Question
In: Biology
Describe the process of protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells. Begin with a gene in the DNA...
Describe the process of protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells.
Begin with a gene in the DNA and throughly explain all of the steps of transcription (initiation , elongation, termination and one type of termination.
Describe translation(initiation, elongation, termination) that result in the formation of a functional protein. Be specific as to the mechanism of each step.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Process of protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells. Protein synthesis is the synthesis of proteins and occurs in the cytoplasm. In prokaryotes transcription and translation occurs concurrently (translation starts before the completion of transcription).
Transcription: DNA dependent synthesis of any
type of RNA molecule with the help of RNA Polymerase is called
transcription. Transcription always start at specific site called
promoter. Promoter is specific site on DNA where
RNA Polymerase binds and initiates transcription. Synthesis of RNA
occurs in 5' to 3' direction and continuous, only a strand of DNA
act as template and only a small segment of DNA is
transcribed at a time generally called gene. Prokaryotic
promoters are always present on upstream to transcription start
site, are 70 base pair long and contain two consensus sequence of 6
base pair at -10 region and -35 region (-10 region is also
known as TATA box). In prokaryotes single type of RNA
Polymerase transcribe all types of RNA such as mRNA, rRNA and tRNA.
RNA Polymerase is a multisubunit enzyme and consists of five
different polypeptides called  (holoenzyme).
(holoenzyme). 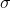 subunit helps in promoter recognition and initiate transcription
whereas core enzyme consists of
subunit helps in promoter recognition and initiate transcription
whereas core enzyme consists of
 subunits and catalyze transcription. Prokaryotic transcription
completed in three sequential steps:
subunits and catalyze transcription. Prokaryotic transcription
completed in three sequential steps:
- Initiation: The
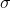 factor associated with core enzyme to form holoenzyme, the
holoenzyme binds with promoter to form closed binary complex.
Unwinding of double strand is done which creates an open complex.
Addition of first nucleoside triphosphate to form ternary complex
and
factor associated with core enzyme to form holoenzyme, the
holoenzyme binds with promoter to form closed binary complex.
Unwinding of double strand is done which creates an open complex.
Addition of first nucleoside triphosphate to form ternary complex
and 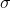 factor is released as RNA Polymerase moves.
factor is released as RNA Polymerase moves. - Elongation: Once RNA Polymerase successfully synthesize a short stretch of RNA. RNA transcript synthesized by RNA Polymerase continuously dissociates from DNA template as well as transcription proceeds. Only 8 to 10 base pair long RNA-DNA complementary is maintained in transcription bubble region.
- Termination: Transcription termination occurs at the end of gene and is always guided by transcribed RNA molecule because transcription termination signal present in RNA. Termination occurs by two types:
1. Rho dependent termination: Have two common features: A DNA sequence that pause transcription and an ill-defined RNA element called rut site (rut utilization). Rho protein binds with rut site and moves towards its 3'end. When RNA Polymerase encounters terminator sequence it pause and catch by rho and interaction of rho by RNA Polymerase. Using RNA-DNA helicase activity rho unwinds RNA-DNA hybrid and release RNA transcript.
2. Rho independent termination: Have two features: Hair pin loop structure includes GC rich region which prevents the movement of RNA Polymerase. A stretch of adenine residue in template strand at the end of gene.
Translation: Translation completed in four sequential steps:
- Activation of amino acid (tRNA charging): Amino acid activation occurs when a specific amino acid covalentally binds with 3'end of its cognate tRNA. Activation of amino acid is catalysed by an ATP dependent enzyme called aminoacyl tRNA synthetase (AATS).
- Initiation: Completed in three sequential steps: 1) Small subunit of ribosome binds with mRNA and is facilitated by two proteinaceous factors called IF-1 and IF-3. 2) Binding of initiating charged tRNA, binding of charged initiating tRNA to the P site of small subunit of ribosome catalysed by IF-2 in GTP bound state. 3) Binding of large subunit with small subunit to form 70S initiation complex.
- Elongation: Elongation phase of translation
includes codon to codon translocation of active ribosomes on mRNA
in 5' to 3' direction and forms peptide bond between codon
specified amino acid. Completed in three sequential steps: 1)
Binding of aminoacyl tRNA (charged tRNA) to the A
site of ribosomes and is catalysed by GTP bound elongation protein
EF-Tu. 2) Peptide bond formation, after the
release of EF-Tu
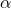 amino group of A site amino acid act as nucleophile on
amino group of A site amino acid act as nucleophile on 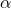 carboxylic group of P site amino acid and makes peptide bond. After
peptide bond formation P site tRNA becomes uncharged and A site
tRNA generates dipeptidyl tRNA. 3) Translocation of ribosomes,
translocation shifts dipeptidyl tRNA from A site to P site and
uncharged tRNA from P site to E site and A site occupy next codon
thus open for incoming aminoacyl tRNA.
carboxylic group of P site amino acid and makes peptide bond. After
peptide bond formation P site tRNA becomes uncharged and A site
tRNA generates dipeptidyl tRNA. 3) Translocation of ribosomes,
translocation shifts dipeptidyl tRNA from A site to P site and
uncharged tRNA from P site to E site and A site occupy next codon
thus open for incoming aminoacyl tRNA. - Termination: Translation termination occurs when A site occupies a stop codon . In this case, A site not entered by an aminoacyl tRNA but by proteinaceous factor called release factor.
Related Solutions
fully describe the process of protein synthesis beginning at DNA
Describe the process of protein synthesis starting with DNA in the nucleus and ending with proteins...
describe in words the process of protein synthesis
The speed of DNA replication in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells DIFFERS because: A.) prokaryotic cells don’t...
describe the process of protein synthesis in a short paragraph
Describe how the information encoded in a gene results in the synthesis of a functional protein...
Describe how the information encoded in a gene results in the synthesis of a functional protein...
A gene is composed of DNA and a protein is composed amino acids. Describe the steps...
Explain the process of how DNA replicates itself to pass on the protein synthesis ability after...
With explanations, outline the steps involved in the elongation of protein synthesis in a prokaryotic cell.
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 amino group of A site amino acid act as nucleophile on
amino group of A site amino acid act as nucleophile on  gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago