Question
In: Finance
Calculate the value of a stock with the following expectations for dividend payments: $1.75 in Year...
Calculate the value of a stock with the following expectations for dividend payments: $1.75 in Year 1, $2.00 in Year 2, and then annual dividend growth of 1.5% per year indefinitely. Assume a discount rate of 9%. Solve the problem two different ways: first by using the algebraic formula for the Gordon Growth Model combined with PV of uneven dividend payments, then by using Excel to calculate and sum the dividends and their respective present values for the next 150 years. hint: Use the Uneven, then Const. Growth Dividend
Solutions
Expert Solution
Dividend in Year 2 = $2
Now using Gordon growth formulae, stock price at the end of year 2 = Dividend at year 2 * growth rate / (discount rate - growth rate)
Stock price at the end of year 2 = 2*1.015 / (9%-1.5%) = $27.07
Now present value of stock is PV of all future payments
PV = 1.75 / 1.09 + (2+27.07)/1.09^2 = $26.07
Now using Excel,
As we can see using excel, the stock price is $26.0697
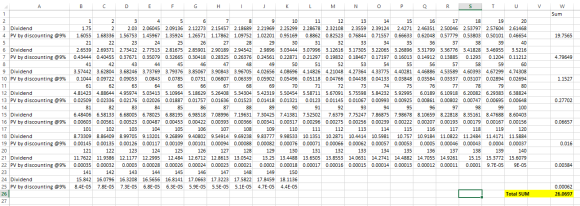
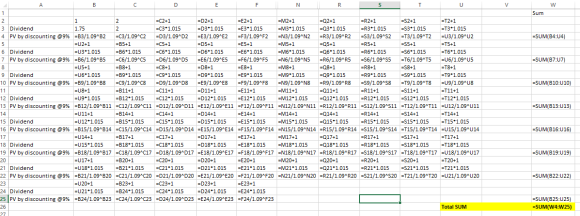
Pasting with formulas (Note that Some columns are hidden with similar formulas so that you are able to see the last column)
Related Solutions
Calculate the value of a stock with the following expectations for dividend payments: $1.75 in Year...
Calculate the present value of a stock if this stock is expectedto pay $1.75 dividend...
Calculate the present value of a stock if this stock is expected to pay $10.60 dividend...
1. You've recorded the following prices and dividend payments for a stock: Month Stock price Dividend...
Crisp Cookware's common stock is expected to pay a dividend of $1.75 a share at the...
Carnes Cosmetics Co.'s stock price is $46, and it recently paid a $1.75 dividend. This dividend...
Carnes Cosmetics Co.'s stock price is $57, and it recently paid a $1.75 dividend. This dividend...
You've recorded the following prices and dividend payments for a stock: Quarter Stock price (end of...
What is the value of a stock which pays a $4 dividend/year (first dividend in one...
Suppose you calculate the value of a stock to be $100 per share. No dividend growth...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
 jeff jeffy answered 1 year ago
jeff jeffy answered 1 year ago