Question
In: Anatomy and Physiology
Trace the path glucose will travel from ghe renal artery to the the renal vein.( Be...
Trace the path glucose will travel from ghe renal artery to the the
renal vein.( Be sure to include all anatomical structurea that
glucose will travel through.)
Solutions
Expert Solution
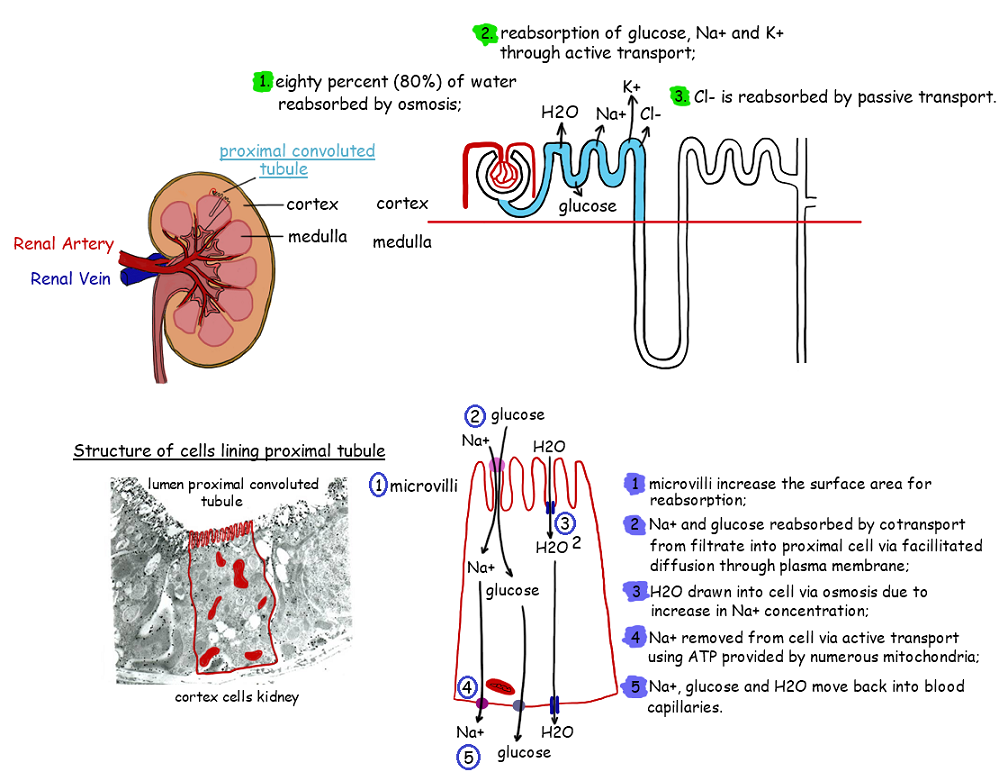
Blood containing glucose enters renal artery followed by the interlobar arteries prompts to actuate artery an then into interlobular artery which in turn flows into afferent arterioles followed by glomerular capillaries for filtration. Then the fluid flows into efferent arterioles followed by peritubular capillaries or vasa recta and then into interlobular vein, arcuate vein and interlobar vein respectively for reabsorption process in Henle’s loop and distal convulated tubule. After the retention of necessary nutrients, proteins, cells, glucose, etc., in the collecting duct,excess glucose and other waste substances are ejected out through the renal vein in the collecting duct.
Related Solutions
Trace the path a molecule of water will travel from the renal artery to the toilet...
Trace the path a molecule of water will travel from
the renal artery to the toilet bowl. Indicate the blood vessels,
Nephron structures, Kidney structures the water molecule will
travel through.
List the flow (path) of an erythrocyte from the renal artery ending in the renal vein...
List the flow (path) of an erythrocyte from the renal artery
ending in the renal vein (assume the RBC stays in the blood vessels
which is what should happen in normal physiology).
1. trace vascular flow from the renal artery to the golmerulus to the renal vein. 2....
1.
trace vascular flow from the renal artery to the golmerulus to the
renal vein.
2. describe filtrate formation from Bowman's capsule to
excretion.
3. discuss the location of nephron processes
Trace a drop of blood from the Right Ulnar Vein to the Splenic Artery.
Trace a drop of blood from the Right Ulnar Vein to the Splenic
Artery.
Part A The left renal vein __________. passes posterior to the superior mesenteric artery is shorter...
Part A
The left renal vein __________.
passes posterior to the superior mesenteric artery
is shorter than the right renal artery
enters the left kidney at the calyx
lies posterior to the abdominal aorta
Part B
Which of the following correctly describes the position of the
kidneys?
The inferior vena cava is medial to the kidneys.
Only the left kidney is retroperitoneal.
The superior surface of each kidney is covered by a lymphatic
gland.
The left kidney is lower than...
Trace a drop of blood beginning in the right renal vein, until it reaches the left...
Trace a drop of blood beginning in the right renal vein, until
it reaches the left basilic vein at the wrist. Before
reaching its final destination, the drop of blood must first pass
through the right dorsalis pedis artery.
List the final steps in a numbered format.
Trace a drop of fluid from renal artery to urethra. Note: you must include all steps...
Trace a drop of fluid from renal artery to urethra. Note: you must
include all steps from entry into kidney until it becomes
urine.
At what point along the vascular path (artery, arteriole, capillaries, venule, vein) is lymph most likely...
At what point along the vascular path (artery,
arteriole, capillaries, venule, vein) is lymph most likely to
collect and why?
If a patient has renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the renal artery) due to atherosclerosis, what...
If a patient has renal artery stenosis (narrowing of the renal
artery) due to atherosclerosis, what is the impact of this on GFR?
Specifically, be sure to discuss the impact on the afferent and/or
efferent arterioles as well as effects on hydrostatic and/or
oncotic pressure.
Trace blood flow from the Inferior Mesenteric Vein to the Brain.
Trace blood flow from the Inferior Mesenteric Vein to the
Brain.
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
ADVERTISEMENT
 Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago
Sydney Mullin answered 2 years ago