Question
In: Physics
A charge of q = 4.00 ✕ 10−9 C is spread evenly on a thin metal...
A charge of q = 4.00 ✕ 10−9 C is spread evenly on a thin metal disk of radius 0.160 m. HINT (a) Calculate the charge density (in C/m2) on the disk. C/m2 (b) Find the magnitude of the electric field (in N/C) just above the center of the disk, neglecting edge effects and assuming a uniform distribution of charge. N/C
Solutions
Expert Solution
Given data:
Charge on thin metal disk = 4 x 10-9 C
Radius of the disk = 0.160 m
Answer a)
Charge density of the disc will be given by:
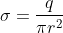
Where q is the charge on the disk
r is the radius of the disk
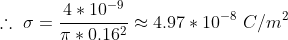
Which is the required answer
Answer b)
Electric field due to a thin circular disk is given by:
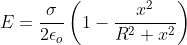
Where  is the surface
charge density
is the surface
charge density
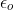 is the
absolute permittivity
is the
absolute permittivity
R is the radius of the disk
x is the distance from the center of the disk where electric field measurement is being made
For electric field just above the center of the disk 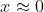 . Therefore
above formula takes the form:
. Therefore
above formula takes the form:
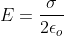
Substituting the values in above formula we get:
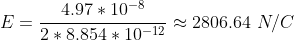
Which is the required answer
Please give a up vote if you like the answer.
If you dislike the answer then put your queries, feedback, or suggestion in comments section.
If it doesn't get resolved then down vote the answer.
Related Solutions
A capacitor stores 8.0 X 10-9 C of charge at 100V. There are two metal plates,...
9) Consider a 4.00 C charge. What is the magnitude of the electric field it creates...
A 1.98 10-9 C charge has coordinates x = 0, y = −2.00; a 3.09 10-9 C charge...
A 2.08 10-9 C charge has coordinates x = 0, y = −2.00; a 3.30 10-9 C charge...
There is a charge -10 C at (1,1,0) and another charge Q located at (2,1,1). What...
A metal sphere carrying an evenly distributed charge will have spherical equipotential surfaces surrounding it. Suppose...
Three metal spheres (A, B, C) all have the same charge +Q on them. The spheres...
How would the answers differ if the same charge was placed on a thin hollow metal...
A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform distribution of positive charge Q is bent into a...
A thin nonconducting rod with a uniform distribution of positive charge Q is bent into a...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 genius_generous answered 1 year ago
genius_generous answered 1 year ago