Question
In: Physics
What is the potential difference ΔVAB?
What is the potential difference ΔVAB?
Solutions
Expert Solution
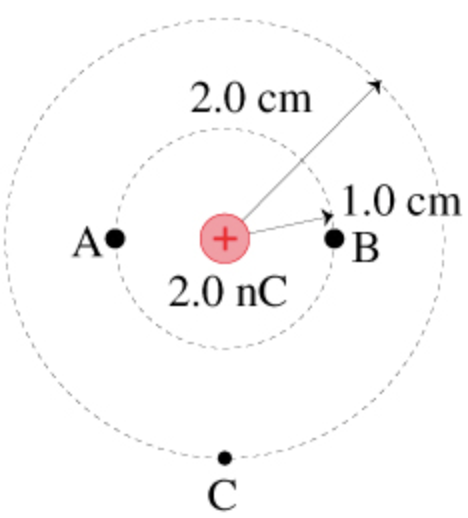
The points \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) are at the same distance from charge \(\mathrm{q} .\)
Hence, potential at \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) are same.
The potential due to a point charge at a distance \(r\) is given by \(V=\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}} \frac{q}{r}\) Here, \(\frac{1}{4 \pi \varepsilon_{0}}=9 \times 10^{9} \mathrm{Nm}^{2} / \mathrm{C}^{2}\)
$$ \begin{aligned} q=& 2.0 \mathrm{nC}=2.0 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{C} \\ r=& 1.0 \mathrm{~cm}=1.0 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m} \\ \text { Hence, } V_{A}=& V_{B}=\left(9 \times 10^{9} \mathrm{Nm}^{2} / \mathrm{C}^{2}\right) \frac{\left(2.0 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{C}\right)}{\left(1.0 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}\right)} \\ &=1800 \mathrm{~V} \end{aligned} $$
Adjusted to two significant figures, \(V_{A}=V_{B}=1800 \mathrm{~V}\) For \(\mathrm{C} r=2.0 \mathrm{~cm}=2.0 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}\) Hence,
$$ \begin{aligned} V_{C} &=\left(9 \times 10^{9} \mathrm{Nm}^{2} / \mathrm{C}^{2}\right) \frac{\left(2.0 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{C}\right)}{\left(2.0 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}\right)} \\ &=900 \mathrm{~V} \end{aligned} $$
Adjusted to two significant figures, \(V_{C}=900 \mathrm{~V}\)
a) As \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) are at same potential, Hence, potential difference between \(\mathrm{A}\) and \(\mathrm{B}\) is \(\Delta V_{A B}=0\)
b) Potential Difference between the points \(\mathrm{B}\) and \(\mathrm{C}\) is
$$ \begin{aligned} \Delta V_{B C} &=V_{B}-V_{C} \\ &=1800-900 \\ &=900 \mathrm{~V} \end{aligned} $$
Adjusted to two significant figures, \(\Delta V_{B C}=900 \mathrm{~V}\)
Related Solutions
What is Electromotive force and potential difference.
What is the difference between an emf (Electromotive force) and a potential difference?
What is the difference between resting potential and repolarization? - Resting potential is maintained by leaky...
What is the potential difference across the 10 ω resistor?
What is difference between actual GDP & potential GDP? If actual GDP > Potential GDP are...
What is the difference between a graded potential and action potential? How does this impact impulse...
What is the difference between Overreaching and Overtraining? What are the potential causes, and what models...
What is the potential difference ΔV between the particles final and initial positions?
An electron was accelerated through a potential difference of 1.00 ± 0.01 kV. What is the...
What is the difference between forms of energy, for example, potential and kinetic, and sources of...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
- How many grams are in a 0.10 mol sample of ethyl alcohol?
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago