Question
In: Biology
Mitosis unfolds through a sequence of stages marked by specific events in the cell.
Mitosis unfolds through a sequence of stages marked by specific events in the cell. The structural changes in the cell are about by a series of tightly coordinated underlying mechanisms.
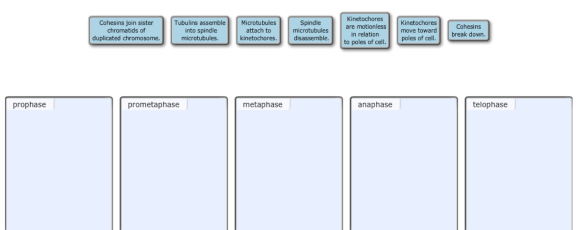
Sort each process into the appropriate bin to indicate the stage of mitosis in which it occurs. If a process occurs in more than one stage, sort it to the stage when it first occurs.
- Cohesins join sister chromatids of duplicated chromosome.
- Tubulins assemble into spindle microtubules.
- Microtubules attach to kinetochores.
- Spindle microtubules disassemble.
- Kinetochores are motionless in relation to poles of cell.
- Kinetochores move toward poles of cell.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Prophase:
-Tubulins assemble into spindle microtubules
-Cohesins join sister chromatids of duplicated chromosomes
Prometaphase:
-Microtubules attach to kinetochores
Metaphase:
-Kinetochores are motionless in relation to cell poles
Anaphase:
-Kinetochores move toward poles of the cells
-Cohesins break down
Telophase:
-Spindle microtubules disassemble
Related Solutions
4. Discuss mitosis: Name all the stages of mitosis. Describe the main events that happen during...
Germ cell proliferation through mitosis: in males, this occurs __
Summarize the events in each phase of mitosis. Compare cytokinesis in a plant cell and an...
What are the stages of mitosis
a. Compare the process of mitosis with the process of meiosis. Describe major cell cycle events....
let's imagine a diploid plant cell. a) draw the five stages of mitosis and meiosis assuming...
The stages of mitosis were originally defined by cellular features observable through a light microscope.
1- Write a comparison of the stages of meiosis to the stages of mitosis. Which stages...
Cell cycle: Explain the function of mitosis. What major events occur during each of the four...
5. Draw a cell with three chromosomes as it moves through mitosis and cytokinesis. 6. Draw...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago