Question
In: Chemistry
The Gabriel synthesis transforms an alkyl halide into a primary amine via a two-step process.
The Gabriel synthesis transforms an alkyl halide into a primary amine via a two-step process. Follow the directions below to draw the initial mechanism and final products. Draw curved arrows to the next step. Draw the missing nonbonding electrons, charge and curved arrows. The first three steps are correct. I am unsure about how to complete the final step.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
Gabriel synthesis: Gabriel synthesis is a synthesis of the primary amine from the primary alkyl halide, in the presence of potassium phthalimide. Potassium phthalimide attacks the carbon atom of the alkyl halide and replaces the halide ion.
Fundamentals
Gabriel synthesis pathway: The primary amine synthesis from the primary alcohol is shown below.
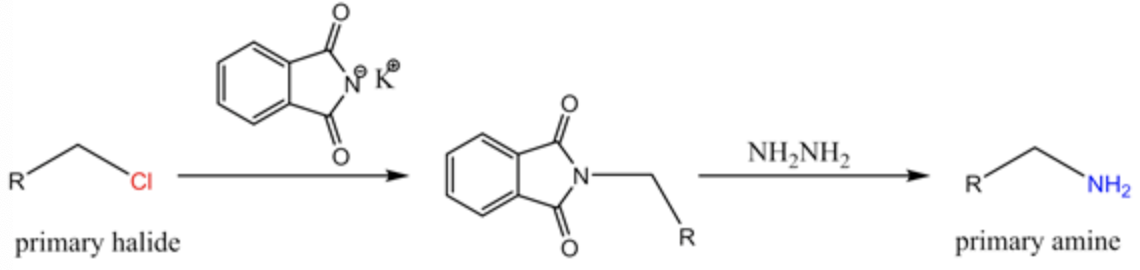
It is clear from the above path that the phthalimide acts as a nucleophile and attacks the primary alkyl halide in the SN2 path way, where chlorine is the leaving group.
The given alkyl halide is drawn below and the expected Gabriel synthesis product is also drawn below.

The curved arrow mechanism of the reaction is drawn below.
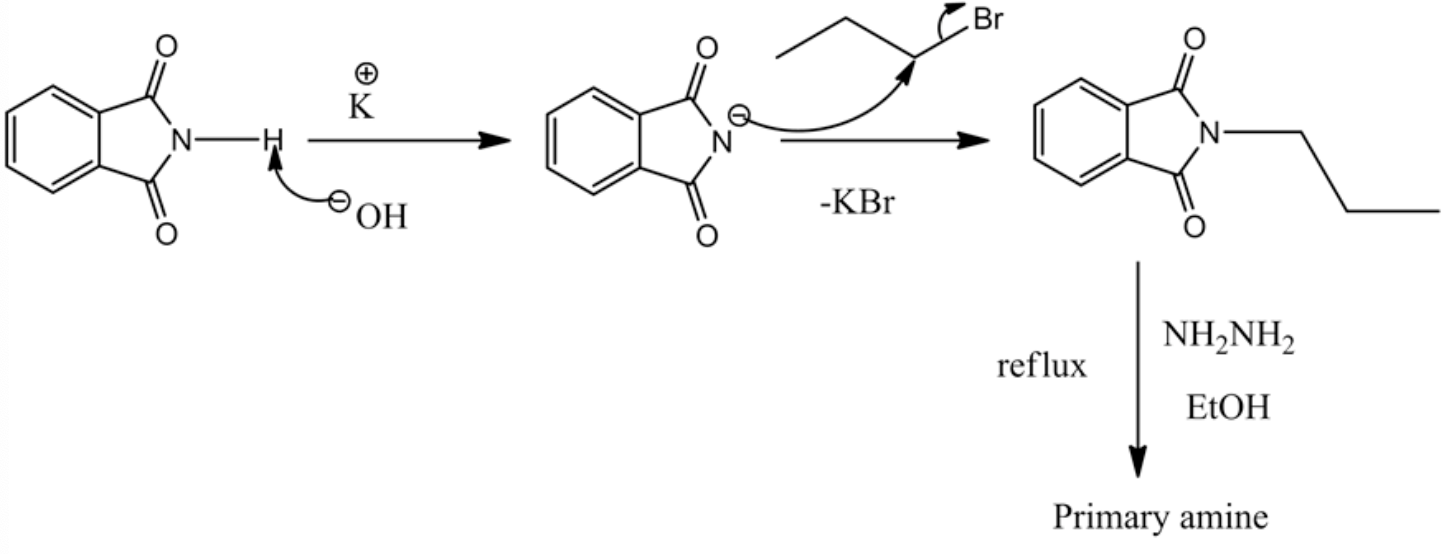
It is clear from the above curved arrow mechanism that the whole reaction represents the Gabriel synthesis process since reagents used in the reaction are phthalimide and hydrazine.
The given mechanism is represented as follows:
1.The first step of the mechanism indicates the abstraction of a proton from phthalimide by using a strong base (potassium hydroxide).
2.In the second step, phthalimide (nucleophile) attacks the alkyl halide in SN2 pathway.
3.The third step represents the formation of the primary amine, which is not shown in the mechanism.
The products are drawn below for the final step of the synthesis.
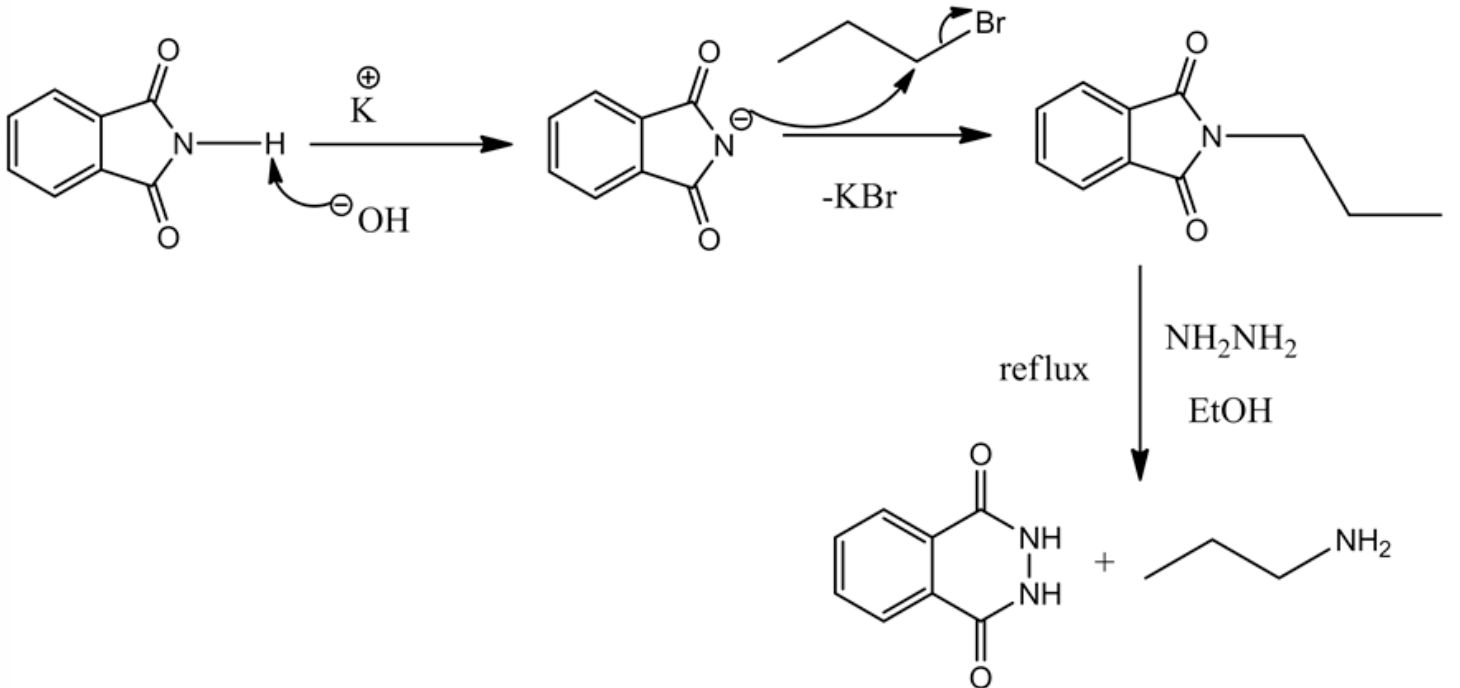
The curved arrow mechanism for the final step is drawn below.
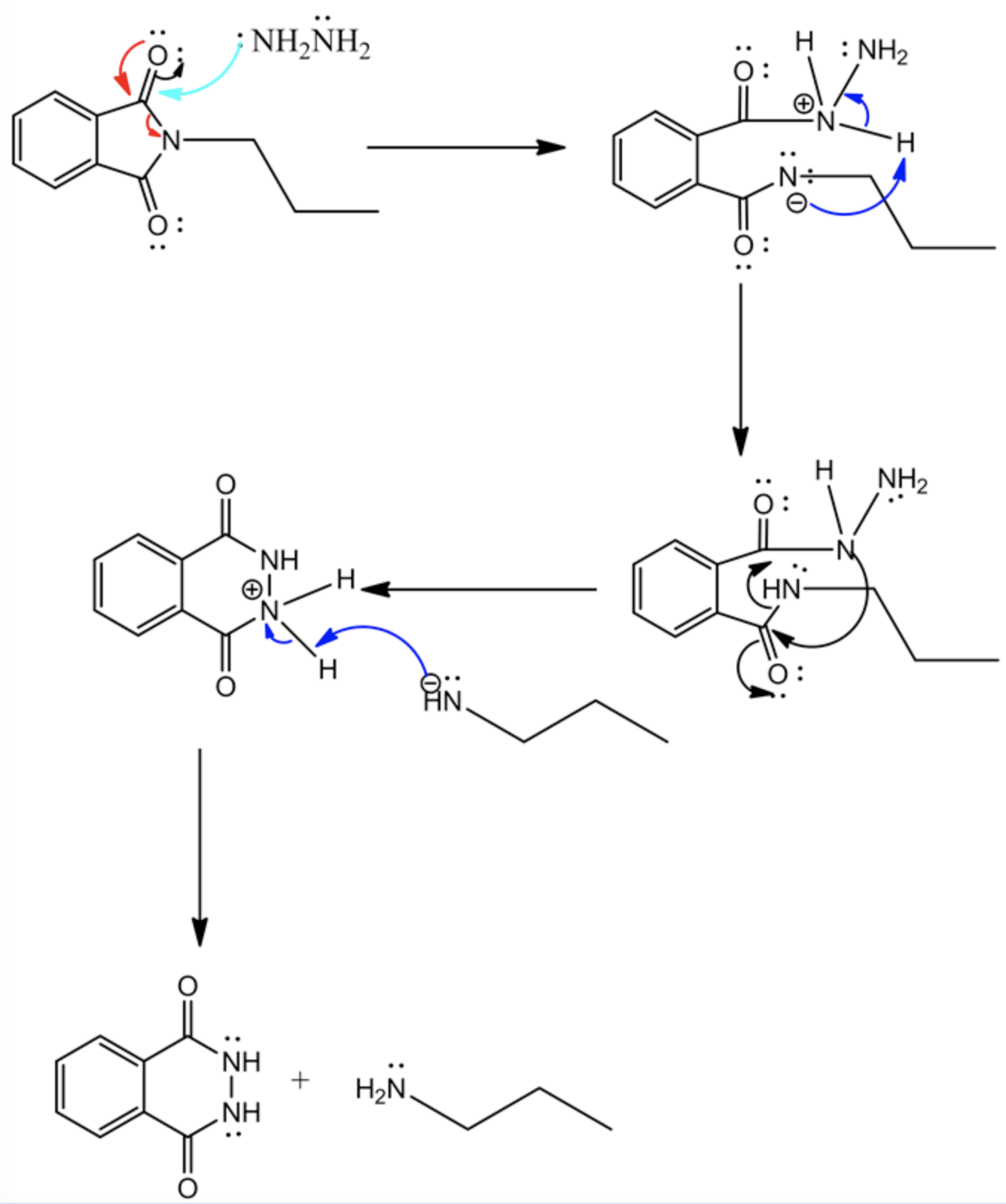
The major product during the Gabriel synthesis process is drawn below.
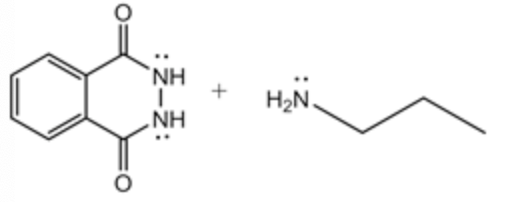
The Gabriel synthesis product has been drawn for the given alkyl halide. First, potassium phthalimide is synthesized; then, the Gabriel process is followed by the alkyl halide to synthesize the primary amine. In the above step, the curved arrow mechanism is clearly shown for the last conversion of the Gabriel synthesis process and it is achieved by following 4 steps as explained below.
Step: 1: The hydrazine acts as a base and attacks the electrophilic site thereby ring opening occurs.
Step: 2: amide abstracts the proton.
Step: 3 : lone pair electrons on nitrogen \(\left(\mathrm{NH}_{2}\right)\) attacks the carbonyl carbon and forms the six membered ring thereby alkyl amine is released as an anion.
Step: 4: The anion abstracts the proton which leads to the formation of a final product.
The major product during the Gabriel synthesis process is drawn below.
Related Solutions
Choose all possible reagents for the reaction of a primary alcohol to alkyl halide and, for...
29. How propyl amine can be synthesized by Gabriel Synthesis? Write the mechanism of the reaction....
How many of the following responses are true? 1. A primary alkyl halide will tend to...
Can anyone explain the complete mechanism for preparation of amines via gabriel synthesis starting with phthalimide?
Give two reasons why tertiary alkyl halides are more likely to eliminate than primary alkyl halides.
In the first step of the Ostwald process for the synthesis of nitric acid, ammonia is...
This is system engineering process. pls explain each step in this process. Problem definition(Analysis), Conceptual Design(Synthesis,...
Draw the structure of the organic product of each reaction in the following two-step synthesis.
Draw the structures of the organic products in each reaction of the following two-step synthesis.
What is the primary goal of the second step of the market positioning process? Multiple Choice...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago