Question
In: Chemistry
A weak acid is titrated with a strong base and the pH is measured at each...
A weak acid is titrated with a strong base and the pH is measured at each interval. It the equivalence point is reached when 30 mL of the base has been added, describe how the pKa of the acid can be determined.
Solutions
Expert Solution
- The method is described for any general monoprotic acid HA
- dissociation of weak acid ---
- HA
 H+ + A-
H+ + A- - dissociation constant of HA , Ka = [H+][A-]/[HA]
- when concentrations of both HA and A- are equal then Ka = [H+]
- this is also revealed by the henderson equation.
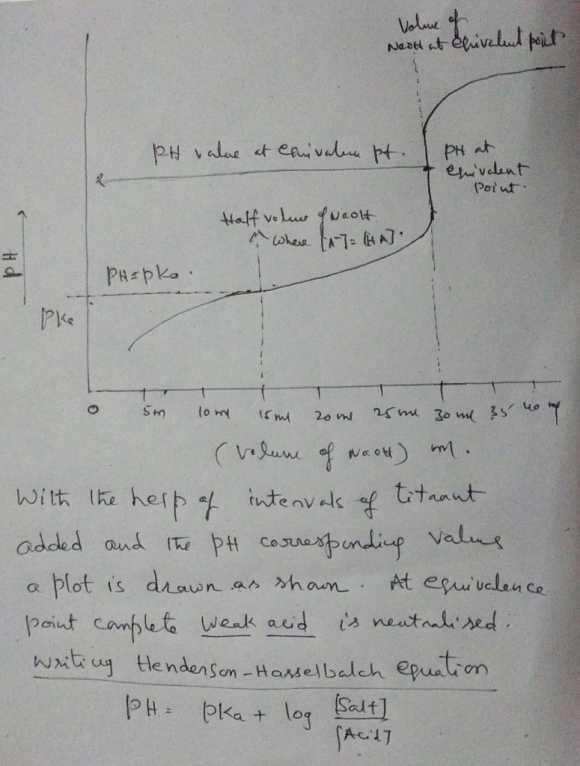
- so pH = pKa when weak acid and it's conjugate base concetrations are same.This occurs at half equivalence point. For the given problem half equivalence volume of NaOH is 15 ml. so the pH value corresponding to 15 ml is noted from the plot , Which is pKa value of the given weak acid.
- Multi protic acids dissociations also can be studied by the same method.
Related Solutions
classify each substance as a strong acid , weak acid , strong base or weak base...
classify each substance as a strong acid , weak acid , strong
base or weak base
KOH, Ca(OH)2, H 2SO4, HI, HCOOH, NaOH, HCN, C5H5N
Classify each substance as a strong acid , weak acid strong base or weak base for...
Classify each substance as a strong acid , weak acid strong base or
weak base for the following compounds
HI
C5H5N
NaOO
HCOOH
KOH
Ca(OH)2
H2SO4
HCN
What is the pH of a weak acid strong base titration after each of the following...
What is the pH of a weak acid strong base titration after each
of the following additions? Ka for HF is 3.5 x 10-4.
a. 10.0 mL of 0.250 M NaOH added to 15.0 mL of 0.400 M HF
b. 25.0 mL of 0.250 M NaOH added to 35.0 mL of 0.1785 M HF
c. 20.0 mL of 0.250 M NaOH added to 20.0 mL of 0.350 M HF
Please show your work so I can better understand this. thanks!...
Consider a monoprotic weak acid (HA) that is titrated with a strong base. What is the...
Consider a monoprotic weak acid (HA) that is titrated with a strong base. What is the relationship between the strength of the weak acid and the pH of the solution at the equivalence point?
There is no relationship between the strength of the acid and the pH at the equivalence point.
The pH at the equivalence point is always 7 in an acid base titration.
The weaker the acid, the higher the pH at the equivalence point.
The stronger the...
When a weak acid (HA) is titrated with NaOH (a strong base), (a) what species...
When a weak acid (HA) is titrated with NaOH (a strong base),
(a) what species are present in the weak acid solution before the titration is started?
(b) what species is/are decreasing during the titration?
(c) what species is/are increasing during the titration?
(d) what species is/are not involved in the reaction?
(e) what is meant by the equivalence point?
(f) what important species concentration increases after the equivalence point?
A 25.0 mL of a weak acid is titrated with a strong base (0.1 M). Calculate...
A 25.0 mL of a weak acid is titrated with a strong base (0.1 M).
Calculate the pH of the solution during the titration if the weak
acid concentration is 0.10 M and its Ka = 1.8 x 10-5 and 10.0 mL of
base has been added. (Hint: use Henderson-Hasselbach equation).
a) pH = 4.56
b) pH= 5.28
c) pH= 4.74
An acid with a Ka= 0.000343, is titrated with a strong base, what would the pH...
An acid with a Ka= 0.000343, is titrated with a
strong base, what would the pH be after half the volume of base
needed to reach the equivalenc point has been added?
Classify each titration curve as representing a strong acid titrated with a strong base
Classify each titration curve as representing a strong acid titrated with a strong base, a strong base titrated with a strong acid, a weak acid titrated with a strong base, a weak base titrated with a strong acid, or a polyprotic acid titrated with a strong base. Calculate the pH of the resulting solution if 20.0 mL of 0.200 M HCl(aq) is added to 30.0 mL of 0.200 M NaOH(aq). pH = Calculate the pH of the resulting solution if 20.0 mL...
Weak Acid - Strong Base Titration Calculate the pH at the given amounts below in the...
Weak Acid - Strong Base Titration
Calculate the pH at the given amounts below in the titration.
You are titrating 35.0 mL of .15 M HNO2 with .1 M NaOH
until you reach 100 mL of NaOH added.
For this problem the Ka value is 4.6 x 10-4
a) 0.00 mL NaOH added
b) 30.0 mL NaOH added
c) 60.0 mL NaOH added
d) 100.0 mL NaOH added
What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point of a weak acid-strong base titration if...
What is the approximate pH at the equivalence point of a weak
acid-strong base titration if 25 mL 21) of aqueous formic acid
requires 29.80 mL of 0.0567 M NaOH? Ka =1.8 × 10-4 for
formic acid.
A) 2.46 B) 8.12 C) 11.54 D) 5.88
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT
 H+ + A-
H+ + A-
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago