Question
In: Physics
The figure shows a combination of two identical lenses
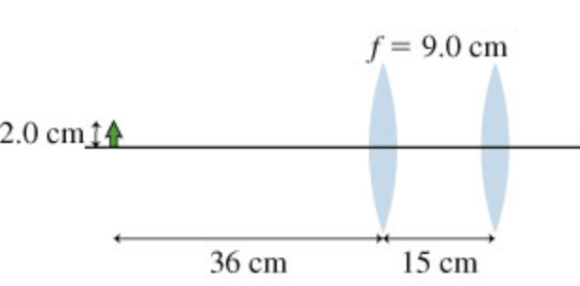
- erect
- inverted
Solutions
Expert Solution
(a)
Deter emine the im age position from the first lense, \(\frac{1}{q_{1}}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{p_{1}}\)
\(=\frac{1}{9 \mathrm{~cm}}-\frac{1}{36 \mathrm{~cm}}\)
\(=0.0833 \mathrm{~cm}^{-1}\)
\(q_{1}=12 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Im age at this location acts as object for the second lens.
The distance of this im age from the second lens is,
\(p_{2}=d-q_{1}\)
\(=15-12\)
\(=3 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Final image position is,
\(\frac{1}{q_{2}}=\frac{1}{f}-\frac{1}{p_{2}}\)
\(=\frac{1}{9 \mathrm{~cm}}-\frac{1}{3 \mathrm{~cm}}\)
\(q_{2}=-4.5 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Therefore, final im age position from the objects,
\(s=p_{1}+d+q_{2}=36 \mathrm{~cm}+15 \mathrm{~cm}-4.5 \mathrm{~cm}\)
\(=46.5 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(b)
Total magnification is, \(m=\left(\frac{-q_{1}}{p_{1}}\right)\left(-\frac{q_{2}}{p_{2}}\right)=\left(\frac{-12}{36}\right)\left(\frac{-(-4.5)}{3}\right)=-0.5\)
Height of the image is,
\(h_{1}=h_{0}(m)\)
\(=2 \mathrm{~cm}(-0.5)\)
\(=-1.0 \mathrm{~cm}\)
Therefore, the height of the image is \(1.0 \mathrm{~cm}\)
(c)
A negative sign of magnification indicates that the final image is inverted.
Related Solutions
The figure below shows two converging lenses placed L1 = 23 cm apart. Their focal lengths...
When two lenses are used in combination, the first one forms an image that then serves...
When two lenses are used in combination, the first one forms an image that then serves...
When two lenses are used in combination, the first one forms an image that then serves...
Two identical diverging lenses are separated by 17 cm. The focal length of each lens is...
A battery is connected across a series combination of two identical resistors. If the potential difference...
Bulbs A, B, and C in the figure(Figure 1) are identical and the switch is an...
The figure shows the equipotential contours in the plane of two point charges. The labels on...
Each of the two identical springs in the figure below has force constant k = 1.16...
Bulbs A, B, and C in the figure(Part A figure)are identical and the switch is an ideal conductor.
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago