Question
In: Biology
A hypothetical population of 300 wolves has two alleles, FB and FW, fora locus that codes for fur color.
| Genotype | Phenotype (fur color) |
Number of individuals in population |
| FBFB | black
|
40 |
| FBFW | gray
|
40 |
| FWFW | white
|
220 |
![]()
- The population is evolving because the actual number of individualswith each genotype differs from the expected number of individualswith each genotype.
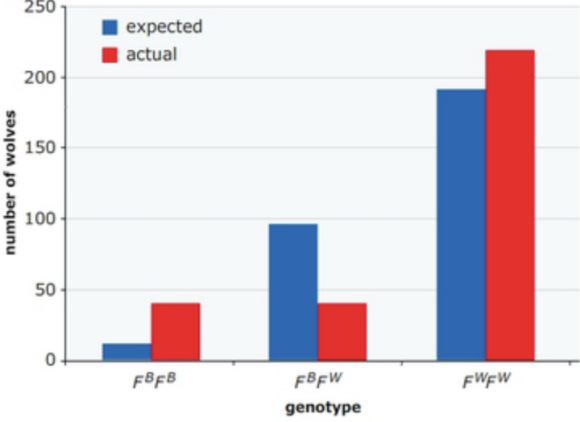
- Based on theequation for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the expected number ofwolves with the \(F^{B} F^{W}\) genotype is 96.
- The population is not at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
- Based on theequation for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the expected number ofwolves with the \(F^{B} F^{W}\) genotype is 40.
- Based on theequation for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the expected number ofwolves with the \(F^{B} F^{B}\) genotype is 12
- The population is not evolving because it is at Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium.
- Based on theequation for Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, the expected number ofwolves with the \(F^{B} F^{B}\) genotype is 40 .
Solutions
Expert Solution
The \(F^{B}\) allele accounts for 120 of the alleles \(\left(40 \times 2=80\right.\) in \(F^{8} F^{B}\) wolves, plus \(40 \times 1=40\) in \(F^{B} F^{W}\) wolves).Therefore, the \(F^{B}\) allele makes up \(20 \%(120 / 600)\) of the alleles in the population, so the value of \(p\) is \(0.2 .\) The allele frequencies of the population must add up to one (n other worts, \(p+q=1\) ) therefore, since the value of \(p\) is 0.2 , the value of \(q\) is \(0.8 .\)
According to the Hardy-Weinberg equation, the expected frequencies of the genotypes should add up to \(1 .\)
$$ \begin{array}{c} p^{2}+2 p q+q^{2}=1 \\ 0.2^{2}+2(0.2)(0.8)+0.8^{2}=1 \\ 0.04+0.32+0.64=1 \end{array} $$
To predict the number of individuals with each genotype, mutipy the expected frequency of each genotype by the number of individuals in the population.
$$ \begin{array}{r} 0.04 \times 300=12 F^{B} F^{B} \text { individuals } \\ 0.32 \times 300=96 F^{B} F^{W} \text { individuals } \\ 0.64 \times 300=192 F^{W} F^{W} \text { individuals } \end{array} $$
The wolf population may be evoling because the expected number of individuals with each genotype, caloulated with the Hardy-Weinberg equation, does not equal the actual number of individuals with each genotype.
Related Solutions
A hypothetical population of 16000 squirrels has two alleles, FB and FW, for a gene that...
A hypothetical population of 200 cats has two alleles, TL and TS, for a locus that codes for tail length.
In a population of mice, coat color is controlled by a gene locus with two alleles,...
Locus A has two alleles (A and a) while locus B has two alleles (B and...
A hypothetical population of 500 cats has two alleles, T and t, for a gene that codes for tail length.
You are studying a population of 100 lizards that has two alleles at a locus for...
The coat color in mink is controlled by two codominant alleles at a single locus. Red...
1.Imagine a locus with two alleles, A and a, in a wild population of touch-me-not (Impatiens...
Assuming that a diploid genomic locus has 3-alleles, A, C and G, in a population of...
2) If a gene locus for has two alleles and p is .33. What is q?...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
- For this assignment you will write a program with multiple functions that will generate and save...
- How many grays is this?Part A A dose of 4.7 Sv of γ rays in a...
- how to operate a business?



 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago