Question
In: Chemistry
A closed system contains 1kg of air initially at 100kPa, 30 deg Celsius and 0.5m3.The air...
Solutions
Expert Solution
The essential difference between the expansion in an closed system and the reversible isothermal expansion of an 1kg gas can also be captured clearly in terms of entropy changes.
For a state change from initial volume V1 and temperature T1, to final volume V2 and (the same) temperature T1, the entropy change is given by

Using equation of state and in isothermal process  for an isothermal process,
for an isothermal process,
There entropy is

Now applying the values
V1 = 0.5 m3 =500 L
V2 = 500x2= 1000 L
N= PV/RT
105 Pa x 0.5 m3
= ----------------------------
8.31 J/mol-1 x 303K
1 bar x 500 L
= ---------------------------
0.0831 L-bar/mol-K x 303K
= 19.8 moles
Now

=(19.8 mol)x(8.31 J/mol-1K) ln (1000/500)
=114 J/K
Entropy is 114 J/K
b) if the temperature is held constant, the internal energy of
the system also is constant, and so  . Since the First Law of Thermodynamics
states that
. Since the First Law of Thermodynamics
states that 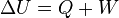 , it follows that
, it follows that  for the isothermal compression or expansion
of ideal gases.
for the isothermal compression or expansion
of ideal gases.
Therefore,the heat transferred to the gas is
 .
.
Heat transfered is also 114 J/K
Related Solutions
A mass of m=1kg of steam is contained in a closed rigid container. Initially the pressure...
A closed, rigid tank fitted with a paddle wheel contains 2.2 kg of air, initially at...
Air at 25 deg Celsius ( m = 0.018 cP) enters a section of 2-inch schedule...
3 kg of air in a closed movable container undergoes a few processes. Initially, the air...
1) Suppose you have a closed rigid container of air at 20 Celsius on the surface...
A flat plates surface tempertures are initially at 120 deg C and 60 deg C with...
An air parcel has a temperature of 30 degrees Celsius and a relative humidity of 50%...
A closed, rigid tank contains water initially at 250 °F with a quality of 0.4. The...
A closed system consists of 0.5kg of superheated steam initially at 1MPa, 300 0C. The system...
A closed system contains an equimolar mixture of n-pentane and isopentane. a) Suppose the system is...
- 1. Describe the function of the FeS04 in the KIA medium. 2. How many days does...
- Cloud computing has a litany of necessary requirements. The business case needs to showcase the necessity...
- # please answer question asap please Write a program in C to insert new value in...
- MINIMUM MAIN.CPP CODE /******************************** * Week 4 lesson: * * finding the smallest number * *********************************/...
- Do you think President Eisenhower had a successful presidency?
- Barbour Corporation, located in Buffalo, New York, is a retailer of high-tech products and is known...
- C PROGRAMMIMG I want to check if my 2 input is a number or not all...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago