Question
In: Chemistry
What is the difference between delta G at equilibrium and delta G at steady state? Do...
Solutions
Expert Solution
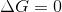 at equilibrium. The Gibb's free energy is a measure of the
incompleteness of a reaction. The more difference between the
Gibb's free energy an standard Gibb's free energy in a reaction,
the more incomplete is the reaction.
at equilibrium. The Gibb's free energy is a measure of the
incompleteness of a reaction. The more difference between the
Gibb's free energy an standard Gibb's free energy in a reaction,
the more incomplete is the reaction.
The standrd Gibbs free energy at equilibrium is given by
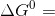 -RT ln Kp , where Kp is the equilibrium constant at
constan pressure.
-RT ln Kp , where Kp is the equilibrium constant at
constan pressure.
In Steady state, we have two or more equilibrium taking place at a constant rate which doesnt change the concentration of a particular intermediate. We have the change in concentration of the intermediate as zero with respect to time. The Gibb's free energy is not zero in this approximation.
Reactions at equilibrium do not have any available energy to do any work, but reactions in steady state do.
If we perturb(disturb) a system in equilibrium, the system would return to its equilibrium with a different Kp, yielding a different Standard Gibb's free energy according to that condition. But if we perturb a system which is in steady state, the Gibbs free energy changes, that is energy available to do any type of work also changes.
Related Solutions
explain the difference between the transient period, and the steady-state operation. with examples
what is the difference between stimulus delta and negative reinforcement
What is steady-state error? What is the type of the system? What is the steady-state error...
What does it mean for a free energy diagram of an equilibrium reaction when delta G...
Dynamic equilibrium vs equilibrium. What is the difference between a reaction in dynamic equilibrium and one...
What is steady state exercise?
For the data shown, what is the Delta IRR for the difference between the cash flows...
What is the difference between the ground state of an atom and an excited state of...
What is the difference between partial equilibrium and general equilibrium? Discuss the advantages of restricting the...
What is the relationship between dose, clearance, bioavailability and steady state plasma concentration?
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago