Question
In: Anatomy and Physiology
Under what nutritional conditions is fatty acid synthesis likely to occur? Discuss the roles of acetyl...
Under what nutritional conditions is fatty acid synthesis likely to occur? Discuss the roles of acetyl CoA and malonyl CoA in the synthesis of fatty acids
Solutions
Expert Solution
Under nutrient-replete conditions, the primary fuel of the liver is glucose rather than fat. Fatty acids are not subjected to β-oxidation and instead are incorporated into triglycerides for storage in lipid droplets or secretion in very low-density lipoproteins (VLDL). Dietary fat in the form of chylomicron remnants is taken up by the liver; de novo synthesis of fatty acids by FAS may make a modest contribution to storing energy as fat when nutrients are present in excess.
Fatty acid synthesis is the creation of fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and NADPH through the action of enzymes called fatty acid synthases. This process takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell. Most of the acetyl-CoA which is converted into fatty acids is derived from carbohydrates via the glycolytic pathway. The glycolytic pathway also provides the glycerol with which three fatty acids can combine (by means of ester bonds) to form triglycerides (also known as "triacylglycerols" – to distinguish them from fatty "acids" – or simply as "fat"), the final product of the lipogenic process. When only two fatty acids combine with glycerol and the third alcohol group is phosphorylated with a group such as phosphatidylcholine, a phospholipid is formed.
synthesis of fatty acid:

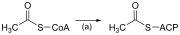
| (a) | Acetyl CoA:ACP transacylase |
|
Activates acetyl CoA for reaction with malonyl-ACP |
| (b) | Malonyl CoA:ACP transacylase |  |
Activates malonyl CoA for reaction with acetyl-ACP |
Acetyl CoA carboxylase plays an essential role in regulating fatty acid synthesis and degradation. Recall that this enzyme catalyzes the committed step in fatty acid synthesis: the production of malonyl CoA (the activated two-carbon donor). Thus, this important enzyme is subject to both global and local regulation.
explanation:
The pyruvate produced by glycolysis is an important intermediary in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids and cholesterol. This occurs via the conversion of pyruvate into acetyl-CoA in the mitochondrion. However, this acetyl CoA needs to be transported into cytosol where the synthesis of fatty acids and cholesterol occurs. This cannot occur directly. To obtain cytosolic acetyl-CoA, citrate (produced by the condensation of acetyl CoA with oxaloacetate) is removed from the citric acid cycle and carried across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the cytosol. There it is cleaved by ATP citrate lyase into acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate. The oxaloacetate can be used for gluconeogenesis (in the liver), or it can be returned into mitochondrion as malate. The cytosolic acetyl-CoA is carboxylated by acetyl CoA carboxylase into malonyl CoA, the first committed step in the synthesis of fatty acids
Related Solutions
Acetyl-CoA carboxylase is an enzyme in fatty acid synthesis. In response to increasing fatty acid levels,...
there is a mutation in a gene impairing fatty acid synthesis. what enzyme is most likely...
can anyone explain the diffence between bacterial Fatty acid synthesis and eukaryotic fatty acid synthesis as...
Compare and contrast triglyceride synthesis, fatty acid synthesis, and phospholipid synthesis
Explain the impact of the body’s glucose levels on fatty acid catabolism and fatty acid synthesis...
1- Fatty acyl CoA synthetase catalyses the 2-step fatty acid activation prior to fatty acid synthesis....
What is the overall “strategy” of fatty acid synthesis, and how does it compare with that...
where does fatty acid oxidation occur?"
What is the role of decarboxylation in fatty acid synthesis? Name another reaction in a different...
For fatty acid synthesis what would be the substrate if you are making an even number...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
 Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago
Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago