Question
In: Chemistry
2NO(g) + Br2(g) 2NOBr(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.70×10-2 moles of NO(g), 4.02×10-2...
2NO(g) + Br2(g) 2NOBr(g) A reaction mixture was found to contain 4.70×10-2 moles of NO(g), 4.02×10-2 moles of Br2(g) and 9.28×10-2 moles of NOBr(g), in a 1.00 Liter container. Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following: Indicate True (T) or False (F) for each of the following:
1. In order to reach equilibrium NOBr(g) must be produced.
2. In order to reach equilibrium Kc must decrease.
3. In order to reach equilibrium NO must be produced.
4. Qc is less than Kc.
5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.
Solutions
Expert Solution
The given equilibrium is
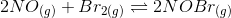
Volume of the reaction container = 1.00 L
The amount of reactants and products in the reaction mixture is
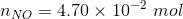
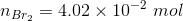
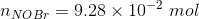
Since the volume in 1.00 L, the concentration and number of moles will be numerically equal.
Hence,
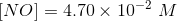
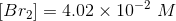
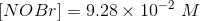
For a generic reaction, 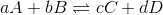 , the reaction quotient is expressed as
, the reaction quotient is expressed as
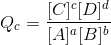
Now, the reaction quotient of our reaction can be expressed and calculated as follows:
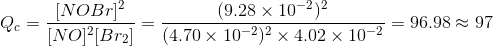
It is also given that the equilibrium constant Kc is 154.
Now, with this information, we can determine whether the given statements are true or false.
1. In order to reach equilibrium NOBr(g) must be produced.
Verdict: True (T)
Reason: Note that the value of reaction
quotient is smaller than the equilibrium constant. 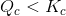 . Hence, there are more reactants than products compared to the
equilibrium composition. Hence, to reach equilibrium, some
reactants need to convert to product. Since NOBr(g) is a product,
it must be produced to reach equilibrium.
. Hence, there are more reactants than products compared to the
equilibrium composition. Hence, to reach equilibrium, some
reactants need to convert to product. Since NOBr(g) is a product,
it must be produced to reach equilibrium.
2. In order to reach equilibrium KC must decrease.
Verdict: False (F)
Reason: Kc is a constant at a particular temperature for a reaction at equilibrium. Hence, its value will not change.
3. In order to reach equilibrium NO must be produced.
Verdict: False (F)
Reason: NO is a reactant in the equilibrium equation. Hence, formation of NO will lead to increase in the denominator in the reaction quotient expression. Hence, Qc value will decrease if NO is produced more. Hence, the reaction will go away from equilibrium to the left as Qc is already smaller than Kc.
4. Qc is less that Kc.
Verdict: True (T)
Reason: We have already calculated the value of Qc above which happens to be smaller than Kc.
97 is less than 154.
5. The reaction is at equilibrium. No further reaction will occur.
Verdict: False (F)
Reason: For the reaction to be at equilibrium, the value of Qc must be equal to Kc. But since it is not the case, the statement must be false.
Related Solutions
Consider the reaction: 2NO(g)+Br2(g)⇌2NOBr(g) Kp=28.4 at 298 K In a reaction mixture at equilibrium, the partial...
The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 6.50×10-3 at 298K. 2NOBr(g)<====> 2NO(g) + Br2(g)...
Consider the following equilibrium: 2NOBr(g) <------> 2NO(g) + Br2(g). An equilibrium mixture is 0.146 M NOBr,...
Consider the following equilibrium: 2NOBr(g) 2NO(g) + Br2(g) An equilibrium mixture is 0.150 M NOBr, 0.395...
The equilibrium constant, Kp, for the followingreaction is 0.160 at 298K.2NOBr(g) 2NO(g)+ Br2(g)...
Consider the equilibrium N2(g)+O2(g)+Br2(g)⇌2NOBr(g) Part A Calculate the equilibrium constant Kp for this reaction, given the...
2NO (g) + O2 (g) -> 2 NO2 (g) if 12 moles of nitrogen monoxide are...
1. Consider the following reaction: Br2(g)+Cl2(g)⇌2BrCl(g) Kp=1.11×10−4 at 150 K. A reaction mixture initially contains a...
For the reaction Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 BrCl Kp = 1.11 x 10-4...
A mixture of 1.374 g of H2 and 70.31 g of Br2 is heated in a...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 months ago