Question
In: Math
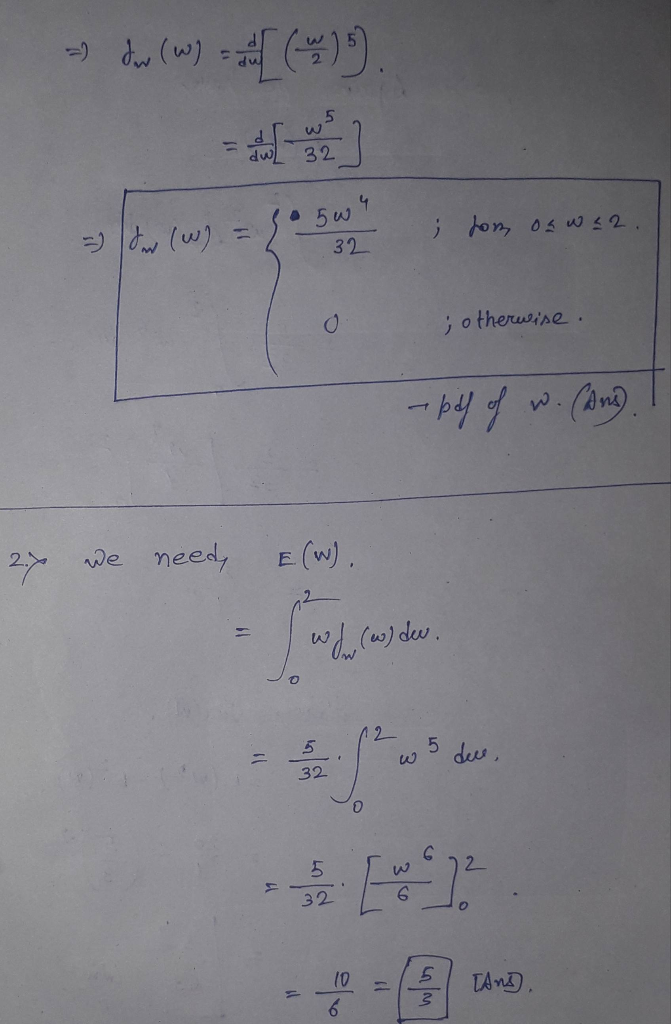
Assume that a sample {Xj : 1 ≤ j ≤ 5} of size 5 is drawn...
Assume that a sample {Xj : 1 ≤ j ≤ 5} of size 5 is drawn from Unif(0, 2). Consider the maximal value, W = X(5).
1. Derive density function of X(5)
2. Find expected value of X(5)
3. Determine variance of X(5)
Solutions
Related Solutions
Assume that a sample X = {Xj : 1 ≤ j ≤ 10} of size n...
Assume that a sample X = {Xj : 1 ≤ j ≤ 10} of size n = 10 was
drawn from the uniform distribution on the interval (0 < x <
4). Let X[k] denote the k th order statistic based on this sample.
1. Evaluate expected value of X[5] 2. Derive conditional
expectation of X[5], given that X[10] = 3.
. Let xj , j = 1, . . . n be n distinct values. Let...
. Let xj , j = 1, . . . n be n distinct values. Let yj be any n
values. Let p(x) = c1 + c2x + c3x 2 + · · · + cn x ^n−1 be the
unique polynomial that interpolates the data (xj , yj ), j = 1, . .
. , n (Vandermonde approach).
(a) Remember that (xj , yj ), j = 1, . . . , n are given. Derive
the n...
A sample size 5 will be drawn from a normal population with mean 60 and standard...
A sample size 5 will be drawn from a normal population with mean
60 and standard deviation 12.
a. Is it appropriate to use the normal distribution to find
probability for ?̅? Explain why?
b. If appropriate find the probability that ?̅will be between 50
and 70.
c. If appropriate find the 80th percentile of ?̅?
Given the likelihood of θ with respect to sample D p(D|θ) = Q j p(xj |θ),...
Given the likelihood of θ with respect to sample D p(D|θ) = Q j
p(xj |θ), where D = {x1, · · · , xn} is identically and
independently distributed (i.i.d) sample points. Briefly describe
how you would find the maximum likelihood estimation and the
Bayesian estimation of θ.
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean is found to be...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean is
found to be 17.6, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found
to be 4.7.
A). Construct a 95% confidence interval about if the sample
size, n, is 51.
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean is found to be...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean is
found to be 17.6, and the sample standard deviation, s, is found
to be 4.7.
Construct a 99% confidence interval about if the sample size,
n, is 34.
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x, is found to...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x,
is found to be 18.5, and the sample standard deviation, s, is
found to be 4.6.
(a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ if the sample
size, n, is 34.
Lower bound: ___
Upper bound: ___
(Use ascending order. Round to two decimal places as
needed.)
(b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about μ if the sample
size, n, is 61.
Lower bound: ___
Upper bound:...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x, is found to...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample
mean, x, is found to be 35.1, and the sample standard deviation, s,
is found to be 8.7
a) Construct a 90% confidence interval for μ if the
sample size, n, is 100.
b) Construct a 90% confidence interval for μ if the
sample size, n, is 40. How does decreasing the sample size affect
the margin of error, E?
c) Construct a 96% confidence interval for μ if...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x , is found...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x
, is found to be 18.5 , and the sample standard deviation, s, is
found to be 4.3.
(a) Construct a 95% confidence interval about mean if the
sample size, n, is 35.
(b) Construct a 95% confidence interval about mean if the
sample size, n, is 71. How does increasing the sample size affect
the margin of error, E?
(c) Construct a 99% confidence interval about...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x is found to...
A simple random sample of size n is drawn. The sample mean, x
is found to be 19.3 and the sample standard deviation, s, is found
to be 4.7
a. Construct a 95% confidence interval about mu if the sample
size, n, is 35
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
ADVERTISEMENT



 milcah answered 4 months ago
milcah answered 4 months ago