Question
In: Biology
In mitochondrial electron transport, what is the direct role of O2?
The role of O2 in electron transport
In mitochondrial electron transport, what is the direct role of O2?
- a)to provide the driving force for the synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi
- b)to function as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain
- c)to oxidize NADH and FADH2 from glycolysis, acetyl CoA formation, and the citric acid cycle
- d)to provide the driving force for the production of a proton gradient
Solutions
Expert Solution
From the given data,
The role of \(\mathrm{O}_{2}\) in electron transport in mitochondrial electron transport is to function as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain. After accepting the final electron oxygen becomes completely reduced into a water molecule. The adjoined picture shows ETC:
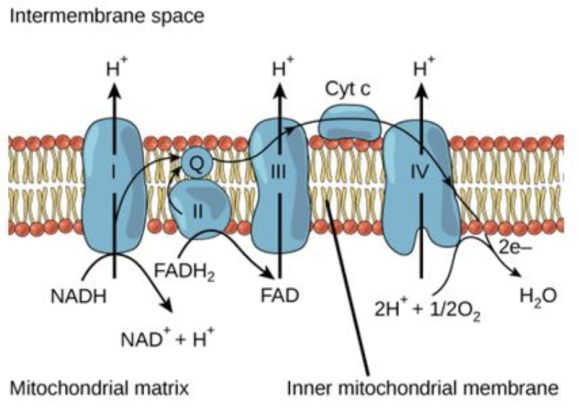
Thus, the correct option is to function as the final electron acceptor in the electron transport chain.
Related Solutions
1. Describe mitochondrial electron transport from NADH to O2 by listing the protein complexes involved, the...
1. Describe mitochondrial electron transport from NADH to
O2 by listing the protein complexes involved, the mobile
electron carriers, at which point protons are transported, and how
many protons at each step.
2. Based on your knowledge of the structure of protein Complex I
of the ETC, describe how electron transport is linked to the
passage of 4 protons through Complex I. Describe the protein
structure changes that occur.
3. . Describe the subunit structure ATP Synthase. What subunits
comprise...
Describe the mitochondrial electron transport pathway and the synthesis of ATP by mammalian mitochondria. Describe the...
Describe the mitochondrial electron transport pathway and the
synthesis of ATP by mammalian mitochondria.
Describe the urea cycle including its function, energy costs and
regulation.
If palmitic acid (16:0) labeled in C-1 were metabolized under
anaerobic metabolism in mammalian tissues, what carbon atom would
be tagged with 14C in what compound?
a) Sketch a model for the electron-transport pathway in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Show the pathways...
a) Sketch a model for the electron-transport pathway in the
mitochondrial inner membrane. Show the pathways of the electrons
transport from the reduced forms of coenzyme in the mitochondrial
electron-transport chain. What is the functional role of electron
transport system in metabolism?
b) What is an uncoupler or uncoupling agent? Provide an example
of an uncoupling agent.
On the basis of the mitochondrial electron transport and ATP synthase inhibitors (myxothaizol, FCCP, Venturicidin, and...
On the basis of the mitochondrial electron transport and ATP
synthase inhibitors (myxothaizol, FCCP, Venturicidin, and
Ventruicidin + FCCP) list the effects of these on the rates
(decrease activity, increase activity, no activity) of oxygen
consumption and ATP synthesis in a mitochondrial suspension
containing all of the metabolites needed to reduce oxygen and
synthesize ATP. Explain your reasoning in each case.
What effect does an absence of oxygen (O2) have on the electron transport chain? What would...
What effect does an absence of oxygen (O2) have on the
electron transport chain? What would happen if, in this anaerobic
environment, you artificially decreased the pH of the intermembrane
space of the mitochondrion? Explain.
Would you expect high levels of ATP to inhibit or
activate glycolysis? Explain your answer.
A glucose-fed yeast cell is moved from an aerobic
environment to an anaerobic one. How would its rate of glucose
consumption change if ATP were to be generated in the...
What role do electron transport chains play in the synthesis of ATP in respiration? What role...
What role do electron transport chains play in the synthesis of
ATP in respiration? What role do electron transport chains play in
the synthesis of ATP in photosynthesis?
Consider the mitochondrial electron transport chain that utilizes NADH a. Write a NET balanced equation for...
Consider the mitochondrial electron transport chain that
utilizes NADH
a. Write a NET balanced equation for the entire reaction run by
Complex I, Complex III and Complex IV together. Include the protons
pumped from the inside to the outside of the matrix.
b. If you assume that the membrane potential is 200 mV and the
pH gradient is 0.5 and the temperature is 37 C, how much energy is
stored by the total reaction you wrote down in (a) as...
What is the role of the electron transport chain in the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
What is the role of the electron transport chain in the light
dependent reactions of
photosynthesis?
1. Which of components of the electron transport chain directly move protons across the inner mitochondrial...
1. Which of components of the electron transport chain directly
move protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane?
2. Consider fermentation.
How much ATP is generated during fermentation?
How does the amount of ATP generated by fermentation compare to
aerobic respiration?
In humans, why can't fermentation sustain life? (Hint: Think of two
reasons—one is related to the product of fermentation and what
happens if it accumulates.)
3. Given this segment of a double-stranded DNA molecule, draw
the two major steps involved...
Question 5: Mitochondrial Function a) Both the mitochondria and chloroplast contain electron transport chains. Describe two...
Question 5: Mitochondrial Function
a) Both the mitochondria and chloroplast contain
electron transport chains. Describe two similarities of the
electron transport chains despite being located in different
organelles.
b) In the mitochondrion, the electron transport chain is
normally coupled to ATP synthase. However, in endothermic animals,
the electron transport chain is uncoupled from ATP synthase when
temperatures drop below a certain threshold. Explain why uncoupling
of the electron transport chain from ATP synthase is advantageous
for an animal under cold...
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Project 7-6: Sales Tax Calculator Create a program that uses a separate module to calculate sales...
- On June 30, Sharper Corporation’s stockholders' equity section of its balance sheet appears as follows before...
- In this journal you are asked to take the role of a mayor or congressional representative...
- Answer correctly the below 25 multiple questions on Software Development Security. Please I will appreciate the...
- 1. The activation energy of a certain reaction is 41.5kJ/mol . At 20 ?C , the...
- Give TWO pieces of evidence that you've successfully made methyl salicylate. Remember when you cite TLC...
- Describe briefly the evolution of Craniata and Vertebrata.
ADVERTISEMENT
 Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago
Dr. OWL answered 5 years ago