Question
In: Civil Engineering
Prepare an earned value schedule for a public construction project improving the drainage system of a...
Prepare an earned value schedule for a public construction project improving the drainage system of a neighborhood street.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Earned value management is a project management technique for measuring project performance and progress. It has the ability to combine measurements of the project management triangle: scope, time, and costs.
In a single integrated system, earned value management is able to provide accurate forecasts of project performance problems, which is an important contribution for project management.
Early EVM research showed that the areas of planning and control are significantly impacted by its use; and similarly, using the methodology improves both scope definition as well as the analysis of overall project performance. More recent research studies have shown that the principles of EVM are positive predictors of project success.
Essential features of any EVM implementation include:
- A project plan that identifies work to be accomplished
- A valuation of planned work, called planned value (PV) or budgeted cost of work scheduled (BCWS)
- Pre-defined "earning rules" (also called metrics) to quantify the accomplishment of work, called earned value (EV) or budgeted cost of work performed (BCWP)
EVM implementations for large or complex projects include many more features, such as indicators and forecasts of cost performance (over budget or under budget) and schedule performance (behind schedule or ahead of schedule). However, the most basic requirement of an EVM system is that it quantifies progress using PV and EV.
Application example:
Project A has been approved for a duration of one year and with the budget of X. It was also planned that the project spends 50% of the approved budget and expects 50% of the work to be complete in the first six months. If now, six months after the start of the project, a project manager would report that he has spent 50% of the budget, one can initially think, that the project is perfectly on plan. However, in reality the provided information is not sufficient to come to such a conclusion. The project can spend 50% of the budget, whilst finishing only 25% of the work, which would mean the project is not doing well; or the project can spend 50% of the budget, whilst completing 75% of the work, which would mean that project is doing better than planned. EVM is meant to address such and similar issues
Project tracking:



It is helpful to see an example of project tracking that does not include earned value performance management. Consider a project that has been planned in detail, including a time-phased spend plan for all elements of work. Figure 1 shows the cumulative budget (cost) for this project as a function of time (the blue line, labeled PV). It also shows the cumulative actual cost of the project (red line, labeled AC) through week 8. To those unfamiliar with EVM, it might appear that this project was over budget through week 4 and then under budget from week 6 through week 8. However, what is missing from this chart is any understanding of how much work has been accomplished during the project. If the project was actually completed at week 8, then the project would actually be well under budget and well ahead of schedule. If, on the other hand, the project is only 10% complete at week 8, the project is significantly over budget and behind schedule. A method is needed to measure technical performance objectively and quantitatively, and that is what EVM accomplishes.
Earned value (EV):

