Question
In: Biology
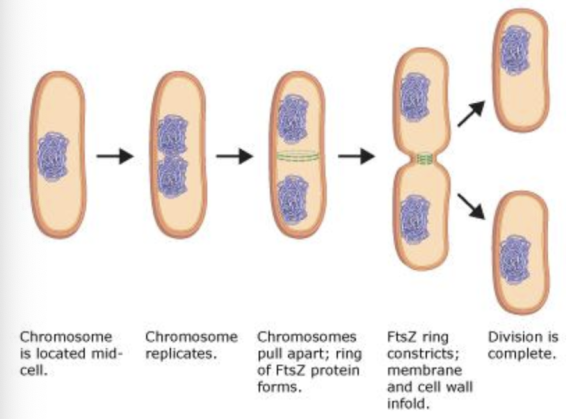
The division of a bacterial cell into two daughter cells is accomplished by a protein called FtsZ. FtsZ is very similar to the tubulin subunits that form microtubules in eukaryotes.
The division of a bacterial cell into two daughter cells is accomplished by a protein called FtsZ. FtsZ is very similar to the tubulin subunits that form microtubules in eukaryotes. After the replicated bacterial chromosomes have moved to opposite ends of the cell, a ring of FtsZ proteins forms inside the plasma membrane in the region where the cell will divide. As the FtsZ ring constricts, the plasma membrane and bacterial cell wall fold in and eventually separate into two cells.
Statement Bacteria Animals Plants
True Cells divide by constriction of a ring of protein __________ _________ ________
False The presence of a cell wall prevents the cell from ... __________ __________ _________
dividing by constriction
Tubulin subunits or tubulin-like molecules function... __________ __________ __________
in the division of the cell
Solutions
Expert Solution
1. Cells divide by constriction of a protein:
Bacteria: True
Animals: True
Plants: False
2. The presence of a cell wall prevents the cell from dividing by constriction
Bacteria: False (bacteria have a cell wall and still divide by constriction)
Animals: False
Plants: True
3.
Tubulin subunits or tubulin-like molecules function in the division of the cell
Bacteria: True
Animals: False
Plants: True
Related Solutions
As the chromosomes of a parent cell are duplicated and distributed to the two daughter cells during cell division
Cytokinesis in animal cells is accomplished by constriction of the cell along the plane of cell division (formation of a cleavage furrow).
A germ cell divides to give rise to two daughter cells. Each of the two daughter...
The cell cycle represents the coordinated sequence of events in the life of a cell from its formation to its division into two daughter cells.
Sakar Cell bio Cells control their own cycle of growth & division very tightly. Please explain...
28) DNA fingerprinting utilizes _________ 29) Bacteria perform a form of cell division called __________ 30)Which...
Which two molecules, an regulatory protein and enzyme regulate cell division in mitosis? How does the...
You have two mutant cells, in which the first mutant cell cannot form dimers, and the...
What are the eight proteins needed for bacterial cells to make two daughter strands of DNA from one parental strand, and what is the function of each of these proteins?
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago