Question
In: Chemistry
For each phase change, determine the sign of ΔH and ΔS. Sublimation , Freezing,Condensation, Deposition, Boiling , Melting
For each phase change, determine the sign of \({\Delta H}\) and \(\Delta S\) Sublimation, Freezing,Condensation, Deposition, Boiling, Melting
a) \(+\Delta \mathrm{H},+\Delta \mathrm{S}\)
b) \(-\Delta \mathrm{H},-\Delta \mathrm{S}\)
c) \(+\Delta H,-\Delta S\)
d) \(-\Delta H,+\Delta S\)
Put the phase change to the correctsign of \(\Delta \mathrm{H}\) and \(\Delta \mathrm{S}\)
Solutions
Expert Solution
Concepts and reason
The change in energy \((\Delta H)\) during phase change or a reaction is known as Enthalpy. When energy is absorbed during reaction or phase change, the sign for enthalpy is taken as positive. When energy is released during reaction or phase change, the sign for enthalpy is taken as negative. The change in entropy (degree of randomness, \(\Delta S\) ) during phase change or a reaction is known as Entropy. When the degree of randomness is increased, it is given a positive sign, and when the degree of randomness is decreased, it is given a negative sign. In the given question, you need to determine the signs of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for various processes mentioned in the question.
Fundamentals
Sublimation - The process in which a solid-state substance is directly converted into the gaseous state is termed sublimation. Freezing - The process in which a substance in the liquid state is converted into the solid-state is termed freezing. Condensation - The process in which a substance in the gaseous state is converted into a liquid state is termed condensation. Deposition - The process in which a substance in the gaseous state is directly converted into the solid-state is termed deposition. Boiling - The process in which a substance in the liquid state is converted into the gaseous state is termed boiling. Melting - The process in which a solid-state substance is converted into a liquid state is termed melting.
For sublimation, the change in energy is positive, and the change in randomness is also positive.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the sublimation process is
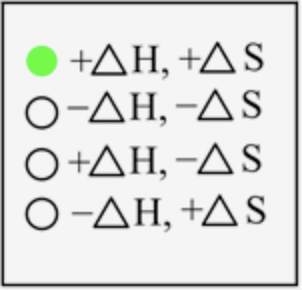
In sublimation, the solid-state is converted directly into a gaseous state, which means energy is required to break the interaction between the solid-state to change it into a gaseous state. Thus, energy is absorbed here, and the sign is positive. The degree of randomness increases on moving from solid to a gaseous state; therefore, entropy is also positive.
For freezing, the change in energy is negative, and the change in randomness is also negative.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the freezing process is
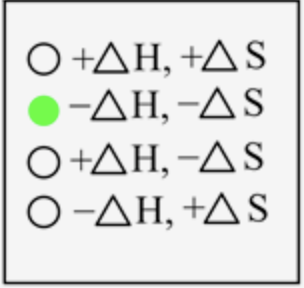
In freezing, the liquid state is converted into a solid-state, which means energy is released when atoms come closer to each other. Thus, energy is released here, and the sign is negative. The degree of randomness decreases when moving from liquid to solid-state; therefore, entropy is also negative.
For condensation, the change in energy is negative, and the change in randomness is also negative.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the condensation process is
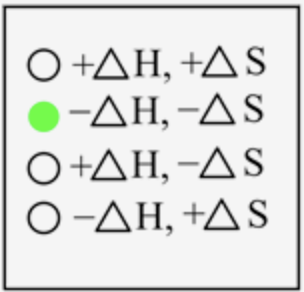
In condensation, the gaseous state is converted into a liquid state, which means energy is released when atoms come closer to each other. Thus, energy is released here, and the sign is negative. The degree of randomness decreases when moving from gas to liquid state; therefore, entropy is also negative.
For deposition, the change in energy is negative, and the change in randomness is also negative.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the deposition process is
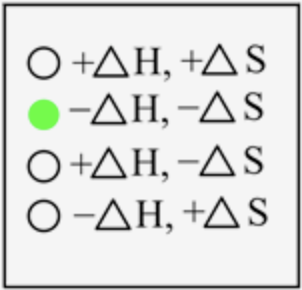
In a deposition, the gaseous state is directly converted into a solid-state, which means energy is released when atoms come closer to each other. Thus, energy is released here, and the sign is negative. The degree of randomness decreases when moving from gas to solid-state; therefore, entropy is also negative.
For boiling, the change in energy is positive, and the change in randomness is also positive.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the boiling process is
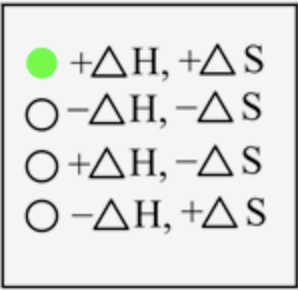
In boiling, the liquid state is converted into a gaseous state, which means energy is required to break the interaction between the liquid state to change it into a gaseous state. Thus, energy is absorbed here, and the sign is positive. The degree of randomness increases on moving from liquid to gaseous state; therefore, entropy is also positive.
For melting, the change in energy is positive, and the change in randomness is also positive.
The sign of \(\Delta H\) and \(\Delta S\) for the melting process is
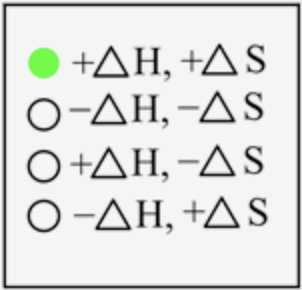
In melting, the solid-state is converted into a liquid state, which means energy is required to break the interaction between the solid-state to change it into a liquid state. Thus, energy is absorbed here, and the sign is positive. The degree of randomness increases on moving from solid to liquid state; therefore, entropy is also positive.
Related Solutions
Classify the following phase changes by the signs of the system's ΔH and ΔS.
Given the values of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn, and Tbelow, determine ΔSuniv. A. ΔH∘rxn=− 118 kJ , ΔS∘rxn=...
Calculate the change in Gibbs free energy for each of the following sets of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn,...
Calculate the change in Gibbs free energy for each of the following sets of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn,...
Calculate the change in Gibbs free energy for each of the following sets of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn,...
1. Of the physical changes listed below, which one absorbs energy? sublimation condensing freezing deposition 2....
Given the values of ΔH∘rxn , ΔS∘rxn , and T below, determine ΔSuniv . a) ΔH∘rxn=...
Given the values of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn, and T below, determine ΔSuniv. Predict whether or not each...
Given the values of ΔH∘rxn, ΔS∘rxn, and T below, determine ΔSuniv. Predict whether or not each...
In which of the following cases is the sign of the entropy change (ΔS) positive? options:...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago