Question
In: Chemistry
Here is a scheme describing the keto-enol tautomerization reaction. Design the catalytic site of an enzyme...
Here is a scheme describing the keto-enol tautomerization reaction. Design the catalytic site of an enzyme that would accelerate the rate of this reaction. The rate enhancement should be as great as possible. Draw the amino acids that would be involved in the reaction and the electron flow during each reaction step. Remember that the enzyme has to be regenerated at the end of catalysis.
Solutions
Expert Solution
In organic chemistry, keto–enol tautomerism
refers to a chemical equilibrium between a keto
form (a ketone or analdehyde) and an enol (an
alcohol). The enol and keto forms are said to be tautomers of each
other. The interconversion of the two forms involves the movement
of an alpha hydrogen and the shifting of bonding electrons; hence,
the isomerism qualifies as tautomerism.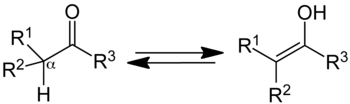
Enzymes are macromolecules that help accelerate (catalyze) chemical reactions in biological systems. This is usually done by accelerating reactions by lowering the transition state or decreasing the activation energy.
Catalysis happens at the active site of the enzyme. It contains the residues that directly participate in the making and breaking of bonds. These residues are called the catalytic groups. Although enzymes differ widely in structure, specificity, and mode of catalysis a number of generalizations concerning their active sites can be made

Related Solutions
What is an advantage of an enzyme with multiple domains each with a different catalytic site?
A zinc ion in the active site of an enzyme can speed up the reaction by:...
the kcat of an enzyme is 1875 sec ^-1, catalytic efficeny of same enzyme is 7.5*10^7,...
The active site of an enzyme is a small portion of the enzyme molecule What is...
3a. The catalytic mechanism of an enzyme involves nucleophilic attack on the substrate by an active...
Ammonia is produced by the catalytic reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen. A) Write the chemical reaction...
1. The active site of an enzyme usually consists of a pocket on the enzyme surface...
define the following terms: biotechnology, plasmid, selectalbe marker, multiple cloning site, restriction enzyme, restriction enzyme site,...
Which of the following binds to the active site of an enzyme?
Understand the following enzymatic terms: substrate, enzyme, active site, induced fit, enzyme specificity, product, enzyme /...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 1 year ago