Question
In: Chemistry
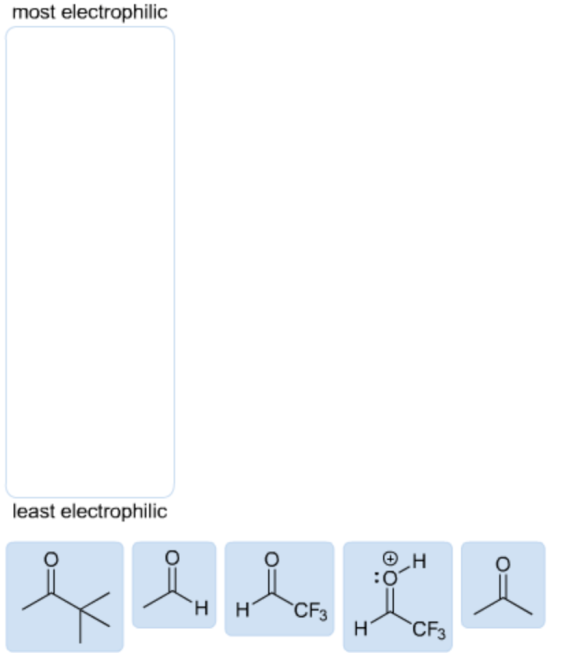
Rank the following structures in order of decreasing electrophile strength.
Rank the following structures in order of decreasing electrophile strength.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
Electrophile:
In organic chemistry, the electrophilic atom is usually a carbon atom, bonded to electronegative atoms such as nitrogen, oxygen, and fluorine. In these kinds of molecules, separation of charges (polarization) occurs. As a result of polarization, the carbon atom contains a partial positive charge while the electronegative atom contains a partial negative charge, and the molecule is known as an electrophile. Resonance:
In a conjugated molecule, the lone/pi-bond pair of electrons move along sigma bonds within a molecule. It leads to different arrangements of electrons for the same molecules. It is called resonance.
Fundamentals
Inductive effect:
The introduction of electronegative atoms (nitrogen, oxygen, or fluorine) causes a negative inductive effect, which is the pulling of bond pair electrons through sigma bonds, making the carbon in a \(\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}\) bond more electrophilic. For example,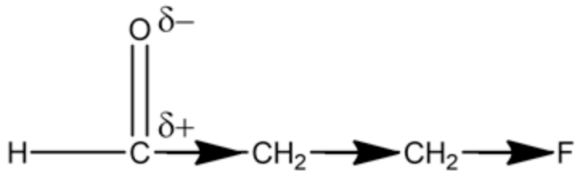
The introduction of alkyl groups causes a positive inductive effect, which is the donation of electrons through sigma bonds, making carbon in a \(\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}\) bond less electrophilic. For example,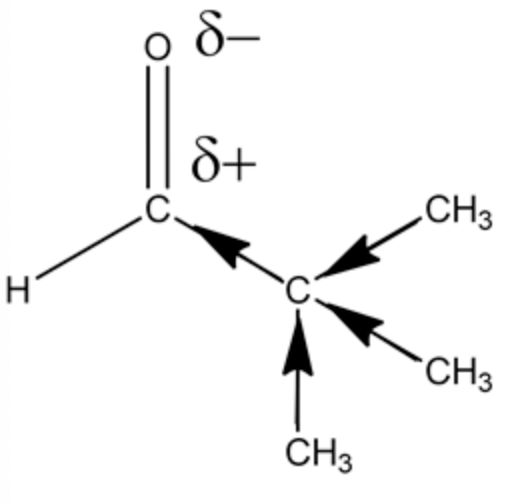
Partial Charge separations:
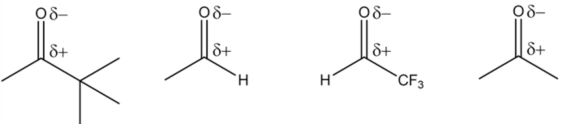
Resonance:
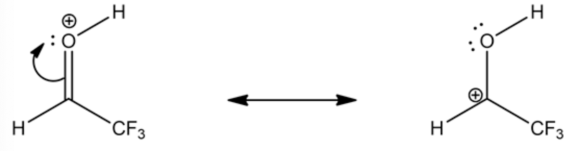
In a carbonyl functional group, the oxygen atom pulls the electrons away from the carbon atom, making the carbon atom more electrophilic in nature because the oxygen atom is more electronegative than the carbon atom. The carbon atom in a protonated carbonyl group gets a positive charge due to its resonance structures.
Descending order of electrophilic strength:
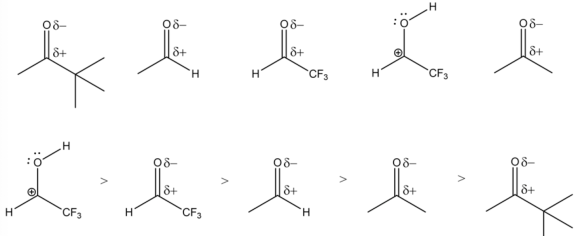
The protonated carbonyl group is the most electrophilic because the carbon atom has a full positive charge. So, it ranks first in the descending order of electrophilic strength.
The carbon atom in fluorine substituted carbonyls is more electrophilic in nature due to the negative inductive effect. Hence, it ranks second in the descending order of electrophilic strength.
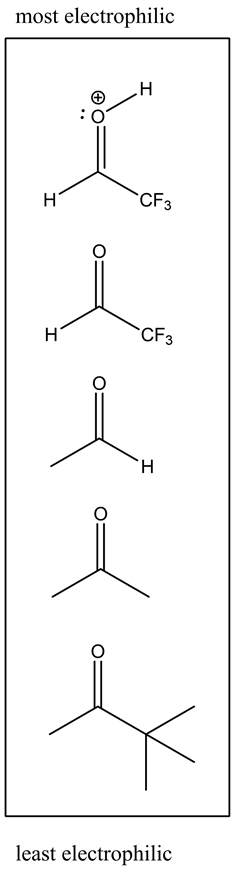
The alkyl-substituted carbonyls are less electrophilic in nature due to the positive inductive effect. So, these molecules are ranked by increasing carbon chain length with the descending order of electrophilic strength.
Related Solutions
Rank these species in decreasing order of bond energies and rank these species in decreasing order...
Rank these systems in order of decreasing entropy. Rank from highest to lowest entropy. To rank...
Rank the following molecules or ions in order of decreasing bond length using their bond order...
rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity. CH3CH2CH2OH CH3CH2CO2H CH3C(O)CH2OH
Rank the following atoms in the order of decreasing electron affinity. Li, Si, Mg, S
Rank the following five salts in order of decreasing solubility, in terms of mass per unit...
Assuming each solution to be 0.10 M , rank the following aqueous solutions in order of decreasing pH.
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing strength of intermolecular attractions: H2O2, CF4, KF, and...
Part A: Rank these transition metal ions in order of decreasing number of unpaired electrons. If...
Rank these systems in order of decreasing entropy. 1 mol of argon gas at 273K and...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago