Question
In: Economics
Assume a nation has an output level of 150 units per year, and that consumption is...
Assume a nation has an output level of 150 units per year, and that consumption is also 150. Suppose there is a sudden temporary drop in GDP by 16%. What does the long-run consumption path look like if this country has access to global financial markets with an interest rate of 5%?
Solutions
Expert Solution
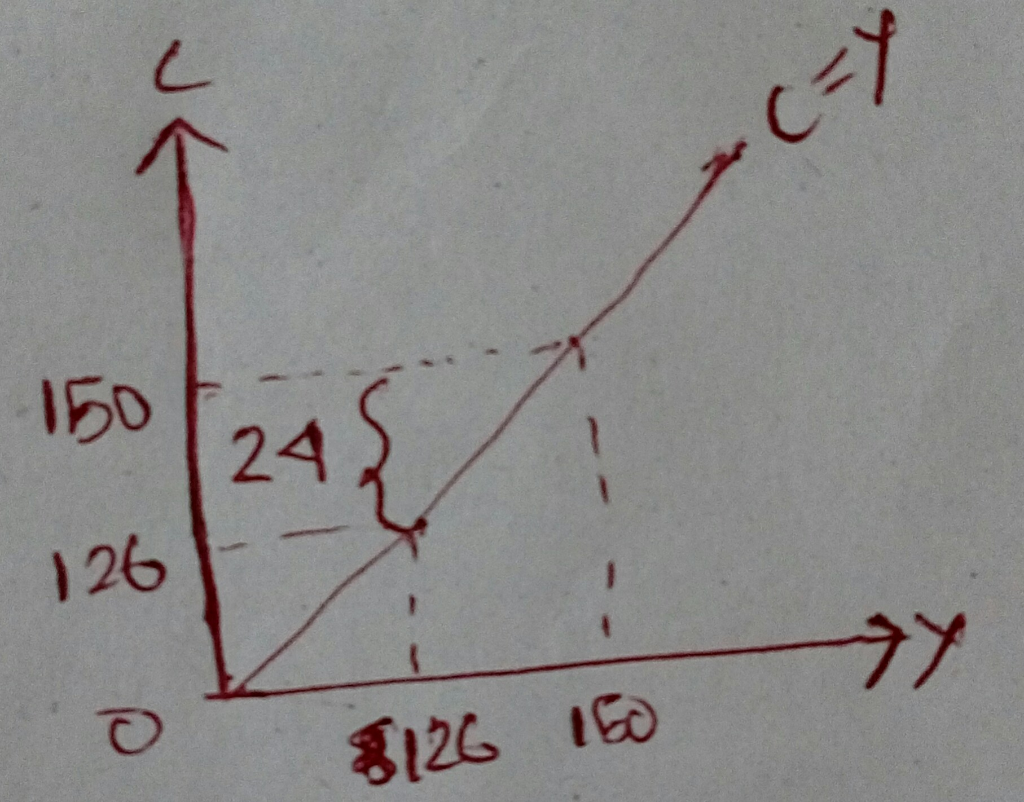
Given that at Output = 150, the economy consumes 150 units, i.e., both the Marginal Propensity to Consume (MPC) and the Average Propensity to Consume (MPC) is 1. Thus, initially, the consumption function is of the form:
C = Y
Thus, people consume (C) whatever they produce (Y).
Now, with a GDP shock of 16%, the output level drops to 126. [150 – 16% of 150]
Thus, at Output Level = 126, the economy is facing a consumption deficit of (150 – 126) units = 24 units.
The households would now borrow the unavailable amount from the international financial market at the rate of interest, r = 5% or 0.05.
Hence, New Consumption = 126 + 24(1 + 0.05)
Thus, the long-run consumption function takes the form:
C(Y,r) = Cbar + (Cbar - Y)(1 + r)
Related Solutions
Assume the following information for an economy: Natural level of output = $190b Autonomous consumption =...
PT corp makes 300 units of A per year. At this level, the cost per unit...
1. Assume that in one year an economy produces 5,000 units of output and they sell...
1. Assume that in year 1 an economy produces 1000 units of output and they sell...
The per capita energy consumption level (in kilowatt-hours) in a certain country for a recent year...
The per capita energy consumption level (in kilowatt-hours) in a certain country for a recent year...
A firm is currently producing 80 units of output. At this level of output produced: its...
A monopolistically competitive firm is currently producing 20 units of output. At this level of output...
Assume that in the short run a firm is producing 100 units of output, has average...
Assume that price equals a rising marginal cost at 50 units of output. At this output,...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 Rahul Sunny answered 4 months ago
Rahul Sunny answered 4 months ago