Question
In: Biology
Describe the carbon fixation reactions of photosynthesis. Be sure to mention the following: (a) the three...
Describe the carbon fixation reactions of photosynthesis. Be sure to mention the following: (a) the three major stages; (b) the name, quantity, and number of carbons for each intermediate; (d) role and quantity of ATP and NADPH; and (d) the number of turns needed to produce a single glucose molecule.
Distinguish among C3, C4, and CAM photosynthesis and name plants that exemplify each process.
Solutions
Expert Solution
Carbon is fixed in the plants by calvin cycle. It is the conversion of inorganic carbon to organic compounds by living organisms.
calvin cycle / calvin benson cycle:
co2 enters into plants through stomata and reaches mesophyll cells and then to the stroma of chloroplast . It is the light independent reaction and occurs in 3 steps.
1) fixation
2)reduction
3) regeneration.
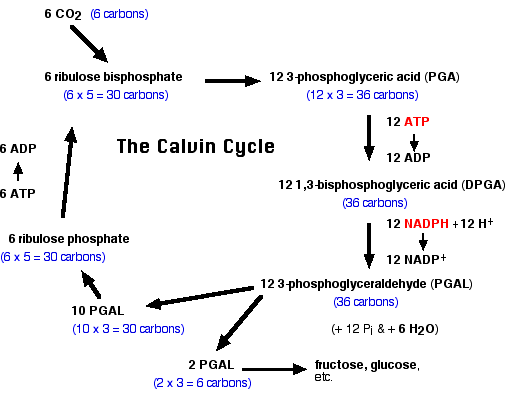
Fixation:
In the stroma, in addition to CO2,two other components are present to initiate the light-independent reactions: an enzyme called ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase (RuBisCO) and three molecules of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP). RuBP has five atoms of carbon, flanked by two phosphates. RuBisCO catalyzes a reaction between CO2 and RuBP. For each CO2 molecule that reacts with one RuBP, two molecules of 3-phosphoglyceric acid (3-PGA) form. 3-PGA has three carbons and one phosphate. Each turn of the cycle involves only one RuBP and one carbon dioxide and forms two molecules of 3-PGA. The number of carbon atoms remains the same, as the atoms move to form new bonds during the reactions (3 atoms from 3CO2 + 15 atoms from 3RuBP = 18 atoms in 3 atoms of 3-PGA). This process is called carbon fixation because CO2 is “fixed” from an inorganic form into organic molecules.
Stage 2: Reduction
ATP and NADPH are used to convert the six molecules of 3-PGA into six molecules of a chemical called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P). This is a reduction reaction because it involves the gain of electrons by 3-PGA. Recall that a reduction is the gain of an electron by an atom or molecule. Six molecules of both ATP and NADPH are used. For ATP, energy is released with the loss of the terminal phosphate atom, converting it to ADP; for NADPH, both energy and a hydrogen atom are lost, converting it into NADP+. Both of these molecules return to the nearby light-dependent reactions to be reused and reenergized.
Stage 3: Regeneration
At this point, only one of the G3P molecules leaves the Calvin cycle and is sent to the cytoplasm to contribute to the formation of other compounds needed by the plant. Because the G3P exported from the chloroplast has three carbon atoms, it takes three “turns” of the Calvin cycle to fix enough net carbon to export one G3P. But each turn makes two G3Ps, thus three turns make six G3Ps. One is exported while the remaining five G3P molecules remain in the cycle and are used to regenerate RuBP, which enables the system to prepare for more CO2 to be fixed. Three more molecules of ATP are used in these regeneration reactions.
Related Solutions
List the three variations of carbon-fixation reactions (C3, C4, and CAM) and write their basic characteristics...
Photosynthesis by land plants leads to the fixation each year of about 1 kg of carbon...
QUESTION 63 Carbon fixation occurs during the “dark reactions”. What does this mean? a. Sugar is...
what is carbon fixation and why is it important?
Describe the light reactions of photosynthesis and, for both a C3 and a C4 plant, trace...
1. What is the overall outcome of the light reactions in photosynthesis? 3. Describe the pathway...
Photosynthesis Light Reactions – Why is this like a battery?
a.) Describe the structure of the GroEL/GroES complex, make sure to mention domains but no need...
How does the shape and stacking of thylakoids contributes to the rate of carbon fixation by...
Plants require carbon dioxide for photosynthesis; despite this, the greater the amount of carbon dioxide released...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
- Cane Company manufactures two products called Alpha and Beta that sell for $150 and $110, respectively....
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
 gladiator answered 2 years ago
gladiator answered 2 years ago