Question
In: Biology
For the regulation of the glycolysis pathways, what the molecules involved are and how they act.
For the regulation of the glycolysis pathways, what the molecules involved are and how they act.
Solutions
Expert Solution
The four regulatory enzymes are Hexokinase (or glucokinase in the liver), phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. And the regulation is also controlled by hormones Insulin and Glycogen.The major regulation step is regulation by phosphofructokinase (PFK).
Regulation by phosphofructokinase:
- Fructose-6-phosphate is converted to Fructose-1,6-biphosphate with the help of PFK. it is allosterically inhibited by ATP, but the inhibition is reversed by AMP. So, this allows glycolysis to be responsive to the energy needs of the cells, speeding up when ATP is in short supply. And slowing down when sufficient ATP is available.
- PFK is also inhibited by citrate, first product of citric acid
cycle. The high level of citrate signals that there is a plentiful
supply of citric acid cycle intermediate and hence no additional
breakdown of glucose is required.
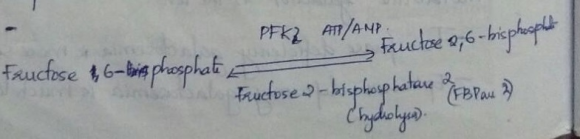
- Fructose-6-phosphate stimulates the synthesis of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate which in turn strongly activates PFK and hence activate the glycolysis pathway.
Regulation by Hormones:
- When blood glucose level falls, Glucagon is released and it triggers a C-AMP cascade that leads to the Phosphorylation of PFK2 and FBPase 2(Fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase) by Protein kinase A. This will activate FBPase and inhibit PFK2, lowering the level of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and decreasing the rate of glycolysis
- When glucose level is rise, the phosphate group is removed from PFK2 and FBPase2 by a phosphatase enzyme and thus inhibiting FBPase2 and activating PFK2, which rises the level of Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate and hence increase the rate of glycolysis
Hexokinase:
Enzyme which catalyses first regulatory step of glycolysis and is inhibited by Fructose-6-phosphate. So when PFK is inhibited Fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate builds up and hence it can inhibit hexokinase.
Pyruvate kinase:
Enzyme catalysis the third Irreversible step of glycolysis. it is activated by the high concentration of Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate and the ATP will allosterically inhibit the enzyme.
Related Solutions
What are some key signaling pathways/intracellular molecules involved in cell signaling (how does this relate to...
What pathways feed glycolysis in biological systems? This is how it is written and all the...
The following are three pathways that are involved in cellular respiration. i. Glycolysis i. Electron transport...
Glycolysis and gluconeogenesis are opposite pathways. What are three different ways that the pathways are kept...
How does regulation of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis overlap?
5.Consider the regulation of glycolysis, gluconeogenesis, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and the TCA cycle, how is the regulation...
Regulation of GNG and glycolysis Describe how high energy charge favors gluconeogenesis over glycolysis based on...
Duting fermentation pathways, what molecule regenerated that is essential for glycolysis to continueallowing the production of...
what organ systems are involved in fluid regulation?
This question is about the pentose phosphate pathway and interconnected metabolic pathways (glycolysis, gluconeogenesis.) a) What...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...

 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago