Question
In: Psychology
What learning theory is teaching someone how to dance?
What learning theory is teaching someone how to dance?
Solutions
Expert Solution
Teaching someone how to dance is a example of Bandura - Social Learning Theory.
- In social learning theory , Albert Bandura agrees with the behaviorists learning theories of Classcal Conditioning & Operant Conditioning. He provided two important aspects :
- Mediating processes occur between stimuli and responses.
- Behavior is learned from the environment through the process of Observational learning.
Bandura's Social learning theory is sometimes seen as a bridge between cognitive and behavioral theories because it encompasses attention , memory and motivation. It focuses on how mental (Cognitive) factors are involved in learning.
- Bandura developed his theory in part by conducting Bobo doll experiment in which Bandura included an adult who is tasked to act aggressively toward a Bobo Doll while the children observe him. Here is the link of the video for more clearity : https://youth.be/dmBqwWIJg8U
- As per Bandura children observe the people around them behaving in various ways. Individuals that are observed are called models. In society, children are surrounded by many influential models, such as parents, teachers, friends. These models provide examples of behavior to observe and imitate.
- Children pay attention to some of these models and encode their behavior. People around the child will respond to the behavior it imitates with either reinforcement or punishment. If consequences are rewarding child is likely to continue performing the behavior.
- In our example to teach someone dance in this process these mental factors mediate in the learning process to determine whether a new response is acquired.
- Please find below picture of behaviorists model and cognitive model :
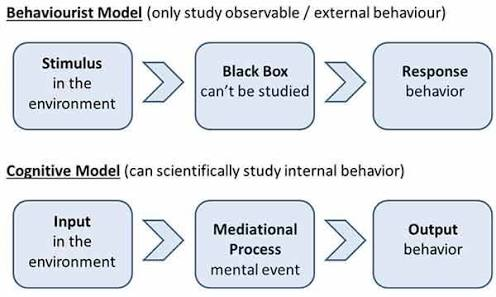
- There are four mediational processes proposed by Bandura :
- Attention : For learning dance , attention is extremely important to observe or learn new things, movements.
- Retention: How well the behavior is remembered . It is important that a memory of the behavior is formed to be performed later. Eg. Dance steps, expression etc
- Reproduction: This is the ability to perform the behavior that the model has demonstrated.
- Motivation: The will to perform a behavior. Sometimes the reward and punishment need to use that follow a behavior will be considered by the observer.
Related Solutions
Differentiate among the theory-based teaching strategies (dialectic learning, problem-based learning, operational instruction, and logistic teaching).
Differentiate among the theory-based teaching strategies
(dialectic learning, problem-based learning, operational
instruction, and logistic teaching).
The Concept of Teaching and Learning Linking the concept of teaching and learning with the concept...
The Concept of Teaching and Learning
Linking the concept of teaching and learning with the concept of
communication:
Question 1
How does the quality of a nurse’s communication skills impact
his ability to teach? If you can, please relate to situations you
have witnessed/experienced in your clinical/work experiences.
Question 2
How does the ability to communicate with those who speak a
different language impact the teaching process? If you can, please
relate to situations you have witnessed /experienced in your...
How is modern social learning theory different than traditional learning theory ?
How
is modern social learning theory different than traditional
learning theory ?
Summarize Robert C. Bolles theory of learning; what is the major learning theory, including components of...
Summarize Robert C. Bolles theory of learning; what is the major
learning theory, including components of how it was discovered and
how learning occurs. Describe the application, relevance, and how
it currently applies to education and psychology.
what are the key aspects of transformative learning theory
what are the key aspects of transformative learning theory
how would integrate e-learning into patient teaching for the population you are caring for in the...
how would integrate e-learning into patient teaching for the
population you are caring for in the community?
how this would impact specific ethnic groups that are
represented in the state of New York?
What are the strengths and limitations of differential association theory and social learning theory?
What are the strengths and limitations of differential
association theory and social learning theory?
how would a nurse apply teaching and learning principles on alcohol addiction to teach patients how...
how would a nurse apply teaching and learning
principles on alcohol addiction to teach patients how to treat the
situation and how to prevent it and apply cognitive, affective and
psychomotor domains... and provide a teaching plan
Skill acquisition theory states that learning a second language is similar to learning how to drive....
Skill acquisition theory states that learning a second language
is similar to learning how to drive. Explain the logic behind this
statement and explain why you agree/disagree with this
statement.
Please write in detail (175-225 words)
SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
SOCIAL LEARNING THEORY
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT

 Hayet Jeridi answered 3 years ago
Hayet Jeridi answered 3 years ago