Question
In: Chemistry
PART A A calorimeter contains 27.0 mL of water at 14.5 ∘C . When 1.70 g...
PART A
A calorimeter contains 27.0 mL of water at 14.5 ∘C . When 1.70 g of X (a substance with a molar mass of 75.0 g/mol) is added, it dissolves via the reaction
X(s)+H2O(l)→X(aq)
and the temperature of the solution increases to 28.5 ∘C .
Calculate the enthalpy change, ΔH, for this reaction per mole of X.
Assume that the specific heat of the resulting solution is equal to that of water [4.18 J/(g⋅∘C)], that density of water is 1.00 g/mL, and that no heat is lost to the calorimeter itself, nor to the surroundings.
Express the change in enthalpy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures.
PART B
Consider the reaction
C12H22O11(s)+12O2(g)→12CO2(g)+11H2O(l)
in which 10.0 g of sucrose, C12H22O11, was burned in a bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 7.50 kJ/∘C. The temperature increase inside the calorimeter was found to be 22.0 ∘C. Calculate the change in internal energy, ΔE, for this reaction per mole of sucrose.
Express the change in internal energy in kilojoules per mole to three significant figures.
THANKS! (Detailed Steps Plz)
Solutions
Expert Solution
Part A
 H = m
Cp
H = m
Cp  T for the
substance X and water.
T for the
substance X and water.
Now here m = mass of water + mass of substance X
= (Volume of water x density of water) + mass of substance X
= 27 X1 + 1.70 = 28.70 gm
Cp = 4.18 J/(gm ˚ C)
 T = 28.5 - 14.5 =
14 ˚ C
T = 28.5 - 14.5 =
14 ˚ C
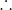
 H =
28.7 X 4.18 X 14 = 1679.52 J
H =
28.7 X 4.18 X 14 = 1679.52 J
Now mole of subtance X = mass / molar mass = 1.70 / 75 =0.02
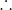
 Hsolution
= 1679.52 / 0.02 J/mole = 83976 J/mole = 83.98 KJ/mole
Hsolution
= 1679.52 / 0.02 J/mole = 83976 J/mole = 83.98 KJ/mole
Part B
Here  E = - m
Cv
E = - m
Cv T
T
m = 10 g
Cv = 7.5 KJ/gm ˚ C
 T = 22 ˚ C
T = 22 ˚ C
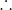
 E =
- 10 X 7.5 X 22 = -1650 KJ
E =
- 10 X 7.5 X 22 = -1650 KJ
Molar mass of C12H22O11 = (12*12)+(22*1)+(11*16) = 144+22+176 = 342 g/mole
mole of Sucrose = mass / molar mass = 10 / 342 = 0.03
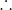
 Erxn =
-1650 / 0.03 = - 55000 KJ/mole
Erxn =
-1650 / 0.03 = - 55000 KJ/mole
Give feedback
Related Solutions
Part A A calorimeter contains 16.0 mL of water at 12.5 ∘C . When 1.70 g...
Part A: A calorimeter contains 18.0 mL of water at 13.5∘C. When 2.30 g of X...
A calorimeter contains 20.0 mL of water at 12.5 ∘C . When 1.40 g of X...
A calorimeter contains 31.0 mL of water at 15.0 ∘C . When 2.50 g of X...
A 200.0 g aluminum calorimeter contains 600.0 g of water at 20.0 °C. A 100.0 g...
A 200 g aluminum calorimeter contains 500 g of water at 20 C. A 100 g...
When 50.0 mL of 60.0°C water was mixed in the calorimeter with 50.0 mL of 25.0°C...
A coffee-cup calorimeter contains 130.0 g of water at 25.3 ∘C . A 124.0-g block of...
A coffee cup calorimeter contains 152.18 g of water at 20.90 °C. A 55.336 g piece...
A coffee cup calorimeter contains 480.0 g of water at 25.0 oC. To it are added:...
- In long paragraphs answer the questions below: Discuss the key components (where, when, what) and causes...
- Sinkal Co. was formed on January 1, 2018 as a wholly owned foreign subsidiary of a...
- Larry’s best friend, Garfield, owns a lasagna factory. Garfield’s financial skills are not very strong, so...
- Redox/Oxidation lab with Metals and Halogens So basically we were testing different reactions and observing changes....
- CORAL LANGUAGE ONLY Write a function DrivingCost with parameters drivenMiles, milesPerGallon, and dollarsPerGallon, that returns the...
- do you believe, as bonilla-silva does, that convert forms of racism are widespread? why or why...
- A bicycle wheel has a diameter of 63.9 cm and a mass of 1.86 kg. Assume...
 queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago
queen_honey_blossom answered 3 years ago