Question
In: Chemistry
2 kilograms of ideal gas air undergoes an isothermal expansion from 3MPa and 300K to 1Mpa....
2 kilograms of ideal gas air undergoes an isothermal expansion from 3MPa and 300K to 1Mpa. Determine the work done, the change in specific internal energy, and the heat transferred.
Solutions
Expert Solution

N moles of air in 2kg mass
21% O2 and 78% N2. (The 1% noble gases will be of no consequence
here).
O2 mol.mass = 32g/mol x 0.21 = 6.72 moles.
N2 mol.mass = 28g/mol. x 0.78 = 21.84 moles.
Total = 28.56 g/mol.
no of moles in 2000grams of air = 2000/28.56 = 70.02 moles
N= m / mass per mole
- NRTln(p1/p2) = 70.2(8.314) * 300 ln(3) = -192.36 Kj
P1 = NRT/ V1
V1 = NRT/ P1
V2 = NRT/P2
By convention, work is defined as the work the system does on its environment. If, for example, the system expands by a piston moving in the direction of force applied by the internal pressure of a gas, then the work is counted as negative, and as this work is done by using internal energy of the system, the result is that the internal energy decreases. Conversely, if the environment does work on the system so that its internal energy increases, the work is counted as positive.
In an Isothermal process the temperature is constant. Hence, the internal energy is constant, and the net change in internal energy is ZERO
t 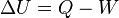
heat transfered Q = W
Related Solutions
An ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion from one state to another. In this process determine the...
Calculate deltaS total for the isothermal irreversible free expansion of 1.00 mol of ideal gas from...
(a)Air, which can be assumed to behave as an ideal gas, undergoes a process from 150kPa...
For the following, assume air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats at 300K. Find...
Nitrogen undergoes an isothermal process from 100 kPa to 500 kPa, T = 300K. How much...
a) Calculate the change in entropy on heating an ideal gas from 300K to 500K at...
A 2.00 mole sample of Ar undergoes an isothermal reversible expansion from an initial volume of...
Explain and discuss another experiment than (Verification of the Ideal Gas Equation using an isothermal expansion...
A gas undergoes an isothermal expansion from V1=1.4L followed by isobaric compression, p=cst. if p1=4.4atm, p2=2.2atm→?Nm2,...
Four kilograms of steam in a piston/cylinder device at 400 kPa and 175 °C undergoes isothermal...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago