Question
In: Physics
show that the relaxation time for a heavily damped rlc circuit is RC
show that the relaxation time for a heavily damped rlc circuit is RC
Solutions
Expert Solution
Relaxation oscillators can be divided into two classes
- Sawtooth oscillator: In this type the energy storage capacitor is charged slowly but discharged rapidly, essentially instantly, by a short circuit through the switching device. The charging period thus takes up virtually the entire period of the waveform. The voltage across the capacitor is a sawtooth wave, while the current through the switching device is a sequence of short pulses.
- Astable multivibrator: In this type the capacitor is both charged and discharged slowly through a resistor, so both the charge and discharge periods contribute to the period and the output waveforms consist of two parts. The voltage generated by the capacitor is a triangle waveform, while the voltage from the switching device is a square wave.
-
 is set by
is set by  across a resistive voltage divider:
across a resistive voltage divider:
 is obtained using Ohm's law and the
capacitor differential equation:
is obtained using Ohm's law and the
capacitor differential equation:
Rearranging the
 differential equation into standard form
results in the following:
differential equation into standard form
results in the following:
Notice there are two solutions to the differential equation, the driven or particular solution and the homogeneous solution. Solving for the driven solution, observe that for this particular form, the solution is a constant. In other words,
 where A is a constant and
where A is a constant and  .
.

Using the Laplace transform to solve the homogeneous equation
 results in
results in
 is the sum of the particular and homogeneous
solution.
is the sum of the particular and homogeneous
solution.

Solving for B requires evaluation of the initial conditions. At time 0,
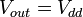 and
and 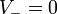 . Substituting into our previous
equation,
. Substituting into our previous
equation,
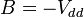
Related Solutions
Readng Question 31.027 In a damped RLC circuit, what happens to the current and the capacitor...
Design a parallel RLC circuit to have an a) overdamped, b) underdamped, and c) critically damped...
Show that energy is conserved in a simple charging RC circuit. That is show that the...
Consider a RC circuit. At time t=0, the circuit is closed. ( a) Draw how the...
Consider a RC circuit. At time t = 0, the circuit is closed. (a) Draw how...
Find and Sketch the Step response of following RLC circuit. 1) Series RLC circuit 2)Parallel RLC...
Derive the expression for RLC parallel circuit. Compare the series and parallel RLC circuit and discuss...
In an RC circuit the time constant is defined as Select one: True False
In an RC circuit as depicted in the figure above, what happens to the time required...
What is a time constant and what does it mean for a decaying RC circuit?
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?
 genius_generous answered 3 years ago
genius_generous answered 3 years ago