Question
In: Biology
What is the OEC, what reaction does it carryout? What is the basic structure of a...
What is the OEC, what reaction does it carryout? What is the basic structure of a plastoquinone molecule?
Solutions
Expert Solution
OEC(Oxygen-evolving complex):The oxygen-evolving complex is the site of water oxidation. It is a metallo-oxo cluster comprising four manganese ions (in oxidation states ranging from +3 to +4) and one divalent calcium ion. When it oxidizes water, producing oxygen gas and protons, it sequentially delivers the four electrons from water to a tyrosine (D1-Y161) sidechain and then to P680 itself. The structure of the oxygen-evolving complex is still contentious. The structures obtained by X-ray crystallography are particularly controversial, since there is evidence that the manganese atoms are reduced by the high-intensity X-rays used, altering the observed OEC structure. However, crystallography in combination with a variety of other (less damaging) spectroscopic methods such as EXAFS and electron paramagnetic resonance have given a fairly clear idea of the structure of the cluster. One possibility is the cubane-like structure. In 2011 the OEC of PSII was resolved to a level of 1.9 angstroms revealing five oxygen atoms serving as oxo bridges linking the five metal atoms and four water molecules bound to the Mn4CaO5 cluster; more than 1,300 water molecules were found in each photosystem II monomer, some forming extensive hydrogen-bonding networks that may serve as channels for protons, water or oxygen molecules.
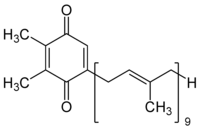
Plastoquinone (PQ) is a quinone molecule involved in the electron transport chain in the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis. Plastoquinone is reduced when it accepts two electrons from photosystem II and two hydrogen cations (H+) from the stromal matrix of the chloroplast), thereby forming plastoquinol. It transports the protons into the lumen of thylakoid discs, while the electrons continue further along the electron transport chain, into the cytochrome b6f protein complex.
The prefix plasto- means either plastid or chloroplast, alluding to its location within the cell.
Structurally it is a 2,3-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone molecule with a side chain of nine isoprenyl units.
Related Solutions
What is the basic structure of the Internet? What is an IXP?
What is the basic structure of the HIV virus? What is the function of the glycoproteins...
What is the basic structure of the HIV virus? What is the function of the glycoproteins...
What is the basic structure of the HIV virus? What is the function of the glycoproteins...
What is the basic structure of an antibody? What are the antigen‐binding sites? What are the...
What is the basic goal of financial management with regard to capital structure?
What is the basic structure of lecithins, and how do they work as emulsifiers, and in...
1-what is the basic structure of a cell 2-what are the three function of the cell...
What are the basic differences between SNAr reaction with SN1 and SN2 reactions?
Balance the following redox reaction if it occurs in basic solution. What are the coefficients in...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
 gladiator answered 3 years ago
gladiator answered 3 years ago