Question
In: Math
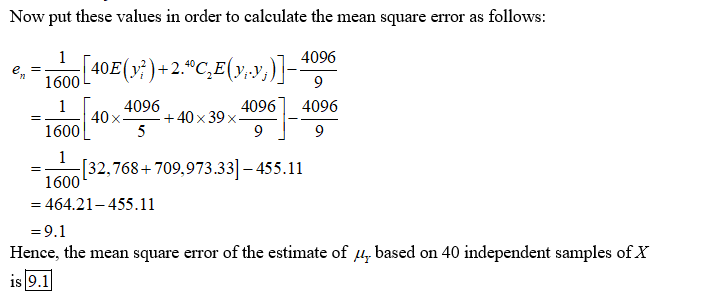
X is a continuous uniform (0,8) random variable. Define Y=X^2. What is the mean square error...
X is a continuous uniform (0,8) random variable. Define Y=X^2.
What is the mean square error of the estimate of μY based on 40 independent samples of X?
en = ?
Solutions
Related Solutions
Random variable X is a continuous uniform (0,4) random variable and Y=X^(1/2). (Note: Y is always...
Random variable X is a continuous uniform (0,4) random variable
and Y=X^(1/2). (Note: Y is always the positive root.)
What is the P[X>=E[X]] ?
What is the E[Y] ?
what is the P[Y>=E[Y]]?
what is the PFD of fY(y)?
Let X be a continuous random variable that has a uniform distribution between 0 and 2...
Let X be a continuous random variable that has a uniform
distribution between 0 and 2 and let the cumulative distribution
function F(x) = 0.5x if x is between 0 and 2 and let F(x) = 0 if x
is not between 0 and 2. Compute
1. the probability that X is between 1.4 and 1.8
2. the probability that X is less than 1.2
3. the probability that X is more than 0.8
4. the expected value of X...
Let U be a uniform continuous random variable on the interval [2, 8]. (a) What is...
Let U be a uniform continuous random variable on the interval
[2, 8].
(a) What is P(U = 4)?
(b) What is P(U ≤ 4)?
(c) What is P(4 ≤ U ≤ 7)?
(d) Find a formula for FU(x).
(e) Find a formula for fU(x).
(f) What is E(U)?
(g) What is Var(U)?
(h) What is E(1 − U 2 )?
Problem 2. (a) Prove that, if two continuous random variable X and Y are independent P(X...
Problem 2.
(a) Prove that, if two continuous random variable X and Y are
independent
P(X > x, Y > y) = P(X > x)P(Y > y)
(b) Now prove that, under the same conditions, X,Y, independent
continuous random variables, E(XY) = E(X)E(Y).
X is an independent standard uniform random variable X ∼ Uniform(0, 1) Y is an independent...
X is an independent standard uniform random variable X ∼
Uniform(0, 1)
Y is an independent standard uniform random variable Y ∼
Uniform(0, 1)
U = min(X, Y )
V = max(X, Y )
Find the correlation coefficient of V and U , ρ(U, V) =
Correlation(U, V).
A random variable X follows the continuous uniform distribution with a lower bound of ?8 and...
A random variable X follows the continuous uniform
distribution with a lower bound of ?8 and an upper bound of 11.
a.
What is the height of the density function
f(x)? (Round your answer to 4 decimal
places.)
f(x)
b.
What are the mean and the standard deviation for the
distribution? (Round your answers to 2 decimal
places.)
Mean
Standard
deviation
c.
Calculate P(X ? ?6). (Round
intermediate calculations to 4 decimal places and final answer to...
Let X, Y be independent random variables with X ∼ Uniform([1, 5]) and Y ∼ Uniform([2,...
Let X, Y be independent random variables with X ∼ Uniform([1,
5]) and Y ∼ Uniform([2, 4]).
a) FindP(X<Y).
b) FindP(X<Y|Y>3)
c) FindP(√Y<X<Y).
2. Let X be a uniform random variable over the interval (0, 1). Let Y =...
2. Let X be a uniform random variable over the interval (0, 1).
Let Y = X(1-X). a. Derive the pdf for Y . b. Check the pdf you
found in (a) is a pdf. c. Use the pdf you found in (a) to find the
mean of Y . d. Compute the mean of Y by using the distribution for
X. e. Use the pdf of Y to evaluate P(|x-1/2|<1/8). You cannot
use the pdf for X. f. Use...
A random variable Y is a function of random variable X, where y=x^2 and fx(x)=(x+1)/2 from...
A random variable Y is a function of random variable X, where
y=x^2 and fx(x)=(x+1)/2 from -1 to 1 and =0 elsewhere. Determine
fy(y). In this problem, there are two x values for every y value,
which means x=T^-1(y)= +y^0.5 and -y^0.5. Be sure you account for
both of these. Ans: fy(y)=0.5y^-0.5
Let x be a continuous random variable that is normally distributed with a mean of 65...
Let x be a continuous random variable
that is normally distributed with a mean of 65 and a standard
deviation of 15. Find the probability that
x assumes a value:
less than 48
greater than 87
between 56 and 70
ADVERTISEMENT
ADVERTISEMENT
Latest Questions
- Menlo Company distrubutes a single product. The company's sales and expenses for last month follow: Sales...
- Starting from the expression for the total differential of enthalpy, H, express (δH/δP)T in terms of...
- 1. What is the weight of a 87.4 kg object? w=? 2.What was the average speed...
- do you think free trade is really free? What are the likely costs of adopting a...
- X is a continuous uniform (0,8) random variable. Define Y=X^2. What is the mean square error...
- A gas mixture with a total pressure of 755 mmHg contains each of the following gases...
- Ref: Yang
ADVERTISEMENT

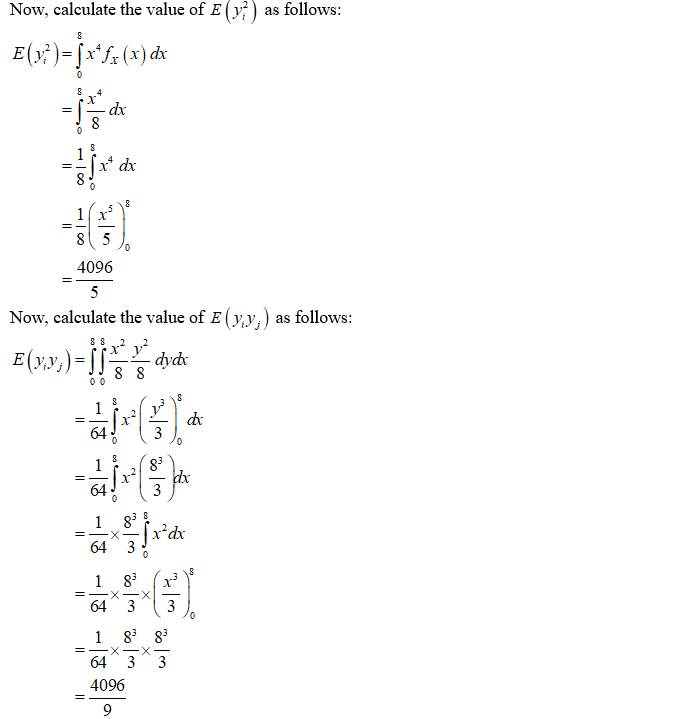
 milcah answered 2 hours ago
milcah answered 2 hours ago