Question
In: Biology
Which Protista can cause diseases, and which diseases do they cause ? Which host organisms are...
Solutions
Expert Solution
Protists tend to remain in environments containing liquid water. Their natural function is to serve as primary producers in the ecosysytem especially in the oceans.
Most protist diseases in humans are caused by animal like protists known as protozoa. Protozoa make humans sick when they become parasites.
Below are the diseases caused by protists along with their host and life cycle.
1. MALARIA
Infectious disease caused by protists of plasmodium genus.Host: Man and female anopheles mosquito.
During a blood meal, a malaria infected anopheles mosquito inoculates sporozoites into human host. Sporozoites infect cells and mature into shizonts which rupture and release merozoits. The parasotes then undergo asexual multiplicationin the erythrocytes.merozoites infect RBCs. There is sexual erythrocytic stage( gametocytes) the gametocytes are ingested by anopheles mosquito during a blood meal. In mosquitos stomach microgametes》zygotes》ookinetes》 invade midgut wall of mosquito》 oocytes》 release sporozoites which enter salivary gland of mosquito.
2. African Sleeping Sickness
Caused by protozoa Trypanosoma brucei
Host: human and tsetse flies
See pic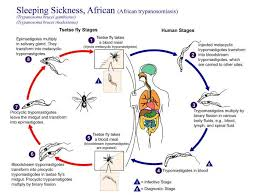
3. CHAGAS DISEASE
caused by trypanosoma cruzi in south america
Host: Man , dogs , mammals
Vector: triatomines...blood sucking insects
Infected insects take blood meals from humans and their domestic
animals and deposit parasite laden feces. Parasites are then
transmitted via contact with breaks in skin , mucosal surface or
conjunctiva. Transmission also occurs congenitally via blood
transfusion by ingestion of food and drink contaminated with feces
from infected bugs. See pic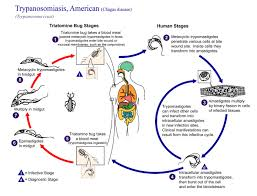
4.GIARDIASIS
Caused by flagellete protozoa Giardia lamblia
Host.: Man
Parasites enter through food or water that has been contaminated
by feces of infected people or animals. These parasites attach to
lining of small intestines of hosts where they prevent host from
fully absorbing nutrients. They also cause diarrhoea, abdominal
pain, fever.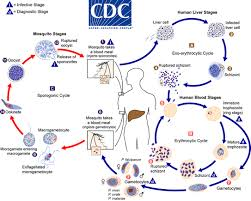
Related Solutions
Which of the following organisms can cause gastrointestinal symptoms without infecting the affected individual? A. Salmonella...
(a) List three bacterial pathogens found in soil and the diseases they cause. (b) How can...
Is processed food okay to eat even if it can cause cancer and other chronic diseases?
What are some mechanisms by which pathogenic bacteria cause diseases? Why is this knowledge important?
What are some mechanisms by which pathogenic bacteria cause diseases? Why is this knowledge important?
Organisms that may be part of the normal bacterial flora, but can--under certain conditions--cause disease are...
1). Which are the three requirements to establish a contributory cause for diseases/deaths? (Please provide 2-3...
2. What are some organisms which might cause filamentous bulking (slow settling sludge) in activate
Although bacteria and viruses are responsible for the majority of human diseases, eukaryotic organisms are also...
What are mad cow disease and scrapie? Explain the cause and of these diseases and their...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago