
The protonation of the ester by acid is as follows.
Alcoholic group (methanol) attacks the carbonyl group and forms tetrahedral intermediate.
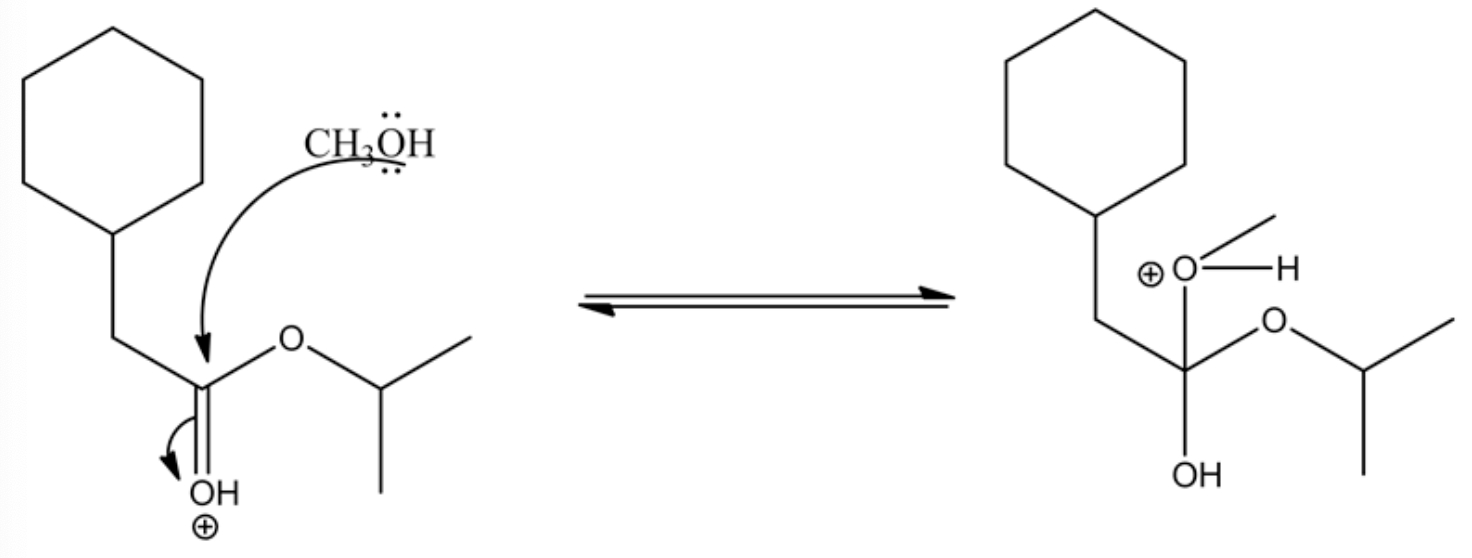
The acid protonates given ester to form an oxonium ion. The positive charge on oxonium ion attracts the bonded electron pair towards itself, which causes the attack of the methanol group on the positively charged carbon in the carbonyl group to give the tetrahedral intermediate.
Deprotonating the tetrahedral intermediate is as follows.
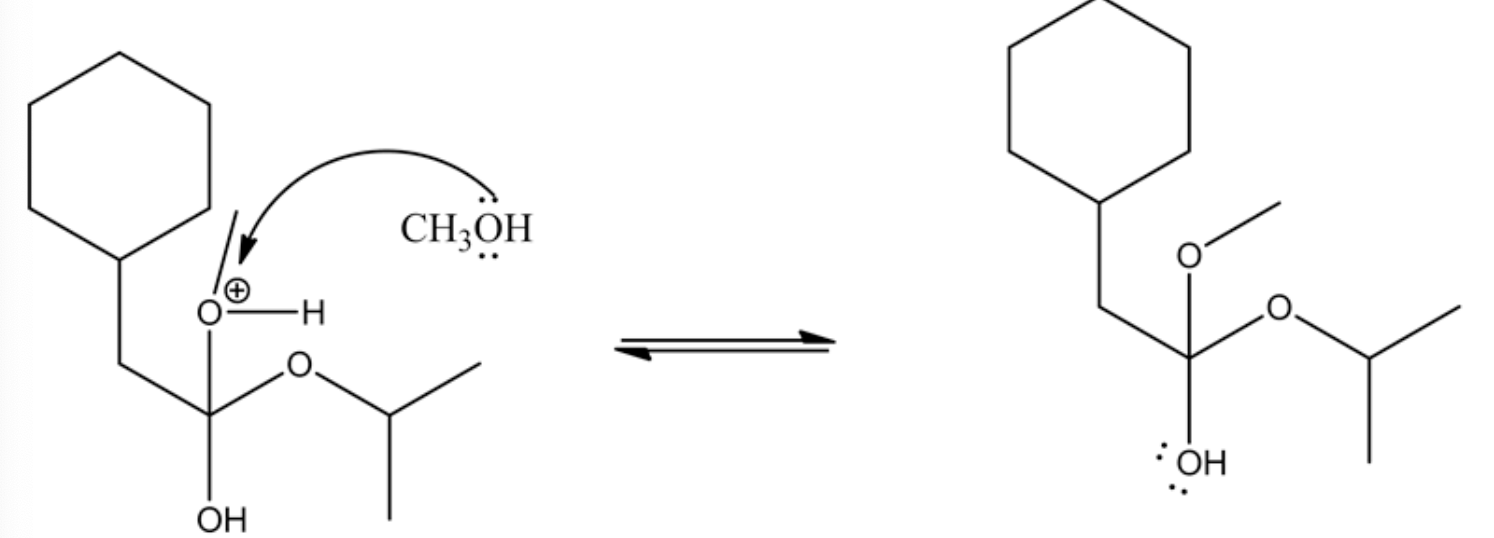
Acid/base reaction is a process where protonation occurs at non-carbonyl oxygen to make methoxide ion to methanol as a good leaving group.
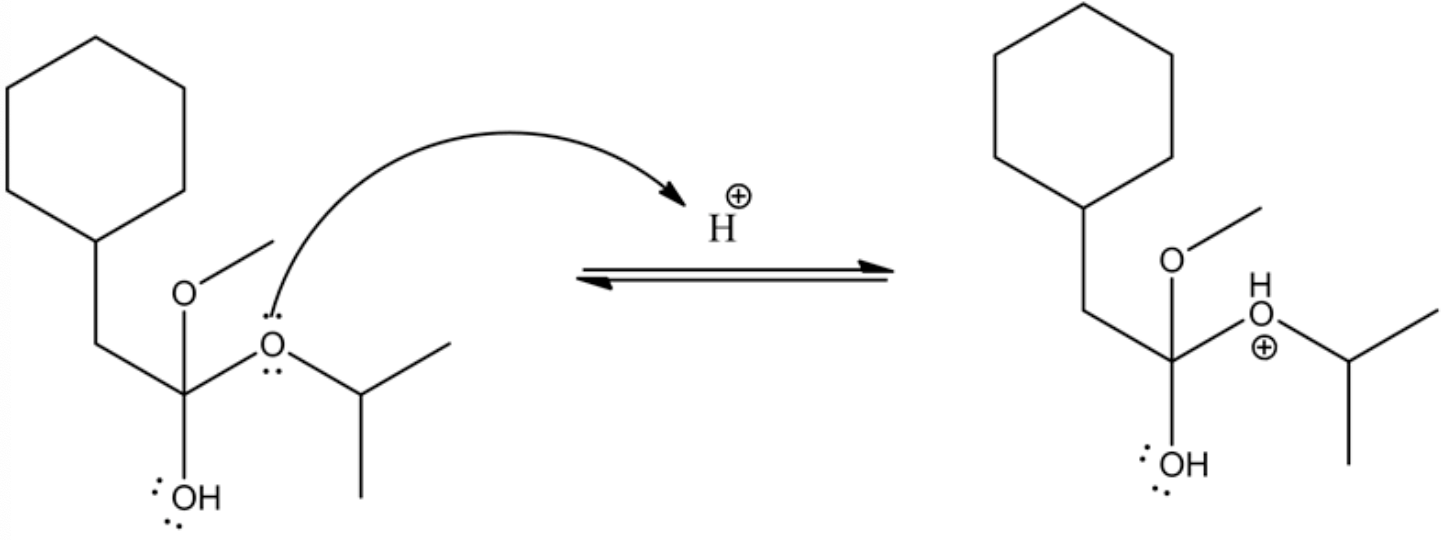
The leaving group goes out by electrons' movement from the adjacent oxygen and forms oxonium ion, which leads the ester by deprotonation.
