Question
In: Statistics and Probability
what conclusion can be drawn from a study with a null result
what conclusion can be drawn from a study with a null result
Solutions
Expert Solution
Solution:
- A null result occurs when we fail to reject
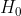 . This is
commonly referred to as a non-significant result or n-s. There are
two possible “realities” when the null is not rejected.
. This is
commonly referred to as a non-significant result or n-s. There are
two possible “realities” when the null is not rejected. - First, is the case where the null is true. If
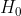 were true,
the probability of failing to reject
were true,
the probability of failing to reject 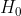 is .95.
is .95. - When the null is true, it is unlikely to make a Type I error.
Second, is the situation wherein
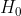 is false but we
fail to reject
is false but we
fail to reject 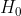 . This reflects
the Type II error probability (1 - Power).
. This reflects
the Type II error probability (1 - Power). - If the null is actually false, this probability is ideally
about .20. This means that, given an ideal situation, when
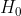 is false it will
not be rejected 1 out of 5 times. This result does not convey
statistical certainty.
is false it will
not be rejected 1 out of 5 times. This result does not convey
statistical certainty. - It is likely that either
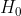 is true or
is true or
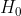 is false.
Neither result is ruled unlikely. This differs sharply from
situations wherein we can reject
is false.
Neither result is ruled unlikely. This differs sharply from
situations wherein we can reject 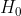 . When we reject
. When we reject
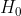 , there is a
comparatively small probability that we have made an error (i.e.,
Type I error rate of 5%).
, there is a
comparatively small probability that we have made an error (i.e.,
Type I error rate of 5%).
Related Solutions
What conclusions can be drawn from the study of circumcision in non-Western societies? Describe using 400...
What conclusions can be drawn from the study of circumcision in
non-Western societies? Describe using 400 words
What is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery?
The storage battery of a car has an emf of 12 Volt. If the internal resistance of the battery is 0.4 Ω, what is the maximum current that can be drawn from the battery?
#1 – 5: Select the proper conclusion from the following list. Assume that the null hypothesis...
#1 – 5: Select the proper conclusion from the following list.
Assume that the null hypothesis is no difference
or no mean difference.
[a] Reject the alternate hypothesis. We have good evidence that
there is a significant difference.
[b] Do not reject the alternate hypothesis. We do not have
enough evidence that there is a significant difference.
[c] Accept the alternate hypothesis. There is no evidence of a
significant difference.
[d] Reject the null hypothesis. There is evidence of a...
Include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis A...
Include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a
conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis
A student claimed that the average grade in the night sections
of Statistics was higher than the day sections. She used a sample
of 35 students from night sections and found they had a mean of 78
with a standard deviation of 8. A sample of 32 day students had a
mean of 75 with a standard deviation of 6. Is the student's
hypothesis supported?...
Include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis Nine...
Include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a
conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis
Nine students took the SAT. After taking it, they then took a
test preparation course and retook the SAT. Can you conclude that
the course changes performance on the SAT? (use α = .1)
Before
720
860
850
880
860
710
850
1200
950
After
740
860
840
920
890
720
840
1240
970
include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis Applicants...
include null and alternate hypothesis, a p-value, and a
conclusion PRIVATE about the null hypothesis
Applicants for a job in a foreign country are given a language
proficiency test. The following data shows the number of years they
have studied the language and their grade on the test.
No. of years, x344536237 Test grade, y616875827390587293
(1.)Plot the scatter diagram for the data on the axes below:
(2.)Find the coefficient of correlation ( r )
(3.)Find the Regression line equation for...
The Facts of Growth 1. What are the three main conclusions that can be drawn from...
The Facts of Growth
1. What are the three main conclusions that can be drawn from an
analysis of growth rates for developed countries?
2. To what extent have the three main facts of growth not held
for certain countries? For which countries have they not generally
held?
3. Explain why an increase in the number of workers will cause a
reduction in output per worker in the long run.
4. Discuss and explain what is meant by the "state...
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value, conclusion about the null hypothesis, and final...
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis,
test statistic, P-value, conclusion about the
null hypothesis, and final conclusion that addresses
both the claim and the significance level
alpha. Use the P-value method.
A sample of 17 jellybeans with a mean weight of 0.8295 g was
taken. Assume that
σ is known to be 0.0565 g. Consider a hypothesis test that uses
a 0.05 significance level
to test the claim that the mean weight of all jellybeans is
equal to 0.8550 g...
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value, conclusion about the null hypothesis, and final...
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test
statistic, P-value, conclusion about the null hypothesis, and final
conclusion that addresses the original claim.
Various temperature measurements are recorded at different times
for a particular city. The mean of 20°C is obtained for 60
temperatures on 60 different days. Assuming that test the claim
that the population mean is 22°C . Use a 0.05 significance level.
Testing Hypothesis Z-Table
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis, test statistic, P-value, conclusion about the null hypothesis, and final...
Identify the null hypothesis, alternative hypothesis,
test statistic, P-value, conclusion about the null hypothesis, and
final conclusion that addresses the original claim.
a) A poll of 1068 adult Americans reveals that 48% of the voters
surveyed prefer the Democratic candidate for the presidency. At the
0.05 level of significance, test the claim that at least half of
all voters prefer the Democrat.
b) In a sample of 167 children selected randomly from one town,
it is found that 37 of...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT
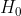 . This is
commonly referred to as a non-significant result or n-s. There are
two possible “realities” when the null is not rejected.
. This is
commonly referred to as a non-significant result or n-s. There are
two possible “realities” when the null is not rejected. orchestra answered 2 years ago
orchestra answered 2 years ago