Question
In: Biology
The cell cycle represents the coordinated sequence of events in the life of a cell from its formation to its division into two daughter cells.
The cell cycle represents the coordinated sequence of events in the life of a cell from its formation to its division into two daughter cells. Most of the key events of the cell cycle are restricted to a specific time within the cycle.
In this exercise, you will identify when various events occur during the cell cycle. Recall that interphase consists of the G1, S, and G2 subphases, and that the M phase consists of mitosis and cytokinesis.
Drag each label to the appropriate target.
Solutions
Expert Solution
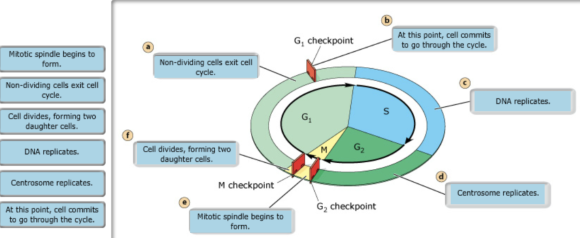
a - non-dividing cells exit cell cycle
b - at this point, cell commits to go through cycle
c - DNA replicates
d - Centrosome replicates
e - Mitotic spindle begins to form
f - cell divides, forming two daughter cells
Related Solutions
As the chromosomes of a parent cell are duplicated and distributed to the two daughter cells during cell division
Changes in DNA structure during the cell cycle
As the chromosomes of a parent cell are duplicated and distributed to the two daughter cells during cell division, the structure of the chromosomes changes.
Answer the three questions for each phase of the cell cycle by dragging the yes and no labels to the appropriate locations in the table. Note: Assume that by the end of the M phase, the parent cell has not yet divided to form two daughter cells.
A germ cell divides to give rise to two daughter cells. Each of the two daughter...
A germ cell divides to give rise to two daughter cells. Each of
the two daughter cells then divides to give rise to two daughter
cells. Is the genetic information found in two daughter cells that
arose from a cell that went through the second division, identical?
Explain your answer.
Cytokinesis in animal cells is accomplished by constriction of the cell along the plane of cell division (formation of a cleavage furrow).
Cytokinesis in animal cells is accomplished by constriction of the cell along the plane of cell division (formation of a cleavage furrow). In plant cells, which have cell walls, a completely different mechanism of cytokinesis has evolved.
Which of the following statements are true of cytokinesis in plant cells? Select the two that apply.
Which of the following statements are true of cytokinesis in plant cells? Select the two that apply.
After chromosome separation is complete, a network of microfilaments...
Genomics: Analyze cellular and chromosomal events that occur during the eukaryotic cell cycle and gamete formation....
Genomics: Analyze cellular and chromosomal events that occur
during the eukaryotic cell cycle and gamete formation. Analyze the
basic structures and mechanisms of DNA and RNA including
replication, transcription, and translation.
The division of a bacterial cell into two daughter cells is accomplished by a protein called FtsZ. FtsZ is very similar to the tubulin subunits that form microtubules in eukaryotes.
The division of a bacterial cell into two daughter cells is accomplished by a protein called FtsZ. FtsZ is very similar to the tubulin subunits that form microtubules in eukaryotes. After the replicated bacterial chromosomes have moved to opposite ends of the cell, a ring of FtsZ proteins forms inside the plasma membrane in the region where the cell will divide. As the FtsZ ring constricts, the plasma membrane and bacterial cell wall fold in and eventually separate into two...
Mitosis and meiosis are both important processes of cell division in the life cycle of a sexual organism.
Mitosis and meiosis are both important processes of cell
division in the life cycle of a sexual organism.1. Discuss why both processes are necessary.2. List the differences between Prophase of mitosis and Prophase
I of meiosis. How do these differences contribute/ lead to genetic
variation?
Describe the process of mitosis, and its role in the cell life cycle.
Describe the process of mitosis, and its role in the cell life
cycle.
Sakar Cell bio Cells control their own cycle of growth & division very tightly. Please explain...
Sakar Cell bio Cells control their own cycle of growth &
division very tightly. Please explain why cell cycle regulators are
often involved in the development of neoplasms (cancers). Include
examples of processes that must be affected in order to have
uncontrolled cell growth. Please do not hand write responses.
Please do not copy and paste from google. Please do not upload a
handwritten cursive response. Type the text only!
1.List the basic sequence of cellular events resulting in protein production and export from the cell,...
1.List the basic sequence of cellular events resulting in protein
production and export from the
cell, beginning at DNA in the nucleus and ending with
vesicular
exocytosis. Include the following terms and describe what
happens at each
organelle or cellular structure: ribosomes, mRNA, DNA, rough
the
endoplasmic reticulum, exocytosis, nuclear pore complex, Golgi
complex (cis and trans
sides), nucleus, microtubules, vesicle.
2. Be able to label and describe the function of the cellular
features of the eukaryotic
mitochondria.
3. Be...
The following sample data represents the life cycle in months of two car batteries: A: 62,...
The following sample data represents the life cycle in months of
two car batteries:
A: 62, 59, 59, 51, 55, 53, 58, 49, 61, 55
B: 45, 50, 47, 46, 48, 46, 45, 46, 51, 49, 47, 49, 48, 45,
57
Is the variation in life cycle the same between batteries at
lambda=.05? Are the means the same as well at lambda=.05? Which
battery would you choose and why?
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago