Question
In: Biology
During the elongation phase of protein synthesis, two tRNA binding sites (A and P) orchestrate the...
During the elongation phase of protein synthesis, two tRNA binding sites (A and P) orchestrate the elongation of a protein. Describe the recognition of the codon and formation of the peptide bond.
Solutions
Expert Solution
A ribosome binds to the mRNA strand that codes for the initiation codon (AUG). This ribosome (70S) consists of two subunits namely, large subunit (50S) and small subunit (30S), here S signifies the Svedberg unit. On the 70S ribosome, there are three tRNA-binding sites present, which bridge the two subunits of the 70S ribosome. They are called the A-site (aminoacyl), P-site (peptidyl), and E-site (exit). The process of initiation, elongation and termination takes place as given below -
- Charging of tRNA - At first, the amino acid gets acylated and binds to the tRNA, this process is called the charging of tRNA which prepares amino acid for the further elongation process. In this process, the uncharged tRNA, an ATP molecule and a amino acid are involved. Upon binding of the amino acid with the tRNA, an ATP molecule gets used up and forms an AMP molecule with the release of a phosphate group.
- Initiation - During initiation the 30S subunit containing the P-site and the A-site bind to the mRNA. This occurs due to the binding of the IF-3 (Initiation Factor )to the 30S subunit and IF-1 and the A-site of the 30S subunit. Further, the charged tRNA (formyl Methionine for the AUG codon) bound to the IF-2 along with a GTP molecule binds at the P-site. At the end of the initiation step, the 50S subunit binds to the mRNA and the IF-1, IF-2 and IF-3 are released. Also, a GDP molecule is released after usage of a phosphate molecule from the GTP.
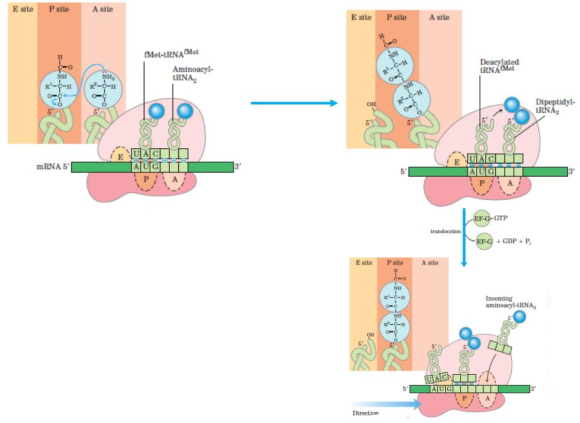
- Elongation - The second
aminoacyl-tRNA binds at the A-site of the 70S ribosome upon
recognition of the codon. Further, the peptide bonding between the
-COO- of the first amino acid and the
-NH3+ of the second amino acid takes place.
Right after the peptide bonding happens the tRNA at the P-site gets
deacylated and the tRNA at the A-site becomes dipeptidyl-tRNA. By
the binding of the Elongation Factor - G (EF-G) along with a GTP
molecule onto the ribosome the translocation takes place. After the
translocation, the EF-G along with the GDP molecule is released
upon usage of a phosphate molecule for energy. Also, the
dipeptidyl-tRNA moves to the P-site making space for another
incoming aminoacyl-tRNA. The steps further repeat causing the
elongation of the peptide molecule.
 ??
?? - Termination - When the ribosome recognises a stop codon (UAA, UGA, UAG) the release factors (RF) are recruited and the peptide chain is cleaved from the tRNA. This occurs as no aminoacyl-tRNA exists for recognising the stop codons. RF-1 recognises UAA and UAG; RF-2 recognises UAA and UGA.
Related Solutions
During the _____ phase of cell reproduction, protein synthesis occurs during the _____ phase of cell...
During the _____ phase of cell reproduction, protein synthesis
occurs during the _____ phase of cell reproduction, rapid protein
synthesis occurs as the cell grows to double in size.
a. G1 :G2
b. S : G2
c. G1 : S
d. G2 : S
Which of the following best describes the tRNA binding sites of the ribosome? Group of answer...
Which of the following best describes the tRNA binding sites of
the ribosome?
Group of answer choices
A. The P site contains the tRNA molecule covalently bound to the
growing chain of amino acids.
B. All tRNAs leave the ribosome through the A site.
C. Only one of the three sites can be occupied by a tRNA
molecule at any given time.
D. Each tRNA that associates with the ribosome must first bind
in the P site and then moved...
With explanations, outline the steps involved in the elongation of protein synthesis in a prokaryotic cell.
With explanations, outline the steps involved in the elongation
of protein synthesis in a prokaryotic cell.
What is the order of binding of a given tRNA on the ribosome during translation? Is...
What is the order of binding of a given tRNA on the ribosome
during translation?
Is this order true for all tRNAs? If not, Why?
The protein synthesis can be divided in three phases: initiation, elongation and termination. a. Describe the...
The protein synthesis can be divided in three phases:
initiation, elongation and termination.
a. Describe the initiation phase as it takes place in
bacteria.
b. The initiation phase in pro- and eukaryotes begin
differently, when it concern the recognition of mRNA, describe
these differences.
c. tRNA transport amino acids to the ribosome. Which part of the
tRNA molecule form a covalent link to the amino acid? And what is
the name for the general class of enzymes that catalyse the...
4. Illustrate the elongation phase of translation where the tRNA is in the site of the ribosome and is bound to codon number 5
4. Illustrate the elongation phase of translation where the tRNA is in the site of the ribosome and is bound to codon number 5. Label the sand 3 ends of all RNA's and label the S'UTR, 3'UTR, the Shine-Dalgamo (Kozac) sequence, and the translational start and stop codons on the template mRNA. Be sure to include the growing peptide chain and the large and small ribosomal subunits. Label each of the three ribosome sites. 5. What is the role of tRNA...
Determine whether each of the events involved in protein synthesis occurs in initiation, elongation, or termination.
Determine whether each of the events involved in protein synthesis occurs in initiation, elongation, or termination. Initiation Elongation Termination Answer Bank The small and large ribosomal subunits combine to form an initiation complex. The tRNA, mRNA, and new protein are released. The small ribosomal subunit attaches to an mRNA molecule. The ribosome moves down the mRNA strand to the next codon. An initial tRNA molecule pairs with the AUG codon of the mRNA molecule. Amino acids are transferred from tRNA molecules to the growing peptide chain. The ribosome reaches...
What catalytic role(s) does rRNA play in protein synthesis? What are the A, P, and E sites on the ribosome? What is their function?
What catalytic role(s) does rRNA play in protein synthesis? What are the A, P, and E sites on the ribosome? What is their function? How is the tRNA delivered to the ribosome?
1. In terms of codon recognition, how is termination fundamentally different than elongation in protein synthesis?...
1. In terms of codon recognition, how is termination
fundamentally different than elongation in protein synthesis?
2. How might splicing increase the versatility of eukaryotic
genes? Provide an example of a gene that undergoes splicing.
3. Describe the process in which rho dependent termination
occurs.
How do Hemogloblin's amino acids dictate the structure & function of the protein? (using binding/active sites,...
How do Hemogloblin's amino acids dictate the structure &
function of the protein? (using binding/active sites,
polar/non-polar residues & catalytic mechanisms)
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT
 ??
?? gladiator answered 2 years ago
gladiator answered 2 years ago