Question
In: Computer Science
Describe the services of the IP protocol, and potentially ICMP protocol, with respect to flow control...
Describe the services of the IP protocol, and potentially ICMP protocol, with respect to flow control (ensuring the sender does not overwhelm the receiver).
Solutions
Expert Solution
IP Protocol
The IP protocol and its associated routing protocols are possibly the most significant of the entire TCP/IP suite. IP is responsible for the following:
-
IP addressing – The IP addressing conventions are part of the IP protocol. Chapter 3, Planning Your TCP/IP Network (Task) describes IPv4 addressing in detail and Chapter 14, IPv6 (Overview) describes IPv6 addressing in detail.
-
Host-to-host communications – IP determines the path a packet must take, based on the receiving host's IP address.
-
Packet formatting – IP assembles packets into units that are known as IP datagrams. Datagrams are fully described in Internet Layer.
-
Fragmentation – If a packet is too large for transmission over the network media, IP on the sending host breaks the packet into smaller fragments. IP on the receiving host then reconstructs the fragments into the original packet.
-

What is Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)?
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is a network layer
protocol used by network devices to diagnose network communication
issues. ICMP is primarily used to determine whether data reaches
its intended destination in a timely manner. Usually, ICMP protocol
is used on network devices, such as routers. ICMP is important for
error reporting and testing, but can also be used for distributed
DDoS attacks.
Why does ICMP work?
The main purpose of ICMP is to report an error. When two devices
are connected to the Internet, ICMP creates sharing errors with the
sending device in case any data does not reach its intended
destination. For example, if the data packet is too large for the
router, the router will discard the package and send the ICMP
message back to the original data source.
The second use of the ICMP protocol is to perform network diagnoses; The most widely used storage devices traceroute and ping both use ICMP. The use of traceroute is used to show the route between two Internet devices. Route is a realistic route for connected routers where the application must pass before it can reach its destination. Trips between one track and another are known as ‘hop,’ and the tracker track also reports the time required for each hop on the way. This can be helpful in determining the sources of network delays.
The use of ping is a simplified version of traceroute. The ping will check the connection speed between the two devices and accurately report how long it takes the data packet to reach its destination and back to the sender device. Although ping does not provide route data or hops, it is still a very useful metrics for measuring latency between two devices. ICMP echo-request and echo response messages are widely used for ping purposes.
Unfortunately network attacks can use this process, creating disruptive mechanisms such as ICMP flood attacks and death ping attacks.
How does ICMP work?
Unlike Internet Protocol (IP), ICMP is not associated with
transaction layer protocols such as TCP or UDP. This makes ICMP a
non-connecting protocol: one device does not need to open a
connection to another device before sending an ICMP message. Normal
IP traffic is transmitted using TCP, which means that any two data
exchange devices will first perform TCP handshakes to ensure that
both devices are ready to receive data. ICMP does not open to open
this way. The ICMP protocol also does not allow directing of a
specific port on the device.
How is ICMP used in DDoS attacks?
ICMP flood attacks
Ping flood or ICMP flood is when the attacker tries to eradicate the device identified by the ICMP echo application packets. The target must be processed and responded to in each package, consuming computer resources until legitimate users can access the service.
ICMP flood attack:
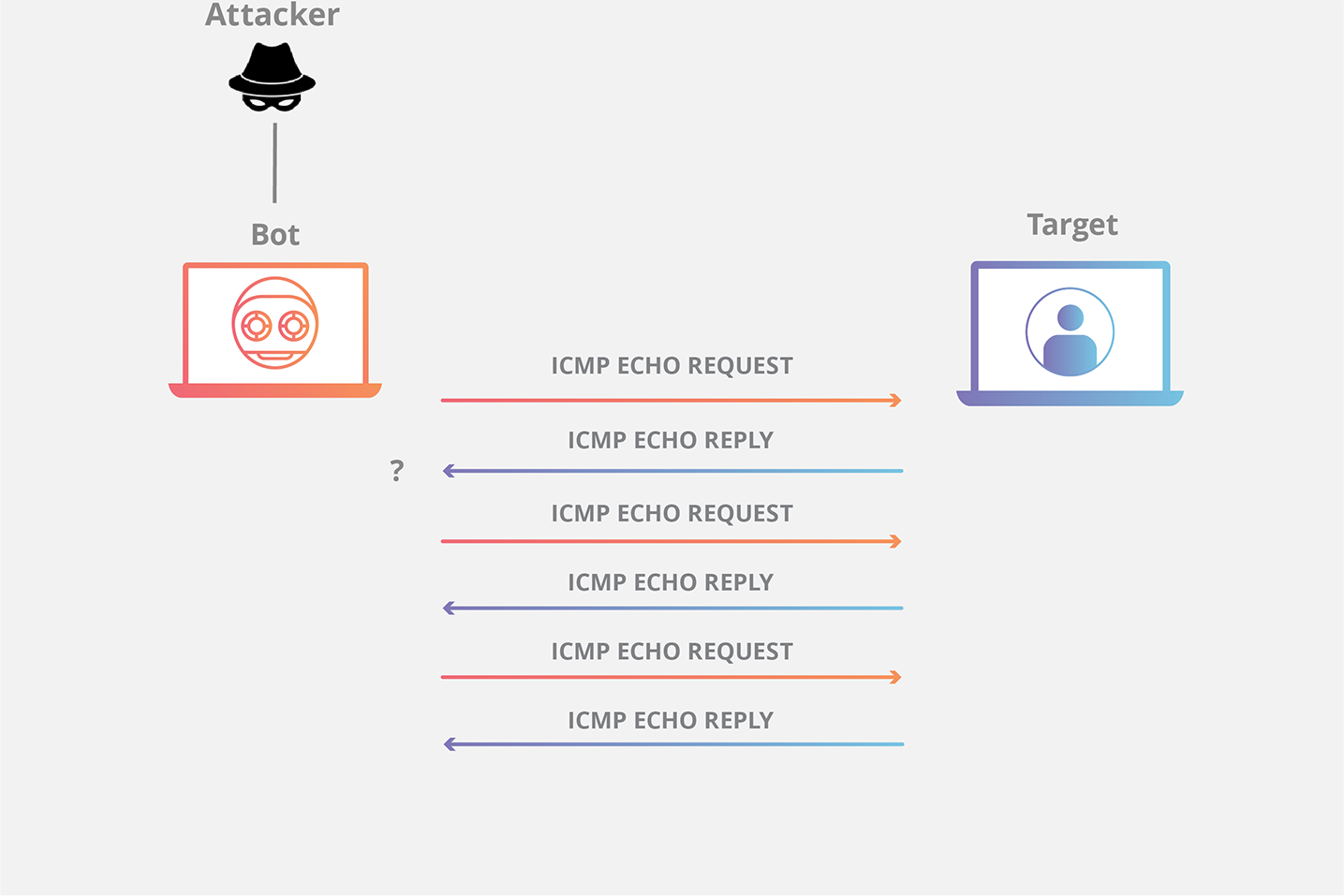
Ping of death attack
A deadly ping attack is when the attacker sends a ping larger than the maximum allowable packet size to the target machine, causing the machine to catch or explode. The packet is split along the path to the target, but when the target reassembles the packet with its original high-rise size, the size of the pack creates buffer overcrowding.
The ping of death attacks is particularly historical at this point. However, older communication devices may still be affected.
Smurf Attack
In an attack on Smurf, the attacker sends an ICMP package containing a fraudulent IP source address. Network resources turn the package on, send responses to the disabled IP and fill the victim with unwanted ICMP packets. Like the ‘ping of death,’ today Smurf attacks are only possible with legacy machines.
ICMP is not the only network layer process used for layer 3 DDoS attacks. Attackers have used GRE packets in the past, for example.
Typically, the DDoS network layer attacks network infrastructure and infrastructure, in contrast to the application layer attack, which identifies web structures. Cloudflare Magic Transit is one of the best ways to protect against DDoS network attacks.
Related Solutions
Describe the concept of flow control and briefly describe the mechanism/s implemented by the TCP protocol...
Briefly explain the Flow Control mechanism in Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
•Describe security problems inherent to the TCP/IP protocol suite..
Describe the service TCP provides with respect to flow control and explain the mechanisms it uses...
1) a) Describe the design principles of the TCP/IP protocol that explain the decentralised nature of...
Describe the difference between IP and Network Access layer in TCP protocol and also explain the...
Describe the major benefits and concerns of installing Internet Protocol (IP) based cameras for surveillance systems....
Explain the sliding window flow protocol and discuss the advantages of this protocol.
Explain both TCP/IP and ISO/OSI communication protocol stacks, identifying each of the protocol layers. How does...
What is the form of an IP address? What protocol is used by all computer connections...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...

 venereology answered 2 years ago
venereology answered 2 years ago