Figure 2 shows the EV curve (in green) along with the PV curve from Figure 1. The chart indicates that technical performance (i.e. progress) started more rapidly than planned, but slowed significantly and fell behind schedule at week 7 and 8. This chart illustrates the schedule performance aspect of EVM. It is complementary to critical path or critical chain schedule management.
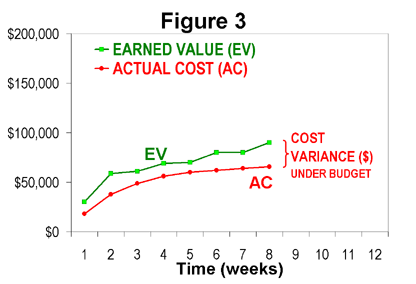
Figure 3 shows the same EV curve (green) with the actual cost data from Figure 1 (in red). It can be seen that the project was actually under budget, relative to the amount of work accomplished, since the start of the project. This is a much better conclusion than might be derived from Figure 1.
Figure 4 shows all three curves together – which is a typical EVM line chart. The best way to read these three-line charts is to identify the EV curve first, then compare it to PV (for schedule performance) and AC (for cost performance). It can be seen from this illustration that a true understanding of cost performance and schedule performance relies first on measuring technical performance objectively. This is the foundational principle of EVM.
Making earned value schedule metrics concordant with the CPM schedule:
The actual critical path is ultimately the determining factor of every project's duration. Because earned value schedule metrics take no account of critical path data, big budget activities that are not on the critical path have the potential to dwarf the impact of performing small budget critical path activities. This can lead to "gaming" the SV and SPI metrics by ignoring critical path activities in favor of big budget activities that may have lots of float. This can sometimes even lead to performing activities out-of-sequence just to improve the schedule tracking metrics, which can cause major problems with quality.
A simple two-step process has been suggested to fix this:
- Create a second earned value baseline strictly for schedule, with the weighted activities and milestones on the as-late-as-possible dates of the backward pass of the critical path algorithm, where there is no float.
- Allow earned value credit for schedule metrics to be taken no earlier than the reporting period during which the activity is scheduled unless it is on the project's current critical path.
In this way, the distorting aspect of float would be eliminated. There would be no benefit to performing a non-critical activity with lots of float until it is due in proper sequence. Also, an activity would not generate a negative schedule variance until it had used up its float. Under this method, one way of gaming the schedule metrics would be eliminated. The only way of generating a positive schedule variance (or SPI over 1.0) would be by completing work on the current critical path ahead of schedule, which is in fact the only way for a project to get ahead of schedule.
Advanced implementations (integrating cost, schedule and technical performance)
In addition to managing technical and schedule performance, large and complex projects require that cost performance be monitored and reviewed at regular intervals. To measure cost performance, planned value (or BCWS - Budgeted Cost of Work Scheduled) and earned value (or BCWP - Budgeted Cost of Work Performed) must be in units of currency (the same units that actual costs are measured.).
In large implementations, the planned value curve is commonly called a Performance Measurement Baseline (PMB) and may be arranged in control accounts, summary-level planning packages, planning packages and work packages.
In large projects, establishing control accounts is the primary method of delegating responsibility and authority to various parts of the performing organization. Control accounts are cells of a responsibility assignment (RACI) matrix, which is the intersection of the project WBS and the organizational breakdown structure (OBS). Control accounts are assigned to Control Account Managers (CAMs).
Large projects require more elaborate processes for controlling baseline revisions, more thorough integration with subcontractor EVM systems, and more elaborate management of procured materials.
In the United States, the primary standard for full-featured EVM systems is the ANSI/EIA-748A standard, published in May 1998 and reaffirmed in August 2002. The standard defines 32 criteria for full-featured EVM system compliance. As of the year 2007, a draft of ANSI/EIA-748B, a revision to the original is available from ANSI. Other countries have established similar standards.
In addition to using BCWS and BCWP, prior to 1998 implementations often use the term actual cost of work performed (ACWP) instead of AC. Additional acronyms and formulas include:
Budget at completion (BAC)
The total planned value (PV or BCWS) at the end of the project. If a project has a management reserve (MR), it is typically not included in the BAC, and respectively, in the performance measurement baseline.
Cost variance (CV)

CV greater than 0 is good (under budget).
Cost performance index (CPI)

CPI greater than 1 is favourable (under budget):
< 1 means that the cost of completing the work is higher than planned (bad);
= 1 means that the cost of completing the work is right on plan (good);
> 1 means that the cost of completing the work is less than planned (good or sometimes bad).
Having a CPI that is very high (in some cases, very high is only 1.2) may mean that the plan was too conservative, and thus a very high number may in fact not be good, as the CPI is being measured against a poor baseline. Management or the customer may be upset with the planners as an overly conservative baseline ties up available funds for other purposes, and the baseline is also used for manpower planning.
Estimate at completion (EAC)
EAC is the manager's projection of total cost of the project at completion.

This formula is based on the assumption, that the performance of the project (or rather a deviation of the actual performance from a baseline) to date gives a good indication of what a performance (or rather deviation of a performance from a baseline) will be in the future. In other words this formula is using statistics of the project to date to predict future results. Therefore it has to be used carefully, when the nature of the project in the future is likely to be different from the one to date (e.g. performance of the project compare to baseline at the design phase may not be a good indication of what it will be during a construction phase).
Estimate to complete (ETC):
ETC is the estimate to complete the remaining work of the project. ETC must be based on objective measures of the outstanding work remaining, typically based on the measures or estimates used to create the original planned value (PV) profile, including any adjustments to predict performance based on historical performance, actions being taken to improve performance, or acknowledgement of degraded performance.
While algebraically, ETC = EAC-AC is correct, ETC should never be computed using either EAC or AC. In the following equation,

ETC is the independent variable, EAC is the dependent variable, and AC is fixed based on expenditures to date. ETC should always be reported truthfully to reflect the project team estimate to complete the outstanding work. If ETC pushes EAC to exceed BAC, then project management skills are employed to either recommend performance improvements or scope change, but never force ETC to give the "correct" answer so that EAC=BAC. Managing project activities to keep the project within budget is a human factors activity, not a mathematical function.
To-complete performance index (TCPI):
The TCPI provides a projection of the anticipated performance required to achieve either the BAC or the EAC. TCPI indicates the future required cost efficiency needed to achieve a target BAC (Budget At Complete) or EAC (Estimate At Complete). Any significant difference between CPI, the cost performance to date, and the TCPI, the cost performance needed to meet the BAC or the EAC, should be accounted for by management in their forecast of the final cost.
For the TCPI based on BAC (describing the performance required to meet the original BAC budgeted total):

or for the TCPI based on EAC (describing the performance required to meet a new, revised budget total EAC):

This implies, that if revised budget (EAC) is calculated using Earned Value methodology formula (BAC/CPI), then at the moment, when TCPI based on EAC is first time calculated, it will always be equal to CPI of a project at that moment. This happens because when EAC is calculated using formula BAC/CPI it is assumed, that cost performance of the remaining part of the project will be the same as the cost performance of the project to date.
Independent estimate at completion (IEAC):
The IEAC is a metric to project total cost using the performance to date to project overall performance. This can be compared to the EAC, which is the manager's projection.

Limitations:
Proponents of EVM note a number of issues with implementing it, further limitations may be inherent to the concept itself.
Because EVM requires quantification of a project plan, it is often perceived to be inapplicable to discovery-driven or Agile software developmentprojects. For example, it may be impossible to plan certain researchprojects far in advance, because research itself uncovers some opportunities (research paths) and actively eliminates others. However, another school of thought holds that all work can be planned, even if in weekly timeboxes or other short increments.[citation needed]
Traditional EVM is not intended for non-discrete (continuous) effort. In traditional EVM standards, non-discrete effort is called "level of effort" (LOE). If a project plan contains a significant portion of LOE, and the LOE is intermixed with discrete effort, EVM results will be contaminated.[13] This is another area of EVM research.
Traditional definitions of EVM typically assume that project accounting and project network schedule management are prerequisites to achieving any benefit from EVM. Many small projects don't satisfy either of these prerequisites, but they too can benefit from EVM, as described for simple implementations, above. Other projects can be planned with a project network, but do not have access to true and timely actual cost data. In practice, the collection of true and timely actual cost data can be the most difficult aspect of EVM. Such projects can benefit from EVM, as described for intermediate implementations, above, and Earned Schedule.
As a means of overcoming objections to EVM's lack of connection to qualitative performance issues, the Naval Air Systems Command (NAVAIR) PEO(A) organization initiated a project in the late 1990s to integrate true technical achievement into EVM projections by utilizing risk profiles. These risk profiles anticipate opportunities that may be revealed and possibly be exploited as development and testing proceeds. The published research resulted in a Technical Performance Management (TPM) methodology and software application that is still used by many DoD agencies in informing EVM estimates with technical achievement.[14] The research was peer-reviewed and was the recipient of the Defense Acquisition University Acquisition Research Symposium 1997 Acker Award for excellence in the exchange of information in the field of acquisition research.
There is the difficulty inherent for any periodic monitoring of synchronizing data timing: actual deliveries, actual invoicing, and the date the EVM analysis is done are all independent, so that some items have arrived but their invoicing has not and by the time analysis is delivered the data will likely be weeks behind events. This may limit EVM to a less tactical or less definitive role where use is combined with other forms to explain why or add recent news and manage future expectations.
There is a measurement limitation for how precisely EVM can be used, stemming from classic conflict between accuracy and precision, as the mathematics can calculate deceptively far beyond the precision of the measurements of data and the approximation that is the plan estimation. The limitation on estimation is commonly understood (such as the ninety-ninety rule in software) but is not visible in any margin of error. The limitations on measurement are largely a form of digitization error as EVM measurements ultimately can be no finer than by item, which may be the Work Breakdown Structure terminal element size, to the scale of reporting period, typically end summary of a month, and by the means of delivery measure. (The delivery measure may be actual deliveries, may include estimates of partial work done at the end of month subject to estimation limits, and typically does not include QC check or risk offsets.)
Related Solutions
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance (schedule, cost mainly)...
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance (schedule, cost mainly)...
Earned Value Management (EVM) is a project management technique for measuring project performance (schedule, cost mainly)...
The Adams Construction Company is bidding on a project to install alarge flood drainage culvert from...
What are the benefits to earned value managment in a project setting?
What are the benefits to earned value managment in a project setting?
As part of the Project Scope Statement of a house construction project, prepare the detailed Milestone...
Discuss the prevalence of the use of earned-value analysis to track and control costs on construction...
Discuss the prevalence of the use of earned-value analysis to track and control costs on construction...
How does project scope, project budget and earned value management conpare and contrast?
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 Ally Wells answered 3 years ago
Ally Wells answered 3 years ago