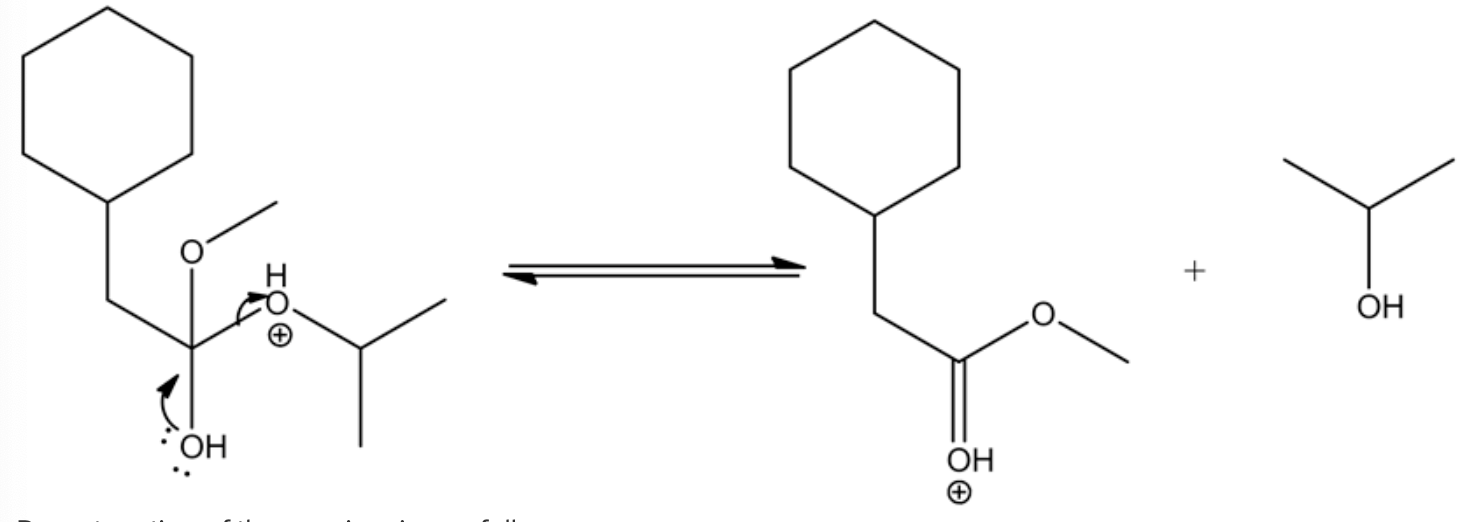
Deprotonating of the oxonium ion as follows.
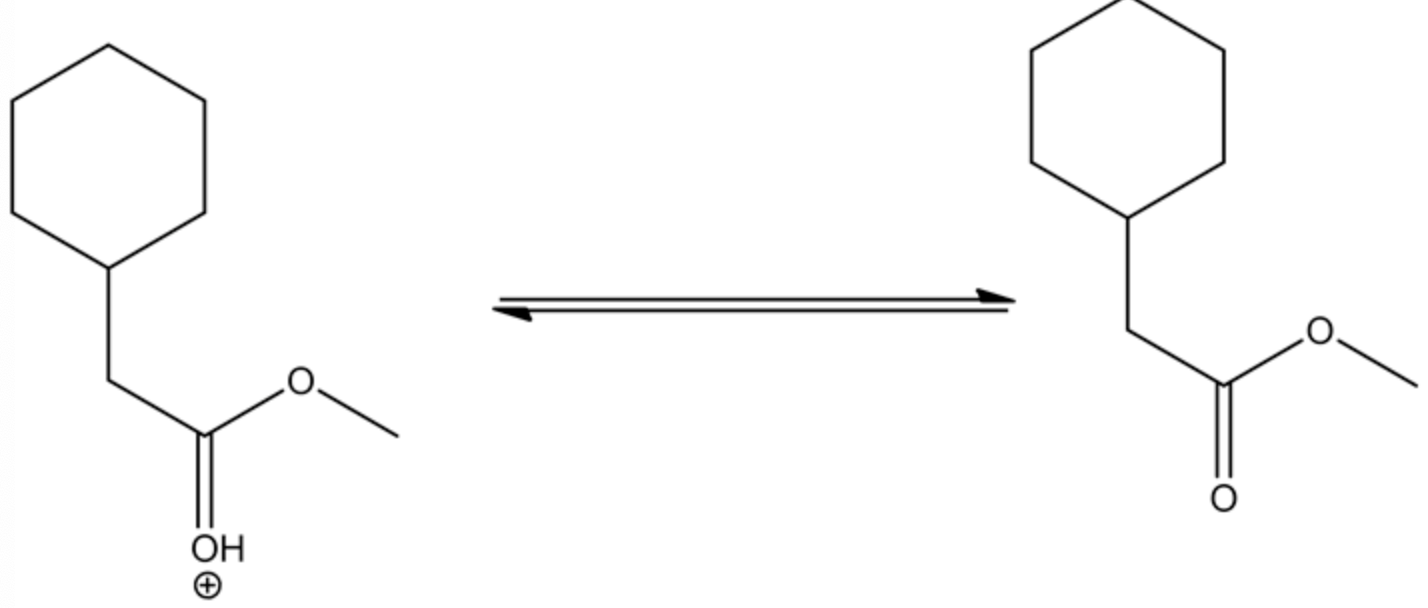
The complete transesterification reaction
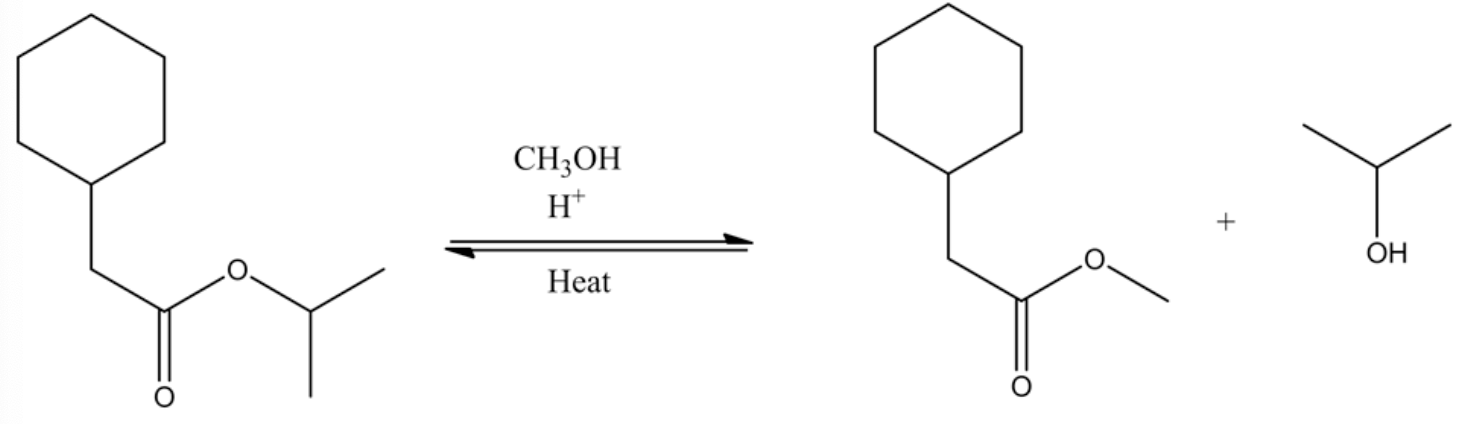
The tetrahedral intermediate formed through the methanol attack on the oxonium ion, which is formed through the protonation of the ester by an acid. This tetrahedral intermediate further undergoes acid/base reaction through deprotonating at carbonyl oxygen and protonation at non-carbonyl oxygen. This leads to a new ester by leaving the alcohol group.
Complete trans esterification reaction
Related Solutions
Draw the organic products formed in the following reaction.
Write a balanced equation for the oxidation of methanol with KMnO4 in acidic solution; show how...
The following compounds can be formed during the Maillard reaction. For each compound: Compound From Caramelization?...
1) Draw the structure of the product formed by addition of vitamin B1 and benzaldehyde. 2)...
1) Draw the structure of the product formed by addition of vitamin B1 and benzaldehyde. 2)...
Draw the product of 2-methylpropene oxide, methyl lithium, hydronium workup Draw the product of (S)-propene oxide,...
Draw a hybrid solar water heating system.
Draw the major alkene product formed from dehydrating the following alcohols? a) 2-methylcyclohexanol b) 2,3-dimethylcyclohexanol c)...
Draw the major organic product(s) for the following reaction. Multiple products may be drawn in one...
A compound dissolved in methanol and need to remove by distillation because heat is sensitive, a...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago