Question
In: Civil Engineering
Please explain in detail the effects of different moisture conditions (saturated/dry) in soil to rainfall-runoff relationships?...
Please explain in detail the effects of different moisture conditions (saturated/dry) in soil to rainfall-runoff relationships? Expound on the concepts of rainfall volume, runoff volume, runoff coefficient, and interflow.
Solutions
Expert Solution
After a particular duration of rainfall, Runoff volume mainly depends on the surface conditions v.i.z.,. Characteristics of soil such as Soil texture, Porosity, Structure and hydraulic conductivity.
Soils having wet / saturated moisture conditions will show a high runoff capacity at initial stages as capillary infringement in the soils prevent water to drain off / percolate at initial stages into the sub surface. This is due to pore water pressure exerted by the saturated soil profile. However, Dry sandy soil will have low runoff than rainfall due to ground water movement.
Higher the infiltration capacity(i.e., directly proportional to porosity), Runoff volume observed will be low with respect to perception taken place(i.e., rainfall amount).
The relation between infiltration and time for different loamy soils are as given below:
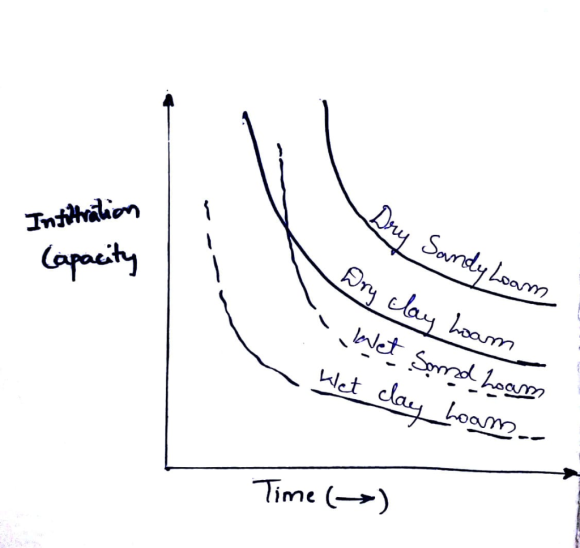
Rainfall volume: The total amount of precipitation observed over a particular area recorded for a particular duration of a total rainfall time is known as Rainfall Volume.
Runoff volume is the observed stream flow after the discharge of run off over the stream after a duration of rainfall. Any runoff stream accompanied by natural abstractions / valleys / streams will have a discharge to duration pattern as drawn below:

Ground water table with infiltrated water gives inflow to the stream, which is considered as Inter flow. Inter flow reduces the initial losses such as loss due to Evaporation, Evapotranspiration etc.,.
Runoff coefficient gives amount of rainfall water passes through a particular area over certain duration. It is denoted by "C".
C = Q/(iA)
where, Q = discharge or runoff
i = hydraulic gradient
A = area over which storm occured / catchment area.
Related Solutions
In batching of aggregates the moisture content is expected to be in saturated surface dry condition....
Compute the runoff from 5 inches of rainfall on a 1000-acre watershed using Soil the Conservation...
Derive the different relationships among the properties of the soil. I have good knowledge but I...
explain the causes and effects of global warming and provide solution ? in detail please provide...
Would the Difference in conditions insurance (DIC) cover political unrest Please explain in detail ?
Walnut Orchard has two farms that grow wheat and corn. Because of different soil conditions, there...
identify and explain in detail three relationships between the geography of an area or region and...
Please explain in detail Please explain in detail he Sarbanes Oxley Act How and why does...
How Accounting Equation Effects Financial Statement Components ( in detail please)
What are the beneficial effects of probiotics to ourbody? (Please give a detail explanation on...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Ally Wells answered 1 year ago
Ally Wells answered 1 year ago