Question
In: Chemistry
for the reaction pcl5(g) ------ pcl3(g)+cl2 (g) K = 0.050 at 150 C. A quantity of...
for the reaction pcl5(g) ------ pcl3(g)+cl2 (g)
K = 0.050 at 150 C. A quantity of pcl5 is placed in a 5 liter container at 150 C when equilibrium is established, the container holds 0.50 moles of cl2. How many moles of pcl5 were originally placed in the container?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Given equilibrium moles of Cl2 is =0.50 mol
Volume of the container is = 5 L
So concentration of Cl2 at equilibrium is = number of moles / volume
= 0.50 mol / 5 L
= 0.10 M
PCl5(g) 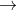 PCl3(g) + Cl2
(g)
PCl3(g) + Cl2
(g)
initial conc c 0 0
change -a +a +a
Equb conc c-a a a
Given Equb concentration of Cl2 is [Cl2] = a = 0.10 M
So the equb concentration of PCl3 is [PCl3]= a = 0.10 M
The Equb concentration of PCl5 is [PCl5]= c-a = c-0.10
Equilibrium constant , K = ([PCl3][Cl2])/[PCl5]
0.050 = ( 0.10 x 0.10 ) / (c-0.10)
c-0.10 = 0.2
c = 0.2+0.10
= 0.30 M
So initial concentration of PCl5 is = 0.30 M
Therefore initial moles of PCl5 is = Molarity x Volume in L
= 0.30 M x 5 L
= 1.50 moles
Therefore 1.50 moles of PCl5 were originally placed in the container
Related Solutions
The equilibrium constant K=0.36 for the reaction PCl5 (g) PCl3 (g) +Cl2 (g). (a) Given...
For the following reaction, Keq is 0.00183 at 390. K: PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) If 2.89...
1.For the reaction, PCl5(g) <-----> PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) Kp = 24.6 at 500 K calculate the equilibrium...
9. The equilibrium constant Kc for the reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) PCl5(g) is 49 at 230°C....
The equilibrium constant for the reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ------- PCl5(g) equals 49 at 230°C. If 0.367...
The reaction below is exothermic: PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) <---> PCl5 (g) Which change will...
The reaction: PCl5(g) <-> PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) has Kc=0.0900. A 0.1000 mol sammple of PCl5 is...
For the equilibrium PCl5(g) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g), Kc = 4.0 at 228°C. If pure PCl5 is...
Consider the following reaction: PCl5 (g)⇄ PCl3 (g) + Cl2 (g) ΔH = 87.9 kJ/reaction For...
What is the percent yield for the reaction PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) --> PCl5(g) if 119.3 g...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago