Question
In: Biology
AcetylCoA is considered a high energy molecule because hydrolysis of the thioester bond is very exergonic...
AcetylCoA is considered a high energy molecule because hydrolysis of the thioester bond is very exergonic (∆G is - ). In contrast, the analogous oxyester would not be nearly as exergonic. Why is that? Provide one free energy diagram to show hydrolysis of both a thioester and an oxyester. Also provide an explanation for the difference in stability between thioesters and oxyesters. Your explanation should include relevant electron configurations and orbital overlap considerations
Solutions
Expert Solution
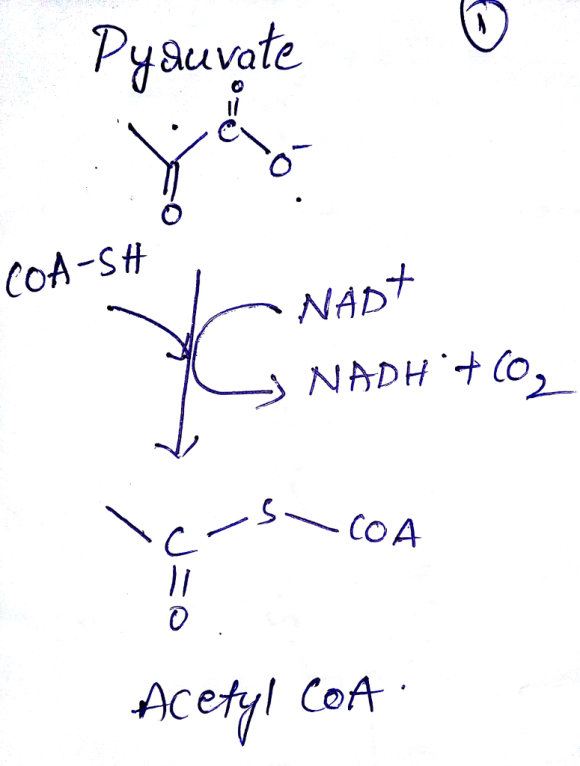
- Acetyl coenzyme A or acetyl-CoA is a molecule that participates in many biochemical reactions in protein, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism.
- Its main function is to deliver to acetyl group to the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) to be oxidized for energy production.
- Coenzyme A (CoASH or CoA) consists of a β-mercaptoethylamine
group linked to the vitamin pantothenic acid through an amide
linkage and 3'-phosphorylated ADP. This thioester linkage is a high
energy bond, which is particularly reactive. Hydrolysis of the
thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).
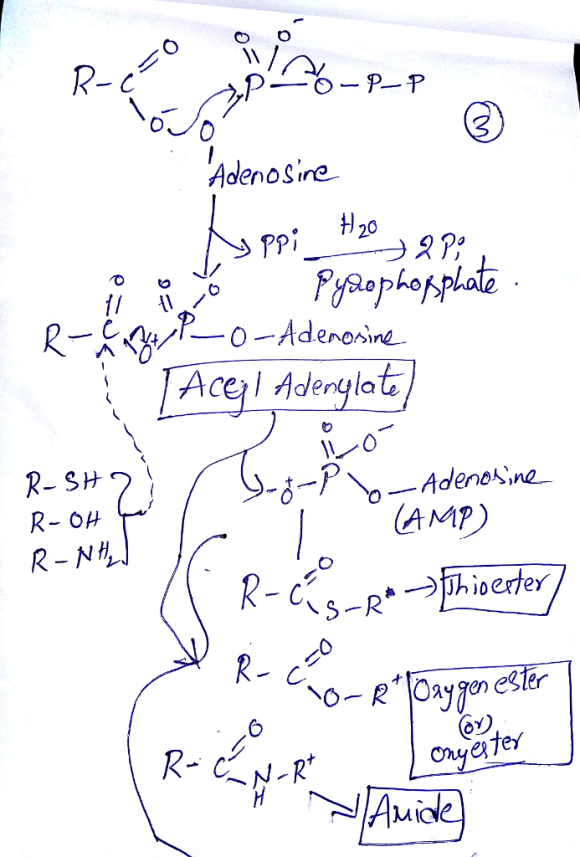
- comparing the resonance structures for an oxyester and a thioester we see by the samethree resonance structures to describe each structure.

However, the resonance structure on the right, the one with the double bond between the carbonyl carbon and the ester oxygen or the thioester sulfur, is less important in the sulfur. Because a double bond between second and third row atoms is not nearly as strong as a double bond between two second row elements having much better electronic overlap results between atoms of similar size).
As a result the thioester carbonyl is not as stabilized by resonance as the ester carbonyl, the thioester carbonyl is more reactive (lower activation energy to react) than the ester carbonyl. The thioester motif provides nature with a more reactive carbonyl. In this way it doesn't have to spend as much energy to bring about reaction at this more reactive carbonyl.
The thioester linkage to acetyl coA is a high energy bond, which is particularly reactive, which is having less stabilization comparing oxyester. Hydrolysis of the thioester bond is exergonic (−31.5 kJ/mol).

The provided answer may be correct and definitely useful.
Related Solutions
2. The hydrolysis of ATP is the cell’s most commonly used exergonic reaction when performing energy...
What is necessary for a bond to be considered polar? What is necessary for a molecule...
Fats are considered the most energy-dense of the three energy-yielding nutrients because each gram od fat...
In a paragraph, relate the following terms: Metabolism, anabolism, catabolism, hydrolysis, condensation, endergonic, exergonic. Relate means group...
Which of the following molecules contains least energy? (hint: which bond has highest energy? Which molecule...
NADH and FADH2 are often considered “energy currency” in cellular metabolism because they are generated directly...
Use molecular orbital theory to explain why the bond energy of an O2 molecule is less...
Given that free energy increases with endergonic processes, and decreases with exergonic processes, fill in the...
Why are very high gross margins so important? What is considered to be the minimum GM...
Which molecule(s) provide high energy electrons to the electron transport chain in oxidative phosphorylation? a. ATP...
- What’s the cost of each component of capital and which need to be adjusted? What do...
- Answer the following questions 1) How does ASC 606 — Revenue From Contracts With Customers(new standard...
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...


 gladiator answered 2 years ago
gladiator answered 2 years ago