Question
In: Physics
A Light of wavelength 650 nm falls on two slits and produces an interference pattern in...
A Light of wavelength 650 nm falls on two slits and produces an interference pattern in which the third-order bright red fringe is 47 mm from the central fringe on a screen 1.4 m away.
What is the separation of the two slits?
B In a double-slit experiment, the third-order maximum for light of wavelength 520 nm is located 17 mm from the central bright spot on a screen 1.6 m from the slits. Light of wavelength 630 nm is then projected through the same slits. How far from the central bright spot will the second-order maximum of this light be located?
C Light of wavelength 620 nm falls on a slit that is 3.70×10−3 mm wide. How far the first bright diffraction fringe is from the strong central maximum if the screen is 10.5 m away.
D A grating that has 3900 slits per cm produces a third-order fringe at a 27.0 ∘ angle.
What wavelength of light is being used?
E Red laser light from a He-Ne laser (λ = 632.8 nm) creates a second-order fringe at 53.2∘ after passing through the grating. What is the wavelength λ of light that creates a first-order fringe at 22.0 ∘ ?
F Light of wavelength 670 nm passes through two narrow slits 0.65 mm apart. The screen is 2.40 m away. A second source of unknown wavelength produces its second-order fringe 1.21 mm closer to the central maximum than the 670 nm light. What is the wavelength of the unknown light?
Solutions
Expert Solution
A) we know that the formula of height of fringe from central fringe
y= n D/d
D/d
putting given value in above equation
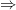 47*10-3=3*650*10-9*1.4/d
47*10-3=3*650*10-9*1.4/d
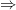 d = 58.08
d = 58.08  separation width of slit
separation width of slit
B) we know that y= n D/d
D/d
comparing two conditions
y1/y2 = (n1 1D1/n2
1D1/n2 2D2)*d2/d1
2D2)*d2/d1
putting given values D1=D2 & d1=d2
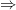 17/y = 3*520/2*630
17/y = 3*520/2*630
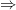 y = 17*2*630/3*520
y = 17*2*630/3*520
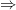 y= 13.73 mm
y= 13.73 mm
C) reusing above formula y= n D/d
D/d
let n=1, y=? , =620
nm ,d= 3.70*10-3mm ,D=10.5 m
=620
nm ,d= 3.70*10-3mm ,D=10.5 m
so y=
1*620*10-9*10.5/3.70*10-6 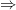 y= 4.60 mm
y= 4.60 mm
D) we know the condition of diffraction
(e+d) sin =
m
=
m
e+d= 1cm/3900= 2.56*10-6m , m=3
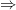 2.56*10-6*
sin27o = 3
2.56*10-6*
sin27o = 3 
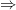
 =
387.4 nm
=
387.4 nm
E) from diffraction condition (e+d)
sin =
m
=
m
comparing for both wavelength
sin 1/sin
1/sin 2
= m1
2
= m1 1/m2
1/m2 2
2
 1=53.2o,
1=53.2o,  2=22o
, m1=2, m2=1,
2=22o
, m1=2, m2=1,  1=632.8,
1=632.8,  2=?
2=?
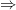 sin53.2 /sin22 = 2*632.8/1*
sin53.2 /sin22 = 2*632.8/1* 2
2
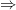
 2
= 592.1 nm
2
= 592.1 nm
F) here difference b/w fringe height produce by different wavelengths is given
so we apply fringe height formula in difference
y1-y2 = nD(  1-
1-
 2)/d
2)/d
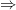 1.21*10-3= 2*2.40(670-
1.21*10-3= 2*2.40(670- 2)
/0.65*10-3
2)
/0.65*10-3
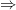 670nm-
670nm- 2
= 163.8 nm
2
= 163.8 nm
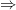
 2=
506.14 nm
2=
506.14 nm
Related Solutions
2. A monochromatic light with wavelength 540.0 nm strikes a pair of narrow slits. An interference...
An interference pattern is produced by light with a wavelength 600 nm from a distant source...
Suppose a certain wavelength of light falls on a diffraction grating and creates an interference pattern....
4. Light incident on a pair of slits produces an interference pattern on a screen 2.5...
(1A) Light of wavelength 534.0 nm illuminates a double slit, and the interference pattern is observed...
Light of wavelength illuminates a pair of slits and the first bright fringe of the interference...
Light from a red laser (650 nm) is incident on two slits separated by 0.5 mm....
Light of wavelength 600 nm passes though two slits separated by 0.25mm and is observed on...
Light of wavelength 600 nm is incident on a pair of slits 2,000 nm apart. Find...
In Young’s experiment, monochromatic light of wavelength 600 nm shines on two slits separated by 0.3...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
 genius_generous answered 2 months ago
genius_generous answered 2 months ago