Question
In: Physics
For what range of object positions does a bi-convex lens of focal length f form a...
For what range of object positions does a bi-convex lens of focal length f form a real image?
Solutions
Expert Solution
The Golden Gate Bridge refracted inrain droplets, which act as lenses
Image of a plant as seen through a biconvex lens.
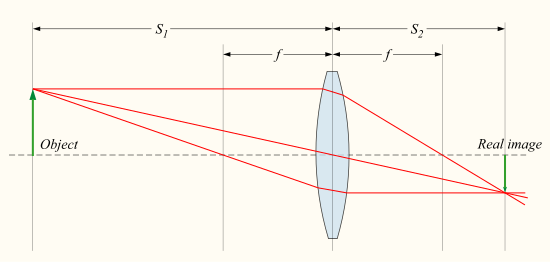
If the distances from the object to the lens and from the lens to the image are S1 and S2 respectively, for a lens of negligible thickness, in air, the distances are related by the thin lens formula
 .
.
This can also be put into the "Newtonian" form:
 [21]
[21]
where  and
and  .
.
What this means is that, if an object is placed at a distance S1 along the axis in front of a positive lens of focal length f, a screen placed at a distance S2 behind the lens will have a sharp image of the object projected onto it, as long as S1 > f (if the lens-to-screen distance S2 is varied slightly, the image will become less sharp). This is the principle behind photography and the human eye. The image in this case is known as a real image.
Related Solutions
a convex lens has a focal length f. if an object is placed at a distance...
An object is located to the left of a convex lens whose focal length is f=34...
7. A convex lens has a focal length of f= 50cm. An object is placed 40cm...
A magnifying glass is a single convex lens with a focal length of f = +9.50...
1. Consider a convex lens with a focal length of 5.50 cm. An object is located...
An object 1cm tall is placed at 4cm from a convex lens with a focal length...
A. A convex lens has a focal length of 5.74704 cm. The object distance is 7.11538...
Q3- lens A to be a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm, lens...
An object is placed 10 m before a convex lens with focal length 5 . 9...
An object is placed in front of a lens with focal length f1, a second lens...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 genius_generous answered 10 months ago
genius_generous answered 10 months